What Is Low Energy WiFi? A Guide to Power-Efficient Wireless Connectivity
telcomatraining.com – In today’s hyper-connected world, wireless technology is everywhere—from smartphones and smartwatches to home automation systems and industrial sensors. But as devices become smaller and more portable, one challenge persists: power consumption. This is where Low Energy WiFi steps in as a solution for efficient, long-lasting wireless communication. But what exactly is Low Energy WiFi, and how does it work? This article breaks it down for you.
Understanding Low Energy WiFi
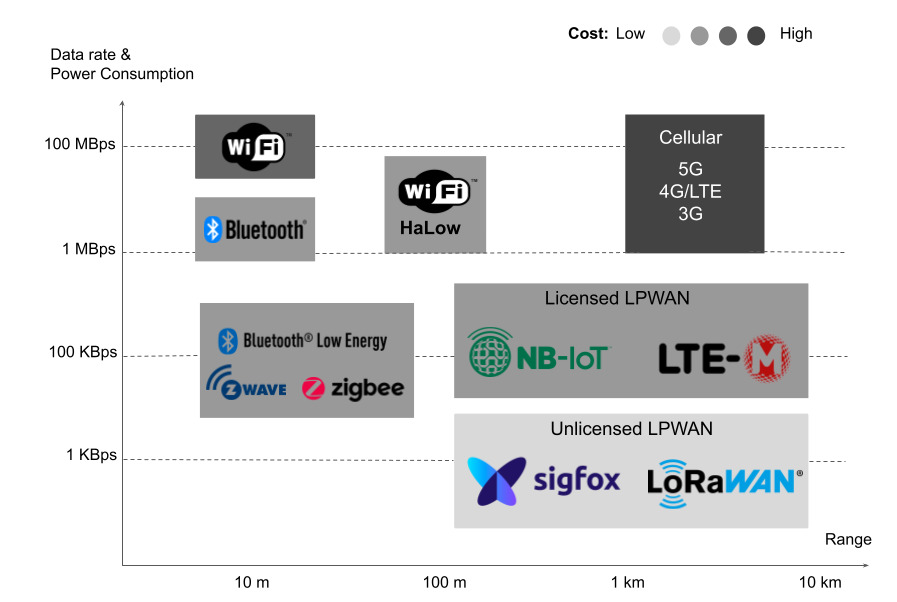
Low Energy WiFi, also known as WiFi HaLow (pronounced “halo”), is a variation of the traditional WiFi protocol designed specifically for low-power, long-range wireless communication. Developed under the IEEE 802.11ah standard, WiFi HaLow operates in the sub-1 GHz frequency bands, which allows it to penetrate walls and reach farther distances while using significantly less power than standard WiFi.
This technology is tailored for applications where devices need to stay connected for months or even years without frequent battery replacements or charging—making it ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) environments such as smart homes, agriculture, healthcare, and industrial automation.
Key Features of Low Energy WiFi
1. Low Power Consumption
One of the main advantages of Low Energy WiFi is its ability to preserve battery life. Devices that use WiFi HaLow can go into sleep mode for extended periods and only wake up to transmit or receive data. This energy-saving feature is essential for devices like sensors and wearables that need to operate autonomously for long durations.
2. Longer Range
Operating at lower frequencies means signals can travel farther and penetrate obstacles better than traditional 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz WiFi. WiFi HaLow can cover distances up to 1 kilometer in open areas, making it suitable for large facilities or outdoor installations.
3. Scalability
Low Energy WiFi supports thousands of devices on a single access point, unlike traditional WiFi, which can become congested with too many connections. This scalability is crucial for building smart cities and large IoT ecosystems.
4. Secure Connectivity
Like regular WiFi, WiFi HaLow includes built-in security protocols such as WPA3 encryption to protect data integrity and user privacy.
How Does Low Energy WiFi Compare to Bluetooth and Zigbee?
While Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Zigbee are also designed for power-efficient wireless communication, they have shorter range and lower data rates compared to WiFi HaLow. BLE is ideal for close-range connections like fitness trackers and audio devices, while Zigbee is often used in mesh networks for home automation.
In contrast, Low Energy WiFi provides a balance between range, speed, and power efficiency, making it a more versatile option for a wide variety of IoT applications.
| Feature | WiFi HaLow | BLE | Zigbee |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Sub-1 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Range | Up to 1 km | Up to 100 m | Up to 100 m |
| Power Use | Low | Very Low | Low |
| Data Rate | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Devices Supported | Thousands | Dozens | Hundreds |
Applications of Low Energy WiFi
The adoption of Low Energy WiFi is growing across industries due to its unique combination of low power consumption and extended range. Key applications include:
- Smart Agriculture: Monitor soil conditions, livestock, and weather data across large farms.
- Healthcare Devices: Enable medical wearables to track patient vitals over long periods.
- Smart Homes: Control lighting, security, and HVAC systems with minimal battery usage.
- Industrial Automation: Connect machinery and sensors in large facilities without excessive wiring or frequent maintenance.
The Future of Low Energy WiFi
As the number of connected devices continues to rise, the need for efficient and reliable wireless solutions becomes more urgent. Low Energy WiFi offers a promising pathway to building sustainable, scalable, and smart systems without draining power resources.
Tech companies and developers are increasingly investing in WiFi HaLow-capable devices, and its inclusion in the WiFi Alliance’s certification programs signals a broader push for adoption.
Conclusion
Low Energy WiFi, or WiFi HaLow, is transforming the way we connect devices—especially in IoT environments. With its energy-efficient design, extended range, and secure communication, it’s paving the way for the next generation of wireless connectivity. Whether you’re managing a smart home or deploying sensors in a remote area, Low Energy WiFi could be the ideal solution to keep your devices online and your batteries lasting longer.