VSF (Virtual Security Function): Meaning and Benefits in Network Security
telcomatraining.com – In an era where cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, organizations must adopt advanced security measures to protect their networks. One such innovation is VSF (Virtual Security Function), a crucial component of modern network security frameworks. VSF leverages virtualization technologies to provide scalable and flexible security solutions, ensuring networks remain secure without the constraints of traditional hardware-based security appliances. This article will explore the meaning of VSF and its benefits in network security.
What is VSF (Virtual Security Function)?
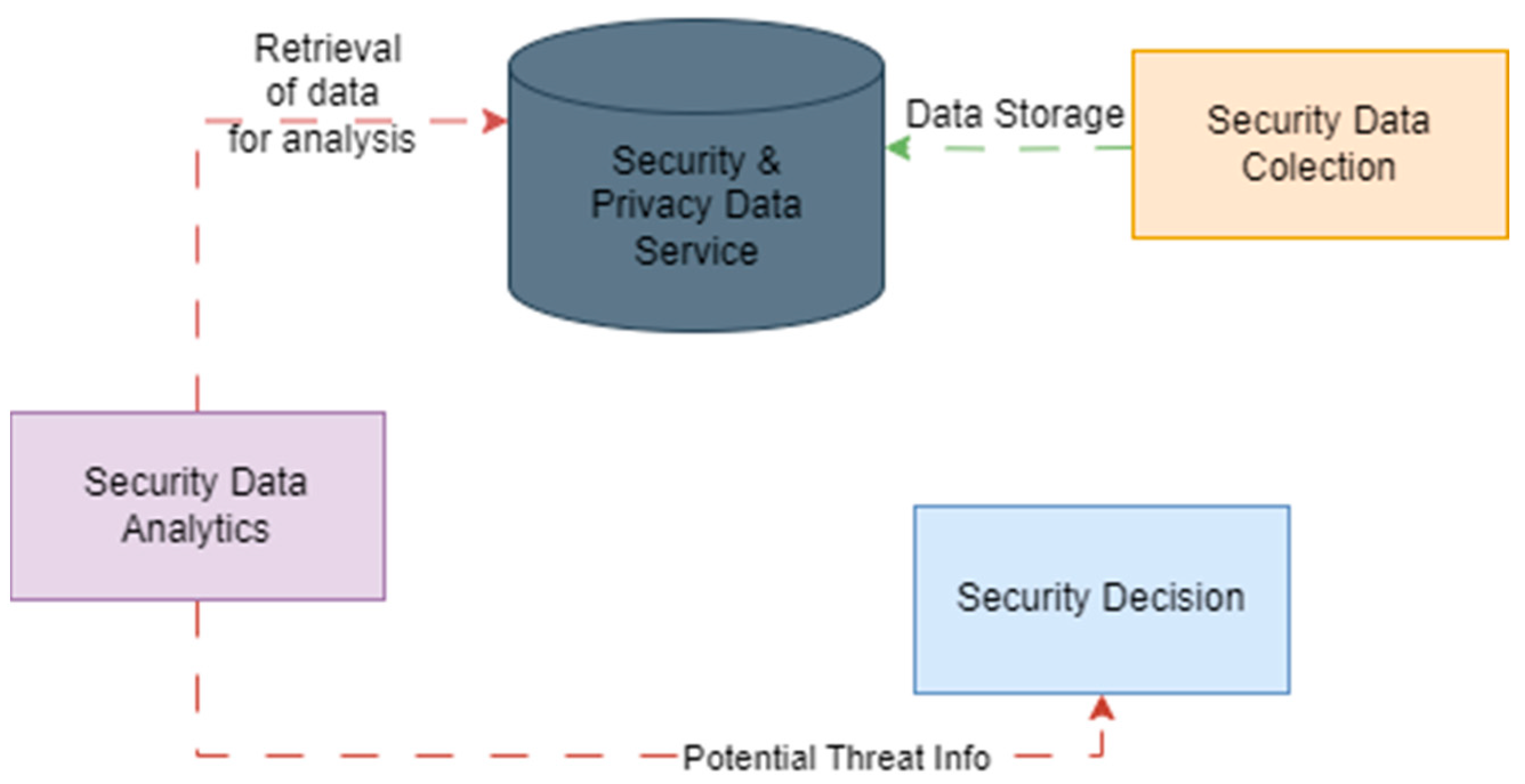
VSF, or Virtual Security Function, refers to security functions that are implemented in a virtualized environment rather than through dedicated hardware appliances. These functions are part of Network Functions Virtualization (NFV), a technology that replaces traditional network hardware with software-based solutions running on standard servers.
Some of the key security functions that can be virtualized using VSF include:
- Firewalls – Virtual firewalls inspect and filter network traffic without requiring physical appliances.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) – These systems monitor and respond to network threats in real time.
- VPN Gateways – Secure remote access is provided through virtualized VPN solutions.
- Antivirus and Malware Protection – Cloud-based antivirus solutions can scan and detect malware across network environments.
- DDoS Protection – Virtual security systems can mitigate Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks dynamically.
By replacing traditional security appliances with virtualized security functions, businesses gain flexibility and scalability while reducing operational costs.
Benefits of VSF in Network Security
1. Scalability and Flexibility
One of the main advantages of VSF is its scalability. Organizations can scale their security functions up or down depending on network traffic demands. Unlike hardware-based security appliances that have fixed capacities, VSF can dynamically allocate resources as needed, ensuring optimal network protection.
Additionally, VSF enables flexibility in deployment. Companies can implement security solutions across multiple locations, cloud environments, and hybrid infrastructures without requiring physical security appliances.
2. Cost Efficiency
Traditional security appliances require significant capital investment, maintenance, and hardware upgrades. VSF reduces these costs by allowing organizations to run security functions on existing virtualized infrastructure. This approach eliminates the need for expensive physical hardware while also reducing energy consumption and space requirements.
Furthermore, since VSF is software-based, updates and patches can be applied remotely, reducing the costs associated with manual maintenance and hardware replacements.
3. Rapid Deployment and Automation
VSF enables rapid deployment of security solutions without the need for complex hardware installations. Security functions can be provisioned and configured in minutes, allowing organizations to respond quickly to new threats.
With the integration of automation and orchestration tools, VSF solutions can be managed efficiently. Automated security policies ensure consistent enforcement across the network, reducing human errors and improving security posture.
4. Enhanced Security in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing and hybrid network architectures, traditional security models struggle to keep up. VSF seamlessly integrates with cloud environments, providing consistent security policies across on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud networks.
Security functions such as Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) and Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP) can be implemented virtually, ensuring secure access control and data protection in cloud environments.
5. Improved Threat Detection and Response
VSF solutions leverage AI and machine learning to enhance threat detection and response capabilities. Advanced analytics and real-time monitoring help detect security threats before they can cause damage.
For example, virtualized intrusion prevention systems (IPS) can analyze traffic patterns, detect anomalies, and mitigate threats without human intervention. This proactive approach ensures networks remain secure against evolving cyber threats.
6. Integration with Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Virtual Security Functions integrate seamlessly with Software-Defined Networking (SDN), allowing security policies to be centrally managed and dynamically enforced across network infrastructures. SDN and VSF together enable intelligent traffic routing, ensuring that security policies adapt to network changes in real time.
This integration enhances network visibility and control, making it easier for security teams to manage security functions across complex, multi-cloud environments.
Conclusion
VSF (Virtual Security Function) is transforming the way organizations approach network security by providing scalable, cost-effective, and flexible security solutions. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the adoption of virtualized security functions becomes essential for businesses looking to protect their digital assets without the limitations of traditional security appliances.
With automated security policies, AI-driven threat detection, and seamless cloud integration, VSF is a game-changer in modern network security. Organizations that leverage VSF can enhance their security posture while optimizing costs and operational efficiency.
By embracing VSF, businesses can future-proof their network security strategies, ensuring they remain resilient in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.