Understanding 3GPP 5G Standards and Applications
Introduction
telcomatraining.com – The rollout of 5G technology marks a turning point in global communications. Unlike its predecessors, 5G is not just about faster internet—it is about enabling entirely new industries and services. At the heart of this evolution is the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), the international body responsible for defining 5G standards. Understanding how 3GPP standards shape 5G networks and their applications is crucial for businesses, developers, and consumers who want to maximize the benefits of this next-generation technology.
What is 3GPP?
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is a collaboration between several telecommunications standards organizations. Established in 1998, its mission is to create globally accepted specifications for mobile systems. While it initially focused on 3G, the scope has since expanded to 4G LTE and now 5G. 3GPP ensures that devices, networks, and infrastructure around the world remain interoperable and reliable.
For 5G, 3GPP introduced a comprehensive framework that includes Release 15, 16, and 17, each expanding on technical capabilities and enabling new use cases. These releases outline everything from radio access technologies to core network functions, ensuring that operators and manufacturers follow the same blueprint.
Key Features of 3GPP 5G Standards
3GPP standards define the unique strengths of 5G technology. Some of the most important features include:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Provides ultra-fast download and upload speeds, supporting high-quality video streaming, virtual reality, and advanced mobile applications.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC): Ensures near-zero delays, which is essential for mission-critical applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and industrial automation.
- Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC): Supports billions of IoT devices with low power consumption, enabling smart cities, agriculture, and large-scale sensor networks.
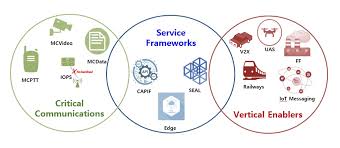
- Network Slicing: Allows operators to divide a single physical network into multiple virtual networks tailored to specific industries, such as healthcare, entertainment, or logistics.
By integrating these features, 3GPP creates a flexible and scalable system capable of supporting both consumer and enterprise needs.
Applications of 5G Based on 3GPP Standards
1. Smart Cities
With mMTC and network slicing, cities can connect sensors, cameras, and infrastructure systems to monitor traffic, reduce energy usage, and improve public safety.
2. Healthcare Innovation
URLLC enables applications such as telemedicine, real-time diagnostics, and remote surgeries, making healthcare more accessible and reliable.
3. Autonomous Transportation
3GPP standards support vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications, ensuring that autonomous cars and drones can operate safely with real-time data exchange.
4. Industrial Automation
Factories can leverage 5G-enabled robotics and IoT devices to monitor production lines, reduce downtime, and improve efficiency under the Industry 4.0 framework.
5. Consumer Experiences
From seamless 4K video streaming to immersive augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), 5G applications enhance everyday mobile experiences for consumers worldwide.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While 3GPP standards provide a strong foundation, global adoption faces challenges such as infrastructure costs, spectrum allocation, and cybersecurity risks. Moreover, achieving seamless coverage in rural and developing regions requires further collaboration between governments, operators, and technology vendors.
Looking ahead, 3GPP Release 18 and beyond aim to bring 6G evolution concepts, more advanced artificial intelligence integration, and even higher network efficiency. These updates will open the door to future technologies that we can only begin to imagine today.
Conclusion
The development of 5G would not be possible without the structured approach of the 3GPP standards. By defining technical requirements and ensuring interoperability, 3GPP enables industries worldwide to embrace transformative 5G applications. From healthcare to smart cities and entertainment, the possibilities are endless. As new releases continue to shape the 5G roadmap, understanding these standards is essential for staying ahead in the digital era.