What Is 5G in Telecommunications? A Complete Overview
telcomatraining.com – In today’s fast-paced digital world, the demand for faster and more reliable connectivity is ever-growing. This is where 5G comes into play. But what exactly is 5G in telecommunications? How does it differ from previous generations of mobile networks? In this comprehensive overview, we’ll explore everything you need to know about 5G technology — its definition, features, benefits, use cases, and potential challenges.
Understanding 5G: The Fifth Generation of Wireless Technology
5G, short for fifth-generation mobile network, is the latest global wireless standard following 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G. It is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together — including machines, devices, and objects — with lightning-fast speed, ultra-low latency, and massive network capacity.
Unlike previous generations that focused mainly on mobile communication, 5G aims to revolutionize a wide range of industries, from healthcare and manufacturing to transportation and entertainment.
Key Features of 5G
1. High Speed
One of the most talked-about advantages of 5G is its blazing speed. It can deliver data rates up to 10 Gbps, which is up to 100 times faster than 4G LTE. This makes downloading large files, streaming 4K videos, and playing online games smoother than ever.
2. Low Latency
Latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination. 5G reduces latency to as low as 1 millisecond, enabling real-time responsiveness — a game-changer for technologies like autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
3. Massive Device Connectivity
5G networks are built to support up to 1 million devices per square kilometer. This makes it ideal for the Internet of Things (IoT), where billions of smart devices need to communicate with each other seamlessly.
4. Improved Reliability
With features like network slicing and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), 5G ensures a more stable and reliable connection, even in crowded areas like stadiums, airports, and concerts.
How Does 5G Work?
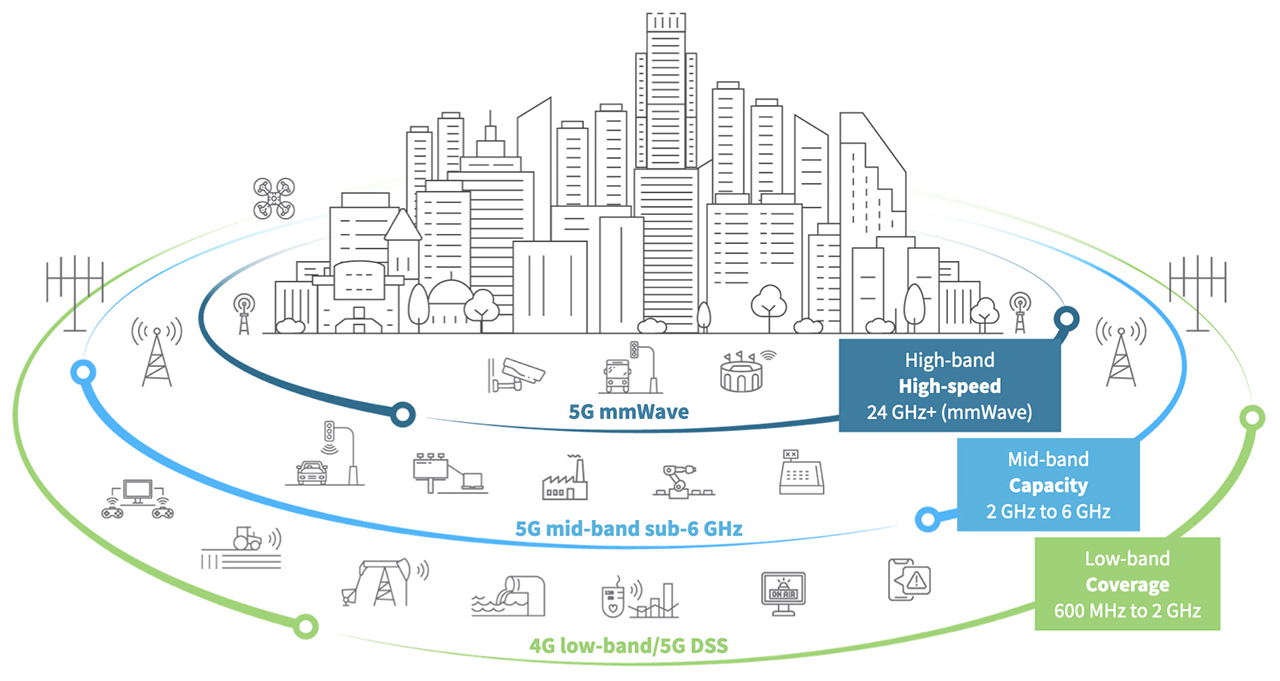
5G operates on three different frequency bands: low-band, mid-band, and high-band (also known as millimeter wave). Each band offers a trade-off between coverage and speed:
- Low-band offers wide coverage but lower speeds.
- Mid-band provides a balance between coverage and performance.
- High-band (mmWave) delivers ultra-fast speeds but has limited coverage and is more affected by obstacles.
To support these bands, 5G uses advanced technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), beamforming, and network slicing, which allow for more efficient use of the spectrum.
Applications of 5G
The real power of 5G lies in its ability to enable new technologies and services across industries:
- Smart Cities: Real-time traffic control, smart lighting, and public safety systems.
- Healthcare: Remote surgeries, telemedicine, and real-time health monitoring.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Instant communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians.
- Industrial Automation: Real-time control of machinery and robotics in factories.
- AR/VR Experiences: Immersive gaming, training simulations, and virtual meetings.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its vast potential, 5G faces some challenges:
- Infrastructure Requirements: Building 5G networks requires significant investment in small cell towers, fiber optics, and new hardware.
- Coverage Limitations: Especially in rural or remote areas, 5G availability may be limited.
- Security Concerns: As 5G expands, so do cybersecurity risks, particularly with billions of connected IoT devices.
The Future of 5G
The rollout of 5G is still ongoing across many parts of the world. As more regions adopt this technology, we can expect to see innovations that were previously unimaginable. From smart homes to connected vehicles and digital healthcare, 5G will serve as the backbone of the next digital revolution.
Conclusion
5G in telecommunications is more than just an upgrade — it’s a transformative force that will shape the future of how we live, work, and communicate. With its high speed, low latency, and capacity to connect millions of devices, 5G opens up endless possibilities. As it continues to evolve, businesses, governments, and consumers alike must stay informed and prepared to harness its full potential.