Inside the 5G Core Network: Architecture, Functions, and Use Cases (600+ words)
telcomatraining.com – The arrival of 5G marks a revolutionary leap in mobile network technology, not just in terms of speed, but also in how the network is structured and operates. At the heart of this transformation lies the 5G Core Network (5GC) — a completely redesigned architecture that enables ultra-low latency, massive device connectivity, and enhanced data throughput. This article delves into the core architecture of 5G, outlines its primary functions, and highlights real-world use cases that showcase its impact.
What is the 5G Core Network?
The 5G Core Network (5GC) is the backbone of the 5G mobile network, responsible for managing data traffic, user mobility, and service delivery. Unlike previous generations such as 4G LTE, 5GC is designed based on a service-based architecture (SBA). This modular design allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and interoperability among network functions.
In simpler terms, the 5G core is what makes it possible for your device to connect seamlessly to different services—whether you’re streaming video, managing smart home devices, or enabling critical communications for autonomous vehicles.
Architecture of the 5G Core Network
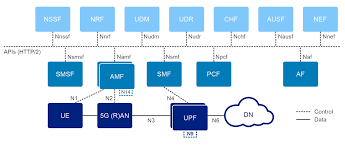
The 5GC architecture introduces several key components that work together to deliver a next-gen experience. Major elements include:
1. Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF):
Handles user registration, connection, and mobility management. It replaces the MME from 4G.
2. Session Management Function (SMF):
Manages sessions and IP address allocation, separating control and user planes for better efficiency.
3. User Plane Function (UPF):
Responsible for data routing and forwarding, ensuring that user data reaches its destination quickly and securely.
4. Network Exposure Function (NEF):
Allows third-party applications to securely interact with network services via APIs.
5. Policy Control Function (PCF):
Implements real-time policy and charging rules across the network.
6. Unified Data Management (UDM):
Stores and manages user subscription data, replacing the HSS in 4G networks.
This architecture is fully cloud-native, meaning it can operate within virtualized or containerized environments, allowing network operators to scale services more efficiently.
Core Functions of 5GC
The 5G Core provides a variety of essential functions that distinguish it from its predecessors:
- Network Slicing: Allows multiple virtual networks to run on the same physical infrastructure, enabling customized services for different use cases like gaming, IoT, or emergency response.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC): Supports mission-critical applications that require minimal delay.
- Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC): Enables connectivity for billions of IoT devices.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Delivers higher data rates for streaming, AR/VR, and mobile broadband.
Each of these capabilities serves a distinct category of services, offering unprecedented flexibility and performance.
Real-World Use Cases
The 5G Core Network is already powering transformative changes across industries:
1. Autonomous Vehicles:
5G’s ultra-low latency allows vehicles to communicate with infrastructure and each other in real time, reducing accidents and improving traffic flow.
2. Smart Factories:
With support for IoT and private network slices, manufacturers can monitor and control machinery remotely with high precision and minimal downtime.
3. Remote Healthcare:
5G enables high-quality video consultations, remote surgery using robotic arms, and constant patient monitoring using wearables.
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
eMBB and edge computing combine to deliver immersive experiences without lag, revolutionizing gaming, training, and remote collaboration.
5. Public Safety:
Dedicated network slices ensure first responders have reliable, high-speed connections during emergencies, even when public networks are congested.
Conclusion
The 5G Core Network is not just an upgrade—it’s a complete reimagining of mobile connectivity. With its service-based architecture, cloud-native design, and support for innovative applications, the 5GC lays the foundation for a hyper-connected future. As adoption grows and more use cases emerge, the 5G core will be the driving force behind next-generation digital transformation across all sectors.