Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI): How It Works in ATM Networks
telcomatraining.com – Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks are designed to provide high-speed data transmission, making them essential for telecommunication and broadband services. A crucial component in ATM networks is the Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI), which plays a key role in ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission. This article explores what VCI is, how it functions in ATM networks, and its significance in maintaining seamless communication.
What is a Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI)?
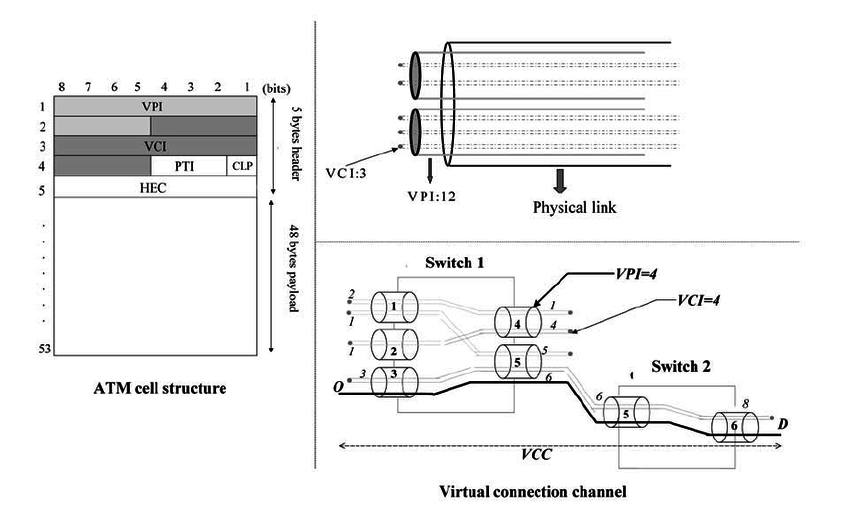
In ATM networks, data is transmitted in fixed-size cells, each consisting of a 5-byte header and a 48-byte payload. The VCI is a unique identifier located within the header of an ATM cell. It is used to distinguish different virtual connections within an ATM network and facilitate proper data routing.
Each ATM cell carries a Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) and a VCI, which together form a virtual circuit. The VCI ensures that the data reaches the correct destination by allowing network switches to identify and direct the cells efficiently.
How VCI Works in ATM Networks
The Virtual Channel Identifier operates by enabling the ATM switches to differentiate between multiple data streams traveling through the same physical connection. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how VCI functions in an ATM network:
- Cell Creation and Labeling
- When data is transmitted, it is segmented into ATM cells.
- Each cell is assigned a VCI, which, along with the VPI, forms a unique identifier for the connection.
- Data Transmission
- The ATM cell moves through the network, with each switch using the VCI to determine the appropriate output link.
- The VCI may be changed at each switching point to align with the new connection setup.
- Routing and Switching
- ATM switches analyze the VCI in each cell’s header.
- The switch replaces the incoming VCI with a new one as per the routing table and forwards the cell to the next hop.
- Data Reception and Reassembly
- When the cell reaches its final destination, the receiving device uses the VCI to identify the data stream.
- The payload is then extracted and reassembled into the original information.
Significance of VCI in ATM Networks
The VCI is essential for several reasons:
- Efficient Data Management: It helps manage multiple virtual connections over a single physical link, optimizing network resources.
- Flexible Routing: Since the VCI can be changed at each switch, ATM networks can dynamically allocate paths for better performance.
- Low Latency and High Throughput: By using small, fixed-size cells with VCIs, ATM networks minimize transmission delays and maximize data flow.
- Enhanced Quality of Service (QoS): ATM networks use VCI-based routing to ensure priority handling for critical applications like voice and video calls.
VCI vs. VPI: Understanding the Difference
While VCI is responsible for identifying virtual channels, the Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) groups multiple VCIs into a single virtual path. Here’s how they differ:
- VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier): Identifies individual data streams within a virtual path.
- VPI (Virtual Path Identifier): Groups multiple VCIs under a common path to simplify routing.
The combination of VCI and VPI allows ATM networks to scale efficiently, supporting a vast number of virtual circuits with minimal overhead.
Conclusion
Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI) plays a vital role in ATM networks by ensuring accurate and efficient data transmission. By enabling dynamic routing, optimizing bandwidth, and enhancing network performance, VCI is an indispensable component of ATM communication. As networking technology continues to evolve, the principles of VCI remain relevant in modern data transport systems, including MPLS and other advanced networking protocols.