Integrating AI/ML in NG-RAN: A New Era for Intelligent 5G Networks
telcomatraining.com – As 5G networks continue to evolve, the demand for higher performance, efficiency, and intelligence has never been greater. One of the key innovations driving this transformation is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into the Next-Generation Radio Access Network (NG-RAN). This integration marks a paradigm shift toward more autonomous, self-optimizing networks, enabling telecom providers to meet the ever-growing expectations of users and emerging technologies.
What Is NG-RAN?
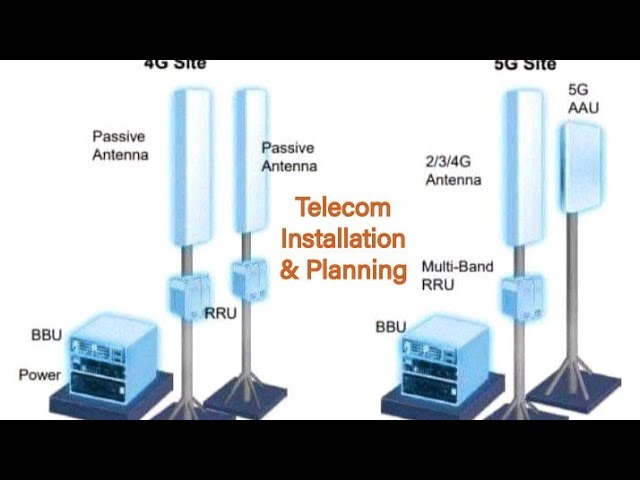
NG-RAN, or Next-Generation Radio Access Network, is a component of 5G architecture that manages radio connections between user devices and the core network. It includes distributed and centralized units (DU and CU), which handle tasks like scheduling, handover, and signal processing. NG-RAN is designed for flexibility, low latency, and scalability—making it the ideal foundation for integrating AI/ML-driven intelligence.
The Role of AI/ML in 5G Networks
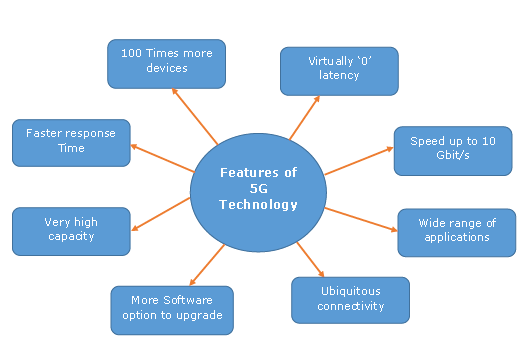
AI and ML provide the tools to analyze vast amounts of real-time data from the RAN environment. By learning from patterns and anomalies, these technologies can make predictions, detect faults, and optimize performance autonomously. For 5G, this means achieving greater efficiency in spectrum use, faster handovers, and smarter resource allocation—benefits that are critical for applications like autonomous vehicles, IoT, and immersive AR/VR.
Key Benefits of AI/ML Integration in NG-RAN
- Real-Time Network Optimization
ML algorithms continuously monitor the network environment, adjusting parameters like power levels, beamforming configurations, and scheduling priorities to ensure peak performance with minimal human intervention. - Predictive Maintenance and Fault Management
AI enables proactive detection of hardware failures or software anomalies. By predicting faults before they occur, operators can reduce downtime and improve service reliability. - Dynamic Resource Allocation
AI can allocate resources dynamically based on real-time traffic patterns, user density, and application requirements, ensuring optimal use of network infrastructure without manual tuning. - Enhanced User Experience
Intelligent RAN decisions result in reduced latency, fewer dropped calls, and higher data throughput, improving overall user satisfaction, especially in high-demand urban environments. - Energy Efficiency
AI/ML models help reduce energy consumption by powering down or reallocating underused resources during off-peak times, contributing to sustainable network operations.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
Telecom giants like Ericsson, Nokia, and Huawei are actively investing in AI-powered NG-RAN solutions. Use cases include self-organizing networks (SON), where the system learns to configure, optimize, and heal itself, and closed-loop automation, where AI continuously improves performance based on feedback loops.
For example, during a high-traffic event like a sports game, AI can predict congestion and reroute traffic to underutilized cells. In rural areas, ML models can optimize beamforming to ensure stable connectivity despite sparse infrastructure.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are clear, integrating AI/ML into NG-RAN is not without challenges. Key concerns include:
- Data Privacy and Security: Handling user data responsibly is critical, especially when ML models require large datasets for training.
- Computational Demands: AI workloads require significant processing power, which may strain edge devices or increase costs.
- Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility across multi-vendor network components is essential for seamless AI integration.
The Road Ahead
As 5G networks expand globally, the role of AI/ML in NG-RAN will only become more prominent. With advancements in edge computing and cloud-native architectures, deploying intelligent, adaptive RAN solutions at scale is increasingly feasible. The convergence of AI and 5G is not just enhancing connectivity—it is redefining how networks operate, respond, and evolve.