Voice Call Continuity (VCC): Ensuring Seamless Mobile Communications
telcomatraining.com – In today’s fast-paced digital world, seamless communication is essential for both personal and professional interactions. Voice Call Continuity (VCC) plays a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted mobile communication, allowing users to transition between different networks without experiencing call drops. This technology is particularly valuable for businesses, remote workers, and individuals who rely heavily on mobile communications. In this article, we will explore the concept of VCC, its benefits, how it works, and its impact on mobile communication.
What is Voice Call Continuity (VCC)?
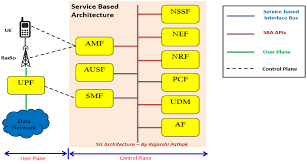
Voice Call Continuity (VCC) is a technology that enables ongoing voice calls to be seamlessly transferred between different network types, such as Wi-Fi, LTE, and 5G, without interruptions. This ensures that users can move freely between coverage areas without experiencing call drops. VCC is widely used in Voice over Wi-Fi (VoWiFi) and Voice over LTE (VoLTE) services, making it a critical component of modern mobile communications.
How Does VCC Work?
VCC functions by leveraging intelligent handover mechanisms that detect network availability and transition calls between different networks accordingly. The process typically follows these steps:
- Call Initiation – A voice call is established over a network (e.g., Wi-Fi, LTE, or 5G).
- Network Monitoring – The system continuously monitors the network quality and availability.
- Handover Decision – When a better network is available or when the current network signal weakens, the system decides to transfer the call.
- Seamless Transition – The call is handed over to the new network without user intervention or disruption.
- Call Continuation – The call continues on the new network without noticeable lag or drop in quality.
Benefits of Voice Call Continuity
1. Uninterrupted Communication
VCC ensures that calls remain uninterrupted even when moving between different network environments. This is particularly useful for individuals who frequently switch between Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
2. Enhanced Call Quality
By selecting the most optimal network, VCC helps maintain superior call quality, reducing issues such as latency, jitter, and dropped calls.
3. Improved Mobility for Professionals
Business professionals and remote workers benefit from VCC as it allows them to remain connected during travel, virtual meetings, and important calls without worrying about losing signal.
4. Cost Savings
VCC allows calls to be routed through the most cost-effective network, such as switching from a mobile network to Wi-Fi, which can help reduce roaming and data charges.
5. Better User Experience
Users no longer have to worry about manually switching networks or reconnecting dropped calls, making mobile communication more convenient and reliable.
VCC and the Future of Mobile Communication
With the advent of 5G technology, Voice Call Continuity is expected to become even more robust. The integration of AI-driven network optimization and edge computing will further enhance seamless transitions between networks. Additionally, businesses adopting Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) will benefit from VCC as it integrates seamlessly with cloud-based communication platforms.
Conclusion
Voice Call Continuity (VCC) is a vital technology that ensures smooth and uninterrupted mobile communication by seamlessly transitioning voice calls between different networks. Its benefits, including uninterrupted communication, improved call quality, cost savings, and better mobility, make it an essential feature in modern telecommunication. As mobile networks continue to evolve, VCC will play an even greater role in enhancing connectivity, ensuring that users stay connected anytime and anywhere without disruptions. Embracing VCC technology is crucial for individuals and businesses looking to optimize their mobile communication experience.