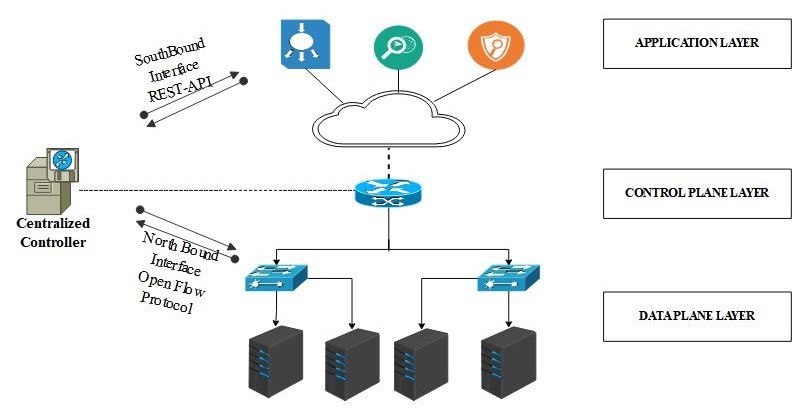
What Is an SDN Controller? Role and Function in Network Management
telcomatraining.com – In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, efficient and dynamic network management is crucial for organizations. Traditional network architectures often struggle to meet the demands of scalability, automation, and flexibility. This is where Software-Defined Networking (SDN) comes in — and at the heart of SDN lies the SDN controller.
Understanding SDN and the Role of the Controller
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is a network architecture approach that separates the control plane from the data plane. In traditional networks, switches and routers make forwarding decisions and also handle data movement. In contrast, SDN decouples these functions, allowing centralized management of the network via a controller.
The SDN controller acts as the brain of the SDN architecture. It is a centralized software application that communicates with network devices such as switches and routers through southbound APIs (typically OpenFlow), and with applications and business logic via northbound APIs.
Core Functions of an SDN Controller
- Centralized Network Intelligence The controller provides a centralized view of the entire network, allowing administrators to make informed decisions. It collects data from all devices in the network, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustments to traffic flow, security policies, and network configurations.
- Policy Enforcement and Traffic Management With the controller in place, administrators can define high-level policies which the controller translates into low-level device instructions. This allows for dynamic traffic routing, load balancing, and bandwidth allocation, all based on business needs.
- Automation and Orchestration One of the biggest benefits of an SDN controller is the ability to automate network tasks. From provisioning new services to updating configurations across multiple devices, the controller reduces the need for manual intervention, minimizing human error and boosting efficiency.
- Improved Network Security The SDN controller enhances security by allowing administrators to program and enforce network policies consistently across the entire infrastructure. It can quickly isolate compromised devices, redirect traffic, or update firewall rules, all in real-time.
- Application Integration Through northbound APIs, the controller integrates with third-party applications such as analytics platforms, firewalls, or intrusion detection systems. This open interface allows businesses to customize their networks based on specific operational or performance goals.
Why SDN Controllers Are Vital in Modern Networks
Modern businesses require agility, scalability, and security — features that traditional networks often cannot provide without significant cost and complexity. SDN controllers bring several advantages:
- Flexibility: Network behavior can be adapted dynamically to meet changing demands.
- Cost-Efficiency: Centralized control reduces the need for expensive, specialized hardware.
- Scalability: SDN controllers simplify the expansion of networks, making it easier to manage large-scale environments.
- Faster Deployment: Services and applications can be rolled out quicker with less manual configuration.
Popular SDN Controllers
Several open-source and commercial SDN controllers are available in the market. Some of the most notable include:
- OpenDaylight: A modular, open-source controller supported by the Linux Foundation.
- ONOS (Open Network Operating System): Designed for carrier-grade networks and scalability.
- Ryu: A component-based SDN controller written in Python, suitable for research and development.
- Cisco APIC-EM: Cisco’s Enterprise Module SDN controller tailored for automation and centralized management.
Conclusion
The SDN controller is a critical component in the software-defined networking model. By decoupling the control and data planes, it brings centralized intelligence, enhanced security, automation, and flexibility to network management. As networks continue to evolve with cloud computing, IoT, and edge technologies, the role of SDN controllers will become even more vital in building resilient, adaptive, and intelligent network infrastructures.
For organizations aiming to stay competitive in a digital-first world, embracing SDN and deploying a robust SDN controller is no longer optional — it’s a strategic necessity.