Glossary of Telecom Terms: Essential Definitions for Engineers and Students
telcomatraining.com – The telecommunications (telecom) industry is the backbone of modern connectivity, enabling communication across the globe through voice, data, and multimedia transmission. For engineers and students entering this rapidly evolving field, understanding key telecom terms is crucial. This glossary provides clear, concise definitions of essential telecom concepts, offering a foundation for anyone involved in network design, mobile technology, or digital communication systems.
1. Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a network connection, usually measured in bits per second (bps). In simple terms, higher bandwidth allows more data to flow simultaneously, improving network performance and speed.
2. Base Station
A base station is a fixed transceiver in a mobile network that communicates with user devices within its coverage area. It forms the bridge between mobile users and the core network, enabling voice and data transmission in cellular systems such as 4G LTE and 5G.
3. Frequency Spectrum
The frequency spectrum encompasses the range of electromagnetic frequencies used for wireless communication. Regulators allocate specific frequency bands for different technologies—like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or mobile networks—to prevent interference and optimize performance.
4. Latency
Latency is the delay between sending and receiving data across a network. Measured in milliseconds (ms), lower latency means faster response times. This is particularly important for real-time applications like video calls, online gaming, and remote surgery powered by 5G technology.
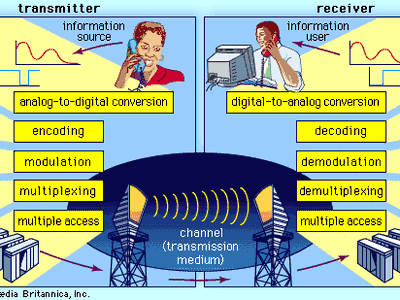
5. Modulation
Modulation is the process of varying a carrier signal’s properties—such as amplitude, frequency, or phase—to encode information for transmission. Common techniques include AM (Amplitude Modulation), FM (Frequency Modulation), and QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), which are vital for efficient data delivery.
6. Multiplexing
Multiplexing allows multiple data streams to share a single communication channel, increasing efficiency. Techniques like Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) enable simultaneous transmission of different signals without interference.
7. Fiber Optics
Fiber optics use thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light. They offer ultra-high bandwidth and low signal loss over long distances, making them essential for high-speed internet and backbone telecom infrastructure.
8. Internet Protocol (IP)
IP defines how data packets are addressed and transmitted across networks. IPv4 and IPv6 are the two main versions, with IPv6 designed to handle the massive growth of connected devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) era.
9. 5G
5G is the fifth generation of mobile communication technology, offering faster speeds, reduced latency, and the ability to connect billions of devices. It supports innovations like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and advanced IoT applications.
10. Network Topology
Network topology describes how devices and nodes are arranged in a network. Common types include star, mesh, ring, and bus topologies. The structure impacts performance, reliability, and scalability in communication systems.
11. Router
A router directs data packets between computer networks, ensuring information reaches the correct destination. It plays a critical role in both home and enterprise networks, managing traffic flow and improving connectivity.
12. Satellite Communication
This refers to data transmission through satellites orbiting Earth, used for global broadcasting, GPS navigation, and remote internet access. Satellites complement terrestrial networks, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
Conclusion
Understanding telecom terminology is fundamental for engineers, technicians, and students who want to excel in communication technologies. As 5G, IoT, and edge computing reshape connectivity, a strong grasp of these core terms helps professionals innovate, troubleshoot, and design efficient networks. This telecom glossary serves as a starting point for mastering the complex yet fascinating world of modern telecommunications.