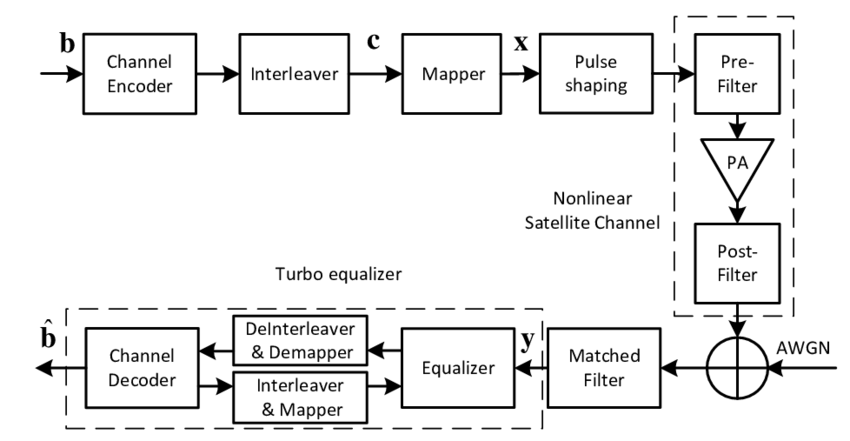
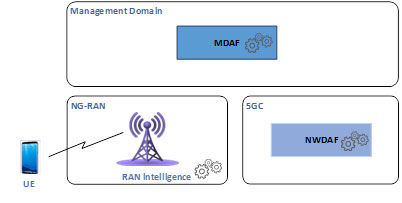
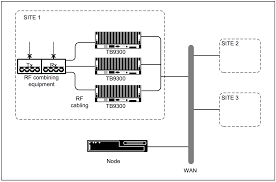
Satellite Communication Fundamentals: Free PDF and PPT Download
telcomatraining.com – Satellite communication has revolutionized global connectivity, enabling instant data transmission, broadcasting, navigation, and defense operations across vast distances. From the internet and television to weather monitoring and GPS, satellites form the invisible infrastructure that keeps the modern world connected. This article explores the fundamentals of satellite communication—its architecture, working principles, key components, and applications—with an opportunity to access a free PDF and PPT download for deeper learning.
1. What Is Satellite Communication?
Satellite communication is a wireless system that uses artificial satellites orbiting the Earth to relay signals between different points on the planet. Instead of relying solely on terrestrial infrastructure like cables or fiber optics, satellite systems use radio waves to transmit and receive data across long distances. This makes them essential for remote areas, maritime navigation, and global broadcasting.
The basic principle is simple: a signal is transmitted from a ground station (the uplink) to a satellite, which amplifies and retransmits it back to another ground station (the downlink). The process ensures seamless communication across continents, oceans, and even polar regions.
2. Core Components of Satellite Communication
A satellite communication system consists of several interconnected components:
- Satellite (Space Segment): The satellite itself houses transponders that receive, amplify, and retransmit signals. It operates in specific frequency bands such as C, Ku, Ka, or L bands.
- Ground Station (Earth Segment): These include antennas, transmitters, and receivers that manage communication between users and the satellite.
- Control Segment: This ensures proper satellite positioning, orbit maintenance, and system health monitoring.
Together, these components ensure continuous and reliable communication links across the globe.
3. Types of Satellites and Orbits
Satellites are categorized based on their orbits and functions:
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO): Positioned about 35,786 km above the equator, GEO satellites remain fixed relative to Earth’s rotation, ideal for TV broadcasting and weather observation.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): Used mainly for navigation systems like GPS and Galileo.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Closer to the Earth (500–2,000 km), LEO satellites offer low latency and are crucial for broadband constellations like Starlink and OneWeb.
4. Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
- Wide area coverage
- Reliable communication in remote locations
- Excellent for broadcasting and real-time data sharing
Challenges:
- High launch and maintenance costs
- Signal delay (especially in GEO systems)
- Vulnerability to space weather and interference
5. Key Applications of Satellite Communication
Satellite communication plays a vital role in multiple sectors:
- Telecommunications: Global voice and data services
- Broadcasting: TV, radio, and internet streaming
- Navigation: GPS and aviation guidance
- Military and Defense: Secure command and surveillance networks
- Disaster Management: Emergency communication in disaster-stricken regions
These applications underline how satellites enable connectivity in both everyday life and mission-critical operations.
6. Learning Resources: Free PDF and PPT Download
For learners, engineers, and students seeking to understand satellite communication more deeply, comprehensive study materials are available for free download:
- Free PDF: Covers system architecture, frequency bands, link budgets, and modulation techniques.
- Free PPT: Ideal for presentations or teaching, illustrating satellite orbits, network topologies, and real-world applications.
These resources are designed to support both academic learning and professional training in telecommunications, networking, and space technology.
Conclusion
Satellite communication forms the backbone of the global information network. As technology evolves—especially with 5G and Low Earth Orbit constellations—the demand for faster, more efficient satellite systems continues to grow. Understanding the fundamentals is key for anyone aspiring to work in telecommunications, aerospace, or defense industries.
Download your free Satellite Communication Fundamentals PDF and PPT today to start your journey into the future of global connectivity.