Understanding 3GPP NR Specifications: Key Insights into 5G Development
telcomatraining.com – The development of 5G networks marks a new era in mobile communications, promising ultra-fast data speeds, low latency, and massive connectivity. At the heart of this technological leap is the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and its New Radio (NR) specifications, which form the global standard for 5G. Understanding 3GPP NR specifications is crucial for telecom professionals, engineers, and stakeholders aiming to navigate the 5G landscape effectively.
What is 3GPP?
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is a collaborative effort between multiple telecommunications standards organizations. It was established to create a globally applicable framework for mobile systems. 3GPP is responsible for standardizing technologies from GSM to LTE and now 5G NR (New Radio). Through a series of technical specifications, 3GPP ensures consistency, compatibility, and innovation across global mobile networks.
Introduction to 5G NR
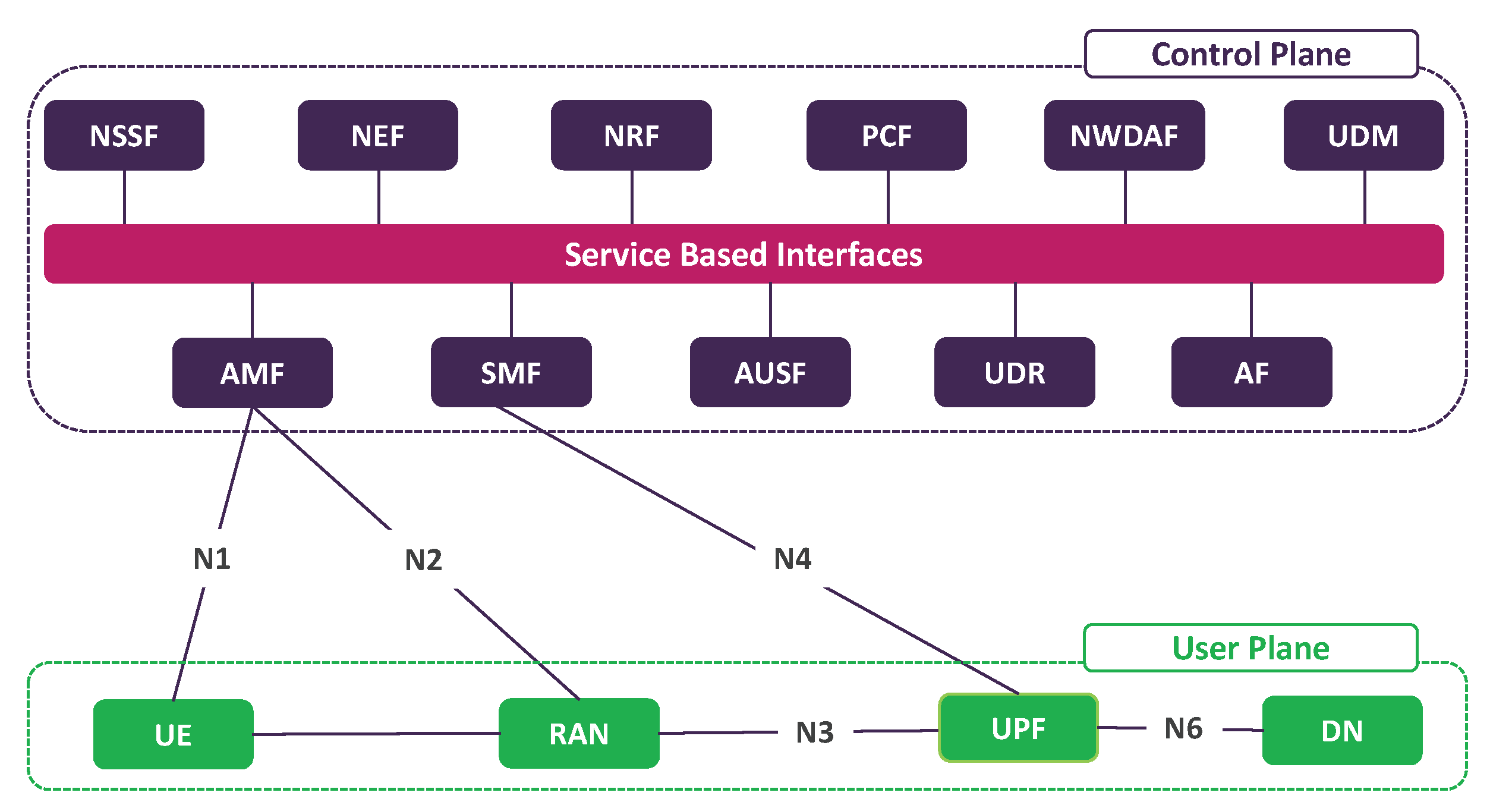
5G NR (New Radio) is the air interface developed by 3GPP for the fifth generation of mobile networks. Unlike previous generations, 5G NR is designed to support a wide range of services—from enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC) and massive machine-type communications (mMTC). These capabilities allow 5G to power applications such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and industrial automation.
Key Elements of 3GPP NR Specifications
The 3GPP NR specifications define the technical blueprint for 5G deployment. These specifications are released in phases, known as “Releases.” Each release builds on previous versions, introducing new features and refinements. The foundational release for 5G NR is Release 15, followed by Releases 16 and 17, which expand 5G’s capabilities further.
Here are the core components of NR specifications:
- Frequency Ranges (FR1 and FR2)
- FR1: Sub-6 GHz spectrum, offering broader coverage and reliability.
- FR2: Millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum, enabling extremely high data rates in dense urban environments.
- Numerology and Subcarrier Spacing
5G NR supports scalable subcarrier spacing, allowing flexibility in deployment scenarios. Depending on the use case and frequency, NR can adjust spacing from 15 kHz to 240 kHz. - Massive MIMO and Beamforming
These technologies are central to 5G performance, using advanced antenna systems to direct signals more precisely and improve spectrum efficiency. - Network Slicing
3GPP NR allows the creation of virtual networks (slices) optimized for specific applications, such as IoT or high-bandwidth streaming. - Standalone (SA) and Non-Standalone (NSA) Architectures
NSA uses existing LTE infrastructure to deliver 5G services, while SA is a fully 5G-native system with its own core network.
The Role of 3GPP in Global 5G Deployment
3GPP’s specifications ensure that 5G technology is interoperable, secure, and scalable. By creating detailed technical guidelines, 3GPP enables equipment vendors, mobile operators, and device manufacturers to develop compatible products and services across regions and markets.
As nations and businesses compete to lead in 5G adoption, compliance with 3GPP NR specifications becomes a strategic necessity. These standards provide the framework for building robust, future-proof networks capable of supporting evolving demands.
Future of 3GPP NR Specifications
With the upcoming Release 18 and beyond, 3GPP is focusing on 6G preparation, further integration of AI/ML into networks, and improvements to energy efficiency. These developments will continue to shape not just mobile communication, but also the broader digital economy.
Conclusion
Understanding 3GPP NR specifications is essential to unlocking the full potential of 5G. These specifications form the backbone of global 5G deployments, setting the stage for innovation across industries. As the 5G ecosystem evolves, keeping up with 3GPP releases and technical updates will be critical for anyone involved in the telecom and technology sectors.