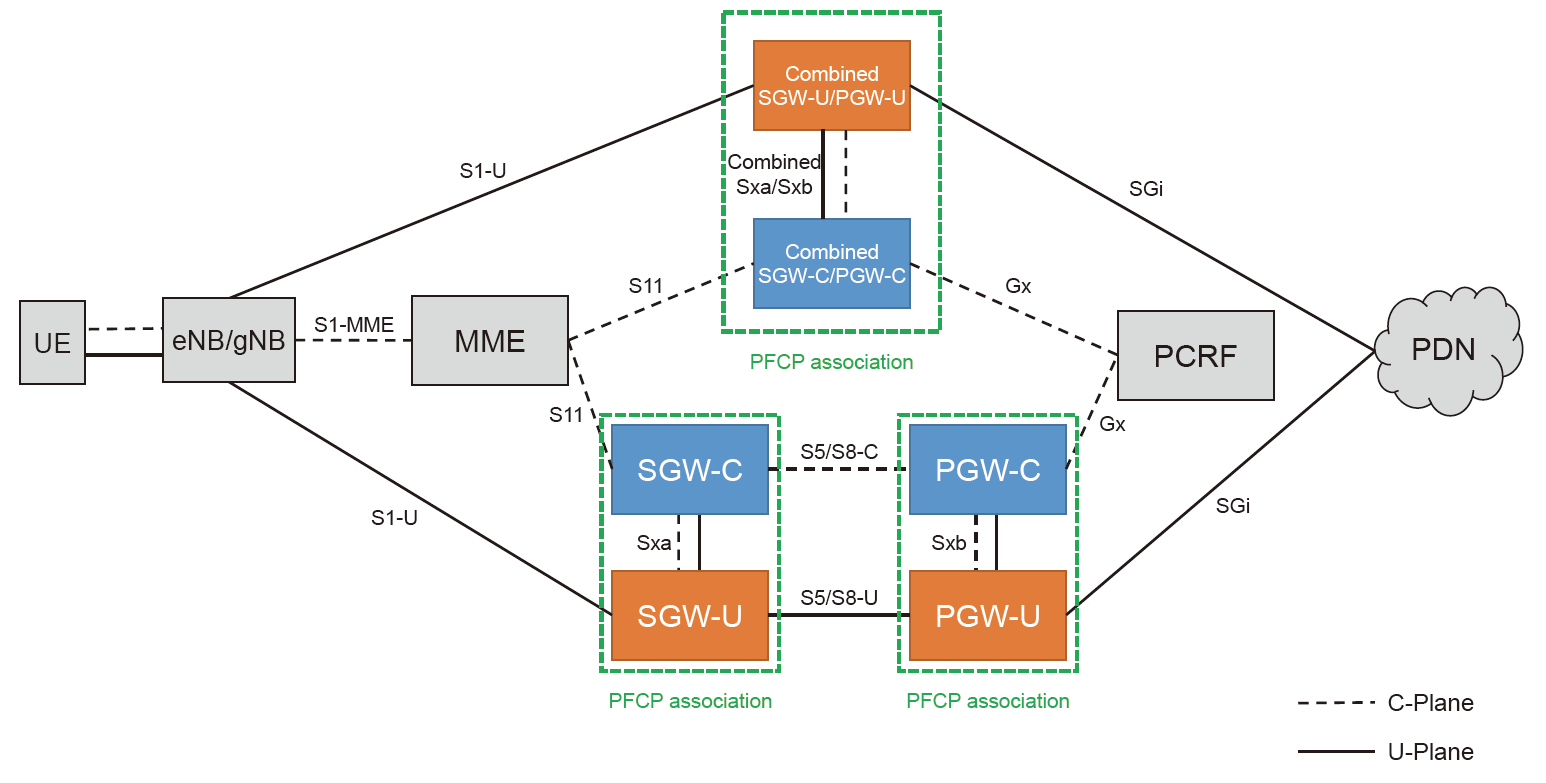
Separation of Control and User Plane in 5G NG-EPC: Key Concepts and Benefits
telcomatraining.com – As we enter the era of 5G, network architecture is evolving to meet the increasing demands for higher speed, lower latency, and greater capacity. One of the key advancements in the 5G Core or Next Generation Evolved Packet Core (NG-EPC) is the separation of the control plane and user plane, known as Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS). This separation offers greater flexibility, efficiency, and scalability compared to previous generations of networks.
What is Control Plane and User Plane?
In a network system, the control plane is responsible for managing signaling, authentication, connection management, and routing. It essentially ensures that the network remains in an optimal state by handling tasks such as mobility management and session control.
On the other hand, the user plane deals with the actual user data traffic, such as web browsing, video streaming, and voice calls. It is responsible for transporting the data packets between the user device and the network.
In previous generations, like LTE, the control and user planes were often combined within a single network entity. However, with the growing demand for more flexible and scalable network architectures, this approach became less efficient. As a result, separating the control and user planes became essential for optimizing performance in 5G networks.
Key Concepts of Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS)
1. Flexibility in Network Deployment:
One of the primary reasons for separating the control and user planes is to provide greater flexibility in network deployment. By decoupling the two planes, operators can distribute them in a way that best suits their network needs. For example, the control plane can be centralized for easier management and maintenance, while the user plane can be distributed closer to the end-users, improving network performance and reducing latency.
2. Scalability and Network Optimization:
With the explosive growth in the number of connected devices and data traffic, scalability becomes a significant concern. Separating the control and user planes allows operators to scale these two planes independently. The control plane can be scaled to handle a larger number of signaling messages, while the user plane can be scaled to accommodate growing data traffic. This approach ensures that the network remains efficient even under heavy loads.
3. Reduced Latency:
The separation of the control and user planes helps to reduce latency, a critical factor in applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT, and real-time communications. By moving the user plane closer to the edge of the network (edge computing), operators can minimize the distance data needs to travel, thus lowering the latency. This results in better performance for end-users and enhances the overall user experience.
4. Enhanced Network Reliability:
By distributing the control and user planes, operators can improve network reliability. If there is an issue in one plane, such as a signaling failure in the control plane, it will not necessarily impact the user plane, which can continue to function independently. This redundancy ensures that the network remains operational, even in the event of failures or congestion.
5. Efficient Resource Management:
The separation of planes also facilitates more efficient resource management. Network resources can be dynamically allocated to either the control plane or user plane based on demand, optimizing the use of available bandwidth and computational resources. This dynamic allocation helps operators maintain a balance between signaling and data traffic, improving overall network efficiency.
Benefits of CUPS in 5G NG-EPC
The separation of the control and user planes offers several key benefits for 5G networks:
- Increased network efficiency by optimizing traffic handling and reducing bottlenecks.
- Improved network performance due to lower latency and more efficient data transmission.
- Enhanced scalability that enables operators to meet the growing demand for data and services.
- Greater flexibility in deploying and managing network resources based on specific requirements.
- Optimized resource utilization, leading to cost savings for operators and better service for users.
Conclusion
The separation of the control and user planes in 5G NG-EPC is a transformative concept that enhances the flexibility, scalability, and performance of next-generation networks. By allowing operators to handle signaling and user data traffic independently, CUPS provides significant benefits, including reduced latency, improved network reliability, and better resource management. As 5G networks continue to evolve, the implementation of CUPS will play a crucial role in supporting the ever-growing demand for data and connectivity.