What Is 5G IoT? Definition, Benefits, and Applications
telcomatraining.com – The world of technology is evolving at an incredible pace, and one of the most exciting advancements in recent years is the combination of 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT). As we continue to move toward a more connected and efficient world, understanding the relationship between these two technologies is essential. This article will explore what 5G IoT is, its benefits, and the potential applications it offers.
What Is 5G IoT?
5G IoT refers to the integration of 5G wireless technology with the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. To better understand this, let’s break it down:
- 5G Technology: 5G is the fifth generation of mobile network technology, succeeding 4G LTE. It offers faster speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connectivity compared to previous generations. It operates across a broad spectrum of frequencies, enabling ultra-fast data transfer and high-capacity networks.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The Internet of Things involves the connection of everyday devices to the internet, allowing them to communicate, collect data, and even make decisions autonomously. Examples of IoT devices include smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, and connected cars.
When combined, 5G IoT refers to the ability of IoT devices to operate at higher speeds and with greater efficiency due to the ultra-fast and low-latency capabilities of 5G networks. This synergy will unlock new possibilities for industries and consumers alike.
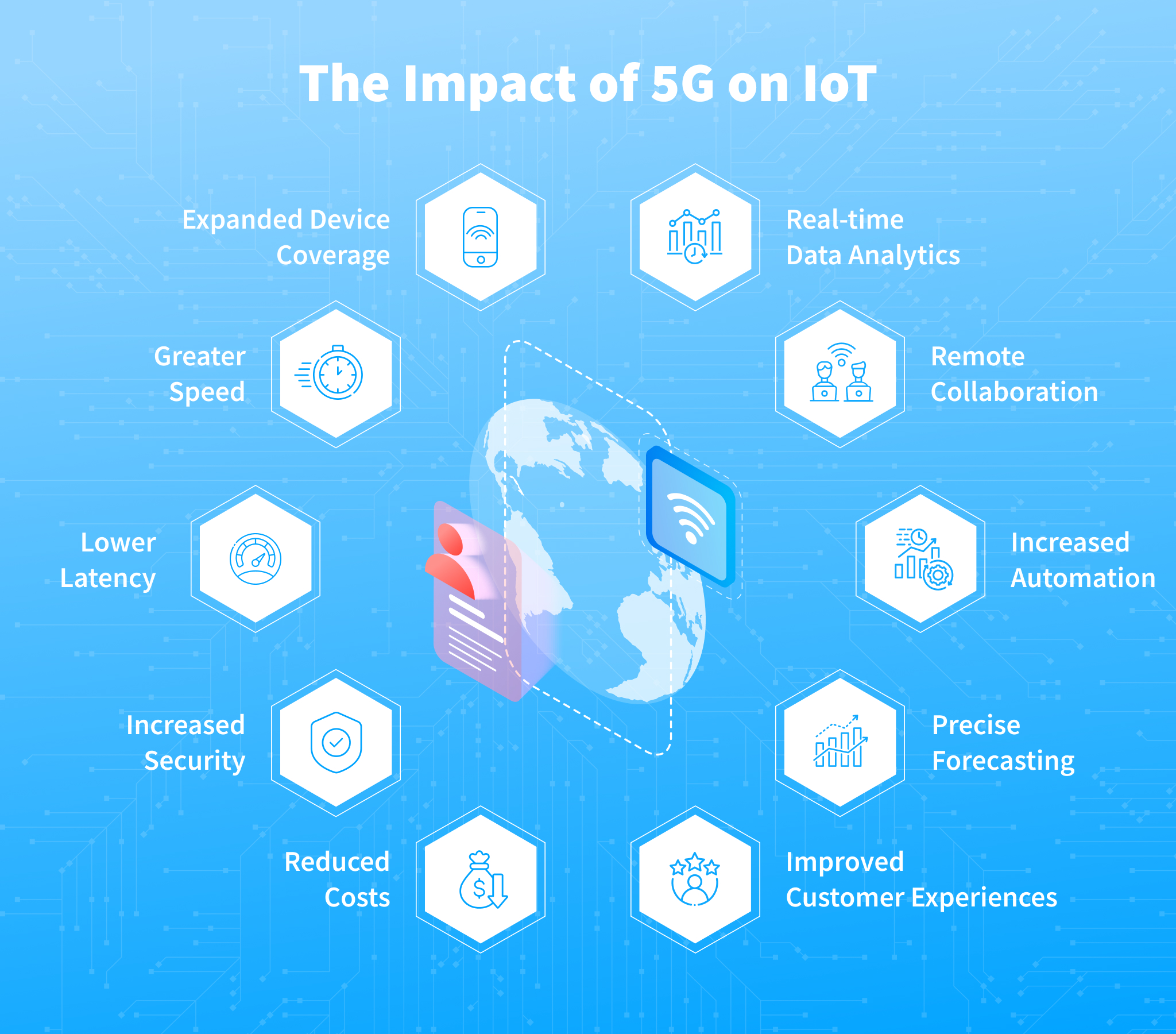
Benefits of 5G IoT
The merger of 5G and IoT brings several benefits that can transform how we live and work. Here are the key advantages:
- Faster Data Speeds: 5G networks offer download speeds that can exceed 10 Gbps, which is significantly faster than current 4G LTE speeds. For IoT devices, this means they can transfer large amounts of data in real time, enabling more seamless and efficient operations.
- Low Latency: One of the standout features of 5G is its incredibly low latency. Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. With 5G, the latency is reduced to as low as 1 millisecond. This is crucial for IoT applications that require immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles or remote surgeries.
- Greater Connectivity: 5G can support a higher density of connected devices compared to 4G. This is important for the growing number of IoT devices being deployed in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities. 5G IoT can handle millions of connected devices within a small area without significant drops in performance.
- Improved Reliability: 5G networks offer a more stable and reliable connection, which is essential for IoT devices that operate in critical environments. Whether it’s a smart factory or healthcare monitoring systems, uninterrupted connectivity is vital for ensuring safety and productivity.
- Energy Efficiency: 5G networks are designed to be more energy-efficient compared to their predecessors. For IoT devices, this means they can operate for longer periods without needing frequent charging or battery replacements, especially for those deployed in remote or hard-to-reach locations.
Applications of 5G IoT
The combination of 5G and IoT opens up numerous possibilities across various sectors. Here are some key applications:
- Smart Cities: 5G IoT is a cornerstone for building smart cities. With faster and more reliable connectivity, cities can implement solutions like intelligent traffic management, smart streetlights, waste management, and enhanced public safety. For instance, traffic signals could communicate with vehicles in real time, improving traffic flow and reducing congestion.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely heavily on real-time data and communication between vehicles, traffic infrastructure, and other entities. The low latency of 5G ensures that these vehicles can communicate instantly with their environment, enhancing safety and efficiency on the road.
- Healthcare: 5G IoT can revolutionize healthcare by enabling telemedicine, remote surgeries, and continuous health monitoring. For example, connected devices can transmit data from patients’ wearables to healthcare providers, allowing for real-time analysis and immediate intervention if necessary.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In industries like manufacturing and logistics, 5G IoT can help optimize production lines, track inventory, and monitor equipment health. Machines can communicate with each other and central systems to predict maintenance needs, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency.
- Agriculture: 5G IoT can be used in precision agriculture, where sensors collect data on soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. This data can be transmitted in real time to farmers, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and improve crop yields while reducing water and resource waste.
- Retail: The retail sector can leverage 5G IoT to enhance customer experiences. For example, smart shelves that detect stock levels and smart carts that offer personalized shopping suggestions can improve the overall retail environment. Real-time inventory tracking can also reduce stockouts and improve supply chain management.
Conclusion
5G IoT is a game-changer that promises to transform numerous industries, from healthcare to transportation to smart cities. By combining the speed and reliability of 5G with the connectivity of IoT, we are entering an era where devices and systems work together more seamlessly than ever before. The benefits of faster speeds, low latency, greater connectivity, and improved energy efficiency make 5G IoT a powerful tool for driving innovation and efficiency across a wide range of applications. As 5G networks continue to expand, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking advancements in how we live and work in an increasingly connected world.