Understanding the Role of Mobile Switching Center in Telecommunications
telcomatraining.com – In the world of telecommunications, the Mobile Switching Center (MSC) plays a vital role in connecting and managing communication within mobile networks. MSC is essentially the backbone of mobile networks, directing calls and data between mobile devices, base stations, and other parts of the network. This article aims to provide a clear understanding of the Mobile Switching Center, its functions, and its significance in the smooth operation of telecommunications.
What is a Mobile Switching Center (MSC)?
A Mobile Switching Center (MSC) is a central component in mobile networks responsible for routing and switching voice and data communication between mobile users and the public switched telephone network (PSTN). It is an essential part of the network’s infrastructure, enabling communication between mobile devices and the outside world.
The MSC acts as a mediator, ensuring that calls made by mobile users are properly directed to their destination, whether it be another mobile phone, a landline, or even a data service. It connects with other MSCs, base stations, and other telecommunications equipment to maintain uninterrupted communication.
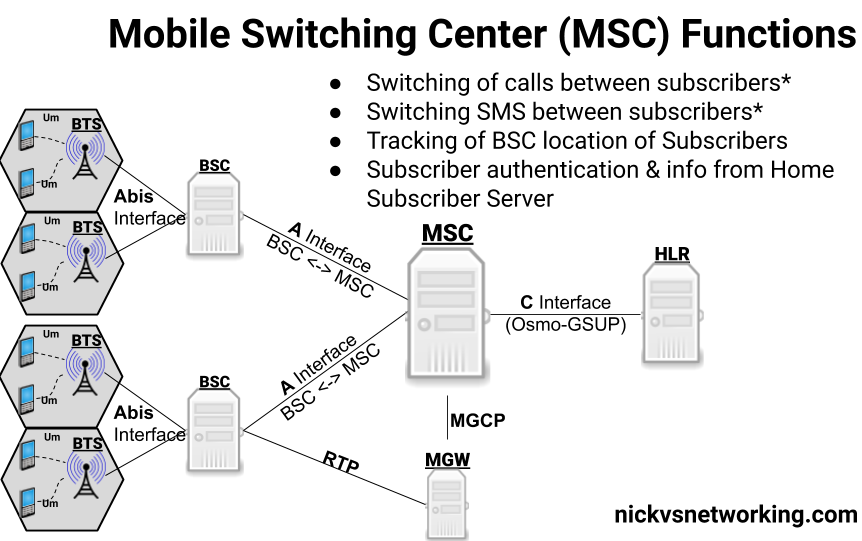
Functions of a Mobile Switching Center
The MSC is responsible for numerous critical tasks that are essential to the functioning of mobile networks. Some of the primary functions include:
- Call Setup and Routing
One of the primary functions of an MSC is to manage the setup and routing of calls between users. It ensures that the call reaches the intended recipient by directing the signal through the appropriate channels. The MSC communicates with base stations, which are responsible for handling the radio frequency connection to the mobile device, to facilitate this process. - Call Handover
During a call, users may move between different areas with different base stations. The MSC handles the “handover” process, which ensures that the call continues seamlessly as the user transitions from one base station to another. This process is crucial for maintaining call quality and preventing dropped calls, especially in mobile environments. - Mobility Management
The MSC is responsible for tracking the location of mobile users within the network. It communicates with the Home Location Register (HLR) and Visitor Location Register (VLR) to authenticate users, update their location, and manage the assignment of resources. This enables the network to efficiently allocate resources and ensure that users are always connected, regardless of their physical location. - Short Message Service (SMS) Routing
The MSC also plays a role in routing text messages (SMS). It works in conjunction with the Short Message Service Center (SMSC) to ensure that messages are delivered from one user to another. This includes managing message queues and ensuring that delivery is successful, even if the recipient’s device is temporarily unavailable. - Interconnection with Other Networks
The MSC acts as a gateway between mobile networks and other types of communication networks. It interfaces with the PSTN, Voice over IP (VoIP) systems, and even the internet for data services. This interconnection is crucial for providing users with the ability to make calls and access services across different types of networks. - Billing and Accounting
The MSC is involved in tracking call duration, data usage, and other metrics for billing purposes. It works with other systems within the network to generate accurate billing information for customers based on their usage. This is particularly important for mobile operators in managing revenue and ensuring proper billing for services provided.
Types of Mobile Switching Centers
There are several types of MSCs based on the architecture and functionality they provide:
- Class 1 MSC: Handles both voice and data traffic for a specific area.
- Class 2 MSC: Primarily responsible for voice call processing, while data services are typically handled by a separate system.
- Class 3 MSC: Used in more advanced configurations, often handling more complex tasks such as mobile internet and multimedia services.
Importance of the MSC in Telecommunications
The Mobile Switching Center is a crucial component that enables seamless mobile communication, both for voice and data services. Without the MSC, mobile networks would lack the necessary infrastructure to route calls, manage mobility, and provide reliable service. Its ability to ensure smooth handovers, manage mobility, and interconnect with other networks makes it indispensable in the world of telecommunications.
Additionally, with the growing demand for high-speed data, 5G services, and the increasing use of mobile applications, the role of the MSC is evolving. Modern MSCs are equipped with advanced features to support newer technologies such as VoLTE (Voice over LTE) and VoWiFi (Voice over Wi-Fi), making them more versatile and capable of handling diverse traffic.
Conclusion
The Mobile Switching Center is integral to the functioning of mobile networks, ensuring that calls and data are properly routed and that users experience uninterrupted service. With its ability to manage call routing, handovers, mobility, and inter-network communication, the MSC is a central player in the telecommunications industry. As mobile networks evolve to meet the demands of 5G and beyond, the MSC will continue to adapt, playing a critical role in shaping the future of mobile communication.
Understanding the MSC’s role is essential for anyone interested in the complexities of modern telecommunications and the infrastructure that supports mobile communication worldwide.