Exploring 5G NR Signaling Radio Bearers: Functions and Use Cases
telcomatraining.com – As 5G technology continues to revolutionize communication networks, understanding the technical components that enable its performance is crucial. One of the key elements in 5G New Radio (NR) is the Signaling Radio Bearer (SRB), which plays a significant role in managing signaling information between user equipment (UE) and the network. This article will dive into the functions of SRBs in 5G NR and explore their various use cases in real-world network deployments.
What are Signaling Radio Bearers?
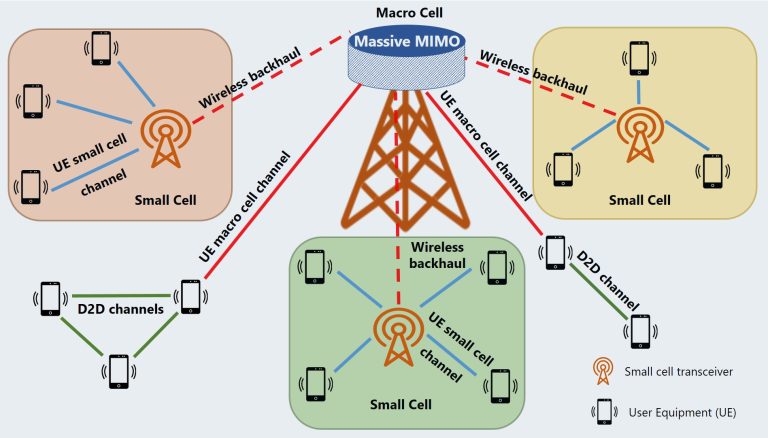
In the context of 5G NR, Signaling Radio Bearers are logical channels responsible for transmitting signaling data between user equipment (UE) and the core network, particularly the gNodeB (gNB), which is the 5G base station. Unlike Data Radio Bearers (DRBs), which carry user data traffic such as browsing or video streaming, SRBs are designed to manage control signals, such as connection setup, mobility management, and other signaling messages essential for maintaining the connection between the UE and the network.
The efficient management of SRBs is crucial for ensuring seamless communication and optimal performance of the network. They support the establishment, modification, and release of the data bearers, which in turn facilitates smooth data transmission for the end users.
Functions of 5G NR Signaling Radio Bearers
- Connection Establishment:
One of the primary functions of SRBs is to manage the connection establishment process between the UE and the gNodeB. This involves the transmission of signaling messages that initiate the connection setup, ensuring that both parties are synchronized and ready to exchange data. - Mobility Management:
As users move between different areas covered by different cells, SRBs facilitate the mobility management process. This ensures that the UE can maintain a stable connection by sending and receiving signaling messages related to handovers, cell reselection, and location updates. - Session Management:
SRBs also play a vital role in managing session contexts between the UE and the network. This involves handling signaling for activities like bearer resource allocation, modification, or release, allowing the network to adjust dynamically to user needs. - Security Functions:
Another essential function of SRBs is to enable secure communication between the UE and the network. Signaling messages carried by SRBs help in the establishment of security parameters, such as encryption and authentication, ensuring that the data exchange is protected against unauthorized access.
Use Cases of 5G NR Signaling Radio Bearers
- Initial Network Access:
When a device first tries to connect to the 5G network, SRBs are used to carry the initial signaling required for registration and authentication. This process involves exchanging critical messages such as Attach Requests and Authentication Requests, which are necessary for securing the connection. - Mobility and Handover:
SRBs play a pivotal role in enabling seamless mobility in a 5G network. During a handover, where a device switches from one base station to another, signaling messages are exchanged via SRBs to ensure that the handover occurs smoothly without any disruption to the user experience. - Quality of Service (QoS) Management:
In 5G networks, different services may require different levels of performance. SRBs help in managing the quality of service by carrying signaling information that enables dynamic adjustments to bearer resources, such as prioritizing certain types of traffic over others. - Support for Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC):
With the advent of applications requiring ultra-reliable low latency, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation, SRBs are crucial in ensuring that the network provides the necessary signaling to maintain reliability and low latency during communication.
Conclusion
5G NR Signaling Radio Bearers are a fundamental component in the 5G ecosystem, providing essential functions for network management and user experience optimization. By handling connection establishment, mobility management, session management, and security, SRBs ensure that the network operates efficiently and securely. As 5G networks continue to expand and evolve, understanding the role of SRBs will become even more critical in supporting diverse use cases, from initial access to high-performance applications like URLLC.
Whether it’s ensuring seamless mobility or supporting complex industrial applications, the versatility of SRBs makes them indispensable in the world of 5G.