XDM Explained: Key Concepts of XML Document Management
telcomatraining.com – In the ever-evolving world of technology, effective document management plays a critical role in ensuring smooth business operations. XML (Extensible Markup Language) has emerged as a popular choice for managing and storing documents due to its versatility and scalability. The combination of XML and document management systems has led to the creation of a powerful model called XDM (XML Document Management). Understanding the key concepts of XDM is essential for businesses and organizations looking to optimize their document handling processes. In this article, we will break down XDM and its key concepts for effective XML document management.
What is XDM?
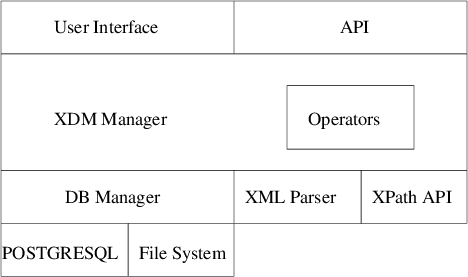
XDM (XML Document Management) refers to the process of storing, managing, and organizing documents in XML format. It is a system that allows businesses and developers to store documents in a structured, machine-readable format that is both flexible and adaptable. The key advantage of XML is that it can represent complex data structures and is widely accepted across different platforms. XDM simplifies document retrieval and manipulation by using XML’s standardized structure.
Why Choose XML for Document Management?
XML is designed to be both human-readable and machine-readable, making it a great option for document management systems. It allows for data to be structured in a hierarchical format, which makes it easier to search, extract, and manipulate. This ensures that businesses can quickly retrieve and modify documents in real time, improving overall workflow and efficiency.
Moreover, XML’s compatibility with other technologies like databases and web services makes it a versatile choice for document management. With XML, businesses can store documents that are accessible across various applications, making it ideal for collaboration in a global setting.
Key Concepts of XDM
- XML Schema An XML Schema is a blueprint that defines the structure and constraints of XML documents. It specifies the rules that an XML document must adhere to, ensuring that the document is valid. In the context of XDM, XML schemas provide a standardized format for creating and validating XML documents, ensuring consistency across the entire document management system. By defining elements, attributes, and relationships between data points, XML schemas allow businesses to ensure that documents meet specific criteria.
- Metadata Management Metadata is critical in document management systems as it provides additional information about the document itself, such as author, creation date, file size, or document type. In XDM, metadata is often stored in separate XML tags that describe the document’s content, purpose, and usage. Efficient metadata management allows for better organization and quicker searchability of documents. Businesses can categorize and tag documents with relevant metadata, enabling easy retrieval based on specific attributes.
- Document Indexing Document indexing involves creating an index of keywords, tags, or other identifiers to facilitate quicker searches within a document management system. In XDM, documents are indexed using XML tags, allowing users to search for specific content with precision. Indexing plays a significant role in making the document retrieval process fast and efficient, as it reduces the time spent sifting through large volumes of unstructured data.
- Version Control Version control is an essential feature of XDM, enabling businesses to track changes and maintain the history of documents over time. With version control, every change made to an XML document is recorded, and users can revert to previous versions if needed. This ensures that the integrity of documents is maintained, and businesses can track the evolution of a document from its creation to the most recent edits.
- Document Security Document security is a top priority when managing sensitive information. XDM leverages XML-based security measures to ensure that documents are protected from unauthorized access. This includes features such as encryption, access control, and digital signatures. By incorporating these security measures, businesses can safeguard their documents and ensure that only authorized personnel have access to specific documents or document sections.
- Document Workflow XDM can integrate document workflows, allowing for the seamless transition of documents through various stages, such as approval, review, and finalization. Workflow automation ensures that documents are processed efficiently and that there are no bottlenecks in the document lifecycle. With XML, businesses can define specific rules and procedures for how documents should flow through the system, streamlining business processes and improving overall productivity.
Benefits of XDM in Document Management
- Interoperability: XDM enables easy integration with other systems and technologies, allowing businesses to leverage existing tools and platforms.
- Scalability: XML’s ability to represent complex data structures allows businesses to scale their document management system as their needs grow.
- Flexibility: XDM can be customized to fit a wide range of business needs, offering a high degree of flexibility for different document management requirements.
- Improved Collaboration: XDM facilitates easier sharing and collaboration between team members, both locally and globally, by using a standardized format.
Conclusion
XML Document Management (XDM) is a powerful system that provides businesses with a robust solution for managing, organizing, and securing documents. By understanding the key concepts of XDM, such as XML schemas, metadata management, version control, document indexing, and security, businesses can ensure that their document management processes are efficient and scalable. As the demand for digital transformation continues to grow, embracing XDM is essential for businesses seeking to streamline their operations and improve productivity.