How 5G Antennas Work to Boost Connectivity
telcomatraining.com – The rollout of 5G networks represents a major leap in mobile communication technology, enabling ultra-fast speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity. Behind this transformation lies one of the most critical components of the infrastructure—5G antennas. These antennas are not just upgraded versions of traditional ones; they are designed with advanced engineering to handle the unique requirements of fifth-generation wireless systems. Understanding how 5G antennas work provides insights into why connectivity is improving worldwide.
The Role of Antennas in 5G Technology
Antennas act as the bridge between devices and the network. In 5G, antennas must transmit and receive signals at much higher frequencies compared to 4G. While 4G primarily operated below 6 GHz, 5G extends into millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies ranging from 24 GHz to 100 GHz. These higher frequencies enable faster data transfer but have shorter ranges and are more easily blocked by buildings, trees, and even weather conditions.
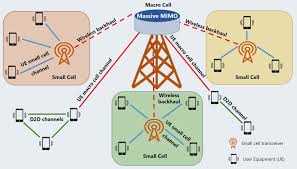
To overcome these challenges, 5G networks employ massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) antennas. Unlike traditional antennas with a few elements, massive MIMO arrays use dozens or even hundreds of smaller antenna elements to increase signal strength, capacity, and efficiency.
Beamforming: Directing the Signal Where It’s Needed
One of the most powerful innovations in 5G antenna technology is beamforming. Instead of broadcasting signals in every direction, beamforming allows antennas to focus wireless signals directly toward users.
This concentrated transmission improves coverage and reduces interference. For example, in a crowded stadium or urban area, beamforming ensures that users receive strong and stable connections without competing heavily with each other. It’s like replacing a floodlight with a laser pointer—more focused, efficient, and reliable.
Small Cells and Distributed Networks
Because high-frequency signals travel shorter distances, 5G relies on small cell antennas to provide localized coverage. These compact base stations are often installed on streetlights, utility poles, or building rooftops. By placing antennas closer to users, networks reduce dead zones and maintain consistent speed even in high-density areas.
This decentralized approach differs from previous generations that depended heavily on large cell towers. In 5G, thousands of smaller antennas work together to create a web of connectivity, ensuring seamless performance in both urban and suburban environments.
Integration with Smart Technologies
Modern 5G antennas are also designed with intelligent features that adjust to real-time demand. Using AI-driven algorithms, antennas can optimize bandwidth, prioritize traffic, and dynamically reconfigure based on network load. For instance, during peak hours in a busy business district, antennas can adapt to serve more users without compromising quality.
Additionally, 5G antennas support the Internet of Things (IoT) by connecting billions of devices, from autonomous vehicles to smart factories. Their ability to handle massive simultaneous connections makes them a cornerstone of digital transformation.
Challenges in 5G Antenna Deployment
Despite their advantages, 5G antennas face deployment challenges. High-frequency signals require a dense infrastructure, which means installing a large number of small cells in cities. This raises concerns about cost, urban planning, and even public perception of radiation exposure, though studies confirm that 5G operates within safe international guidelines.
Moreover, rural areas with lower population density may take longer to benefit from widespread 5G coverage, as network providers prioritize cities where demand is highest.
Conclusion
5G antennas are far more than simple transmitters—they are advanced systems that combine massive MIMO, beamforming, and small cell deployment to deliver faster, more reliable, and smarter connectivity. As these antennas continue to roll out worldwide, they will not only improve mobile communication but also enable innovations in healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and beyond. Understanding how they work highlights the crucial role antennas play in boosting the promise of 5G technology.