RF Basics and Components – PDF & PPT Resource Download
Introduction
telcomatraining.com – Radio Frequency (RF) technology forms the foundation of modern wireless communication. From mobile networks and satellite systems to Wi-Fi and IoT devices, RF signals carry data across the airwaves. Understanding the basics of RF and its core components is essential for students, engineers, and telecom professionals alike. This article provides an overview of RF fundamentals, the critical components used in RF circuits, and a direct link to PDF & PPT training resources for deeper study.
What is RF?
RF, or Radio Frequency, refers to the range of electromagnetic waves that lie between 3 kHz and 300 GHz. These signals are widely used for broadcasting, cellular communication, radar, and satellite transmissions. Unlike wired systems, RF allows data to be transmitted wirelessly, making it a key enabler of mobile and connected technologies.
Key RF Characteristics
- Frequency & Wavelength – Frequency determines how fast the signal oscillates, while wavelength is the distance a wave travels in one cycle.
- Amplitude & Power – These control the strength of the RF signal, affecting coverage and clarity.
- Modulation – Techniques such as AM, FM, QAM, and OFDM are used to encode information into RF signals.
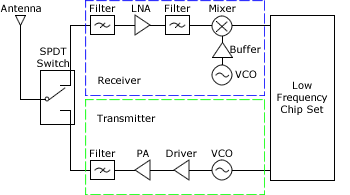
Essential RF Components
RF systems rely on a combination of active and passive components to transmit, receive, and process signals effectively.
1. Antennas
Antennas convert electrical signals into electromagnetic waves (and vice versa). Common types include dipole, patch, Yagi, and parabolic antennas. The choice depends on coverage area, frequency band, and application.
2. Amplifiers
Amplifiers boost RF signal strength. Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) are used in receivers to improve weak signals, while Power Amplifiers (PAs) are used in transmitters for long-distance communication.
3. Filters
Filters allow only desired frequencies to pass while blocking unwanted signals. They include band-pass, low-pass, and high-pass filters, ensuring system stability and reducing interference.
4. Oscillators & Mixers
Oscillators generate RF signals at specific frequencies. Mixers combine signals to shift them up or down in frequency, which is vital in both transmitters and receivers.
5. Transmission Lines
Coaxial cables, microstrip lines, and waveguides carry RF signals between components. Their design impacts impedance matching and signal loss.
Applications of RF Technology
RF principles power a wide range of applications, including:
- Telecom Networks: 4G, 5G, and future 6G systems rely on RF for high-speed data transfer.
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, smart TVs, and IoT devices all use RF links.
- Defense & Aerospace: Radar, satellite communication, and navigation systems depend heavily on RF.
- Medical Systems: MRI machines and wireless health monitoring devices also leverage RF signals.
Why Learn RF Basics?
For anyone pursuing a career in telecommunications, electronics, or wireless networking, a strong understanding of RF is crucial. Learning about components and signal behavior helps in designing efficient systems, troubleshooting interference issues, and optimizing network performance.
Free PDF & PPT Download
To help learners dive deeper, we have prepared comprehensive PDF and PPT resources covering:
- RF fundamentals
- Signal properties
- Detailed component diagrams
- Practical examples and applications
👉 [Download RF Basics and Components PDF & PPT Here]
Conclusion
RF technology is the backbone of our connected world, driving everything from smartphones to satellites. By mastering RF basics and understanding the key components, learners and professionals can build a strong foundation for careers in wireless communication. Use the free downloadable PDF & PPT resources to expand your knowledge and apply RF concepts in real-world projects.