Guide to 5G Network Slice Management and Its Key Functions
telcomatraining.com – As 5G networks continue to evolve, network slicing has emerged as a groundbreaking solution that enables operators to support diverse use cases and industries on a single physical infrastructure. Through 5G network slice management, service providers can allocate specific portions of the network tailored to unique business needs, ensuring optimal performance, security, and reliability. This article explores the fundamentals of 5G network slicing, the importance of efficient slice management, and its key functions.
What is 5G Network Slicing?
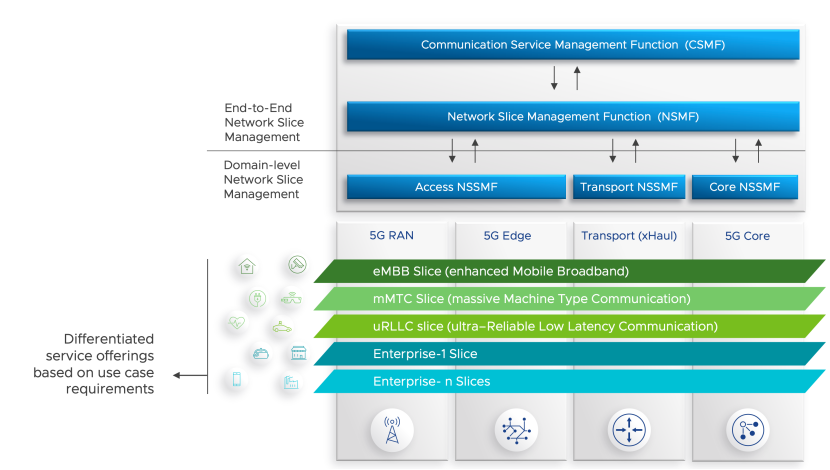
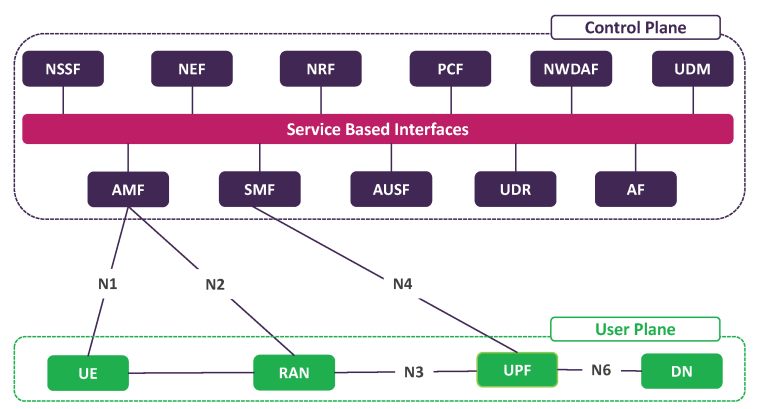
5G network slicing is a virtual networking architecture that allows multiple logical networks to operate on a shared physical infrastructure. Each “slice” functions as an independent end-to-end network designed to fulfill a specific purpose or meet specific service-level requirements (SLAs). For example, one slice could support ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC) for autonomous vehicles, while another focuses on enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) for streaming and mobile gaming.
This ability to create customized virtual networks makes 5G a highly flexible and efficient technology for both telecom operators and enterprises.
The Importance of Network Slice Management
As the number and complexity of slices increase, network slice management becomes critical. Without robust management tools and processes, operators would face challenges in provisioning, monitoring, and maintaining the health and performance of each slice. Effective slice management ensures:
- Dynamic resource allocation
- Service assurance and quality
- Scalability for future growth
- Isolation and security between slices
- Automation and orchestration for operational efficiency
In essence, slice management is the backbone that makes network slicing practical and commercially viable in the real world.
Key Functions of 5G Network Slice Management
To support the full lifecycle of network slicing, slice management encompasses several core functions:
1. Slice Design and Provisioning
The process begins with defining slice templates that outline service requirements, quality of service (QoS) parameters, and resource configurations. Slice provisioning involves translating these templates into real network instances, dynamically allocating compute, storage, and bandwidth resources.
This function is crucial in enabling fast time-to-market for new services, especially in verticals like healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities.
2. Slice Orchestration
Orchestration involves coordinating resources across the RAN (Radio Access Network), transport network, and core network to build and maintain a slice. It leverages AI-driven automation to ensure end-to-end consistency and real-time adaptability.
Slice orchestration also supports multi-domain and multi-vendor environments, allowing operators to scale slice deployments without vendor lock-in.
3. Performance Monitoring and Assurance
Once a slice is live, continuous monitoring is essential to ensure it meets predefined SLAs. Performance metrics such as latency, jitter, throughput, and availability are tracked in real-time.
Advanced analytics tools can detect anomalies, trigger alerts, and automatically adjust configurations to maintain optimal performance. This function is particularly important for mission-critical services like remote surgery or connected vehicles.
4. Slice Scaling and Optimization
As user demand fluctuates, slices must be able to scale dynamically. Network slice management platforms use predictive analytics and AI to forecast usage patterns and reallocate resources accordingly.
This elasticity helps maintain user experience during peak times while optimizing costs during low-traffic periods.
5. Fault Management and Security
Each slice operates independently, but a fault in one slice should not impact others. Network slice management ensures fault isolation and rapid remediation. Security functions include encryption, access control, and continuous threat detection to protect both users and infrastructure.
This robust security and isolation are what make network slicing a suitable solution for sensitive sectors like finance, defense, and emergency services.
Final Thoughts
5G network slicing represents a paradigm shift in how mobile networks are built and operated. However, its success hinges on effective network slice management. With proper design, orchestration, monitoring, scaling, and security measures in place, operators can deliver highly tailored services while maximizing infrastructure efficiency.
As we move further into the era of intelligent connectivity, mastering slice management will be essential for service providers looking to unlock the full potential of 5G.
Let me know if you want this article formatted for blog publishing (with headings, meta description, keywords, etc.) or converted into a PDF.