Understanding UWB (Ultra-Wideband): Technology, Applications, and Benefits
telcomatraining.com – Ultra-Wideband (UWB) is an advanced wireless communication technology that utilizes a broad frequency spectrum to enable high-precision positioning, fast data transfer, and secure communication. Unlike traditional narrowband and wideband systems, UWB transmits data over a wide range of frequencies (typically over 500 MHz), making it highly efficient in terms of accuracy and reliability. Originally developed for military applications, UWB is now gaining traction in consumer electronics, industrial automation, and IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
How UWB Technology Works
UWB technology operates by transmitting short-duration pulses across a wide spectrum, allowing for high data rates and low power consumption. Unlike conventional wireless systems that rely on continuous wave modulation, UWB utilizes pulse-based transmissions, reducing interference and enabling precise distance measurements. The key principle behind UWB is Time-of-Flight (ToF), which calculates the time taken for a signal to travel between two UWB-enabled devices. This feature enables highly accurate positioning and tracking, often with centimeter-level precision.
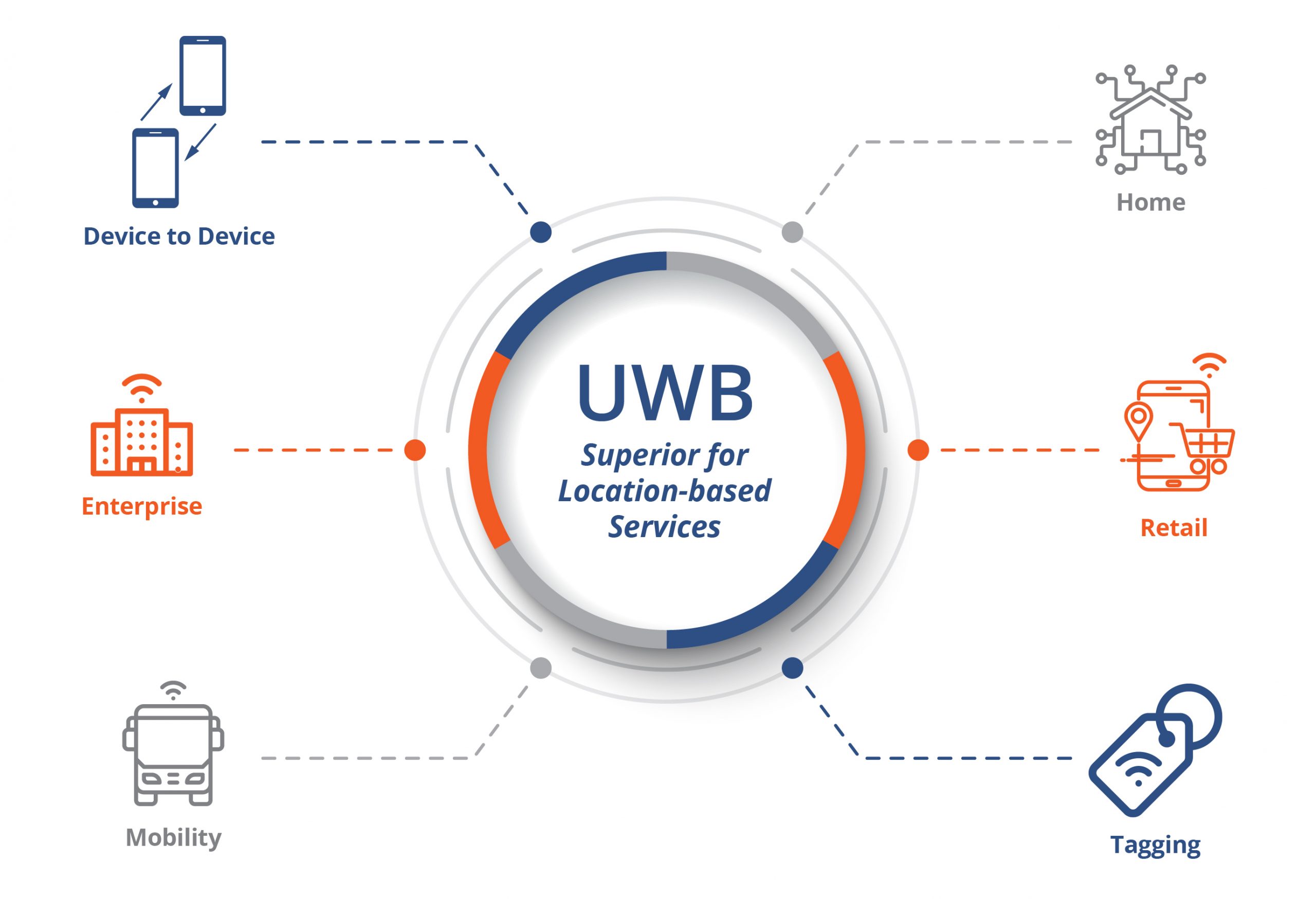
Key Applications of UWB Technology
1. High-Precision Indoor Positioning
UWB is widely used for real-time location systems (RTLS) in environments where GPS signals are weak or unavailable, such as warehouses, hospitals, and smart homes. UWB-based positioning is ideal for tracking assets, personnel, and autonomous vehicles, providing highly accurate location data.
2. Secure Access Control and Authentication
Many modern smartphones and wearable devices are incorporating UWB for secure and contactless access. Apple, Samsung, and other tech companies use UWB to enable digital car keys, allowing users to unlock and start vehicles without physical contact. UWB also enhances authentication security by preventing relay attacks, which are common with traditional NFC and Bluetooth technologies.
3. IoT and Smart Home Automation
UWB technology is transforming smart home ecosystems by enabling precise device tracking and automation. UWB-powered smart assistants can detect user location within a home, adjusting lighting, temperature, and security systems based on real-time movement data. This enhances convenience, energy efficiency, and security.
4. Industrial and Logistics Optimization
In industries such as manufacturing and logistics, UWB is employed for real-time asset tracking and inventory management. Forklifts, machines, and goods can be precisely located in large warehouses, optimizing workflow efficiency and reducing operational costs. UWB’s high accuracy makes it invaluable in environments where traditional RFID or GPS tracking falls short.
5. Healthcare and Medical Applications
UWB plays a crucial role in healthcare, particularly in patient monitoring and medical equipment tracking. Hospitals use UWB to track the movement of critical devices like ventilators and wheelchairs, ensuring they are readily available when needed. Additionally, UWB-enabled fall detection systems can improve elderly care by instantly detecting and responding to emergencies.
Benefits of UWB Technology
1. High Accuracy and Precision
UWB’s ability to measure distances with centimeter-level accuracy makes it superior to Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS in terms of precision. This makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring exact positioning and tracking.
2. Low Power Consumption
UWB transmits data using ultra-short pulses, consuming significantly less power than traditional wireless communication methods. This enhances battery life for UWB-enabled devices, making it suitable for wearables and IoT applications.
3. Enhanced Security
UWB’s highly secure communication reduces the risk of unauthorized access and relay attacks. Its short-range, time-based authentication method ensures that devices must be in close proximity to establish a secure connection.
4. Minimal Interference
Unlike Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, which operate in crowded frequency bands, UWB uses a broad spectrum with minimal interference. This makes it a reliable solution for environments with multiple wireless signals, such as airports and smart buildings.
5. Fast Data Transfer
UWB supports high-speed data transmission, enabling seamless connectivity for media streaming, file sharing, and low-latency communications. This makes it ideal for emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications.
Conclusion
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology is revolutionizing wireless communication, offering high accuracy, low power consumption, and enhanced security across various industries. From smartphones and IoT devices to industrial automation and healthcare, UWB is proving to be a game-changer in modern technology. As more industries adopt UWB for real-time positioning, secure access, and seamless automation, its role in shaping the future of wireless communication will continue to expand. With ongoing advancements and increasing adoption, UWB is poised to become a cornerstone of the next-generation digital ecosystem.