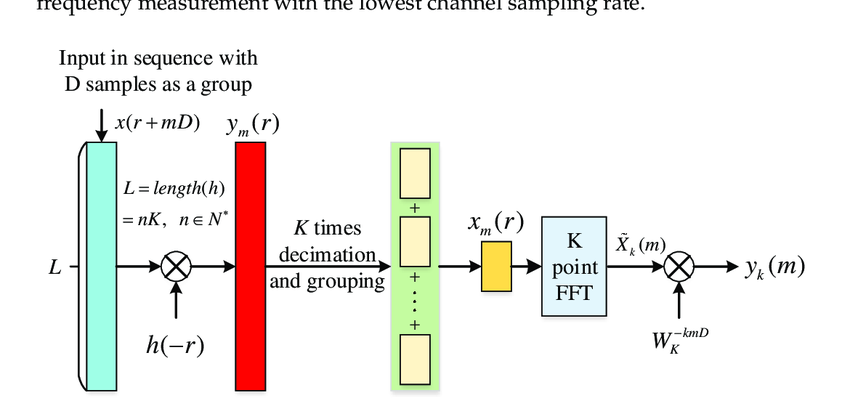
Exploring WOLA: The Weighted Overlap and Add Technique
telcomatraining.com – WOLA, or Weighted Overlap and Add, is a popular signal processing technique commonly used in various fields such as audio processing, speech synthesis, and time-frequency analysis. This method is especially useful for reconstructing signals from a set of overlapping windows and performing tasks like filtering, denoising, and audio enhancement. It combines overlapping segments of a signal and then “adds” them back together, taking into account weighted contributions from each segment. In this article, we will explore what WOLA is, how it works, and its applications.
The Basics of WOLA
To understand WOLA, it’s essential to grasp the concept of windowing. Windowing is a technique where a signal is divided into smaller, overlapping segments or windows. These windows are processed individually, which makes it easier to handle complex signals. WOLA takes this a step further by applying weights to these overlapping windows before summing them up, resulting in a smoother and more accurate reconstruction of the original signal.
The “weighted” part of WOLA refers to assigning different weights to each overlapping segment, rather than treating them all equally. This is typically done to minimize issues like signal distortion, which can arise from the abrupt edges of windows. By using appropriate weights, WOLA can reduce artifacts such as ringing and spectral leakage, improving the overall quality of the processed signal.
How WOLA Works
The process of WOLA can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Windowing: The original signal is divided into smaller, overlapping windows. Each window represents a segment of the signal, and typically, the windows overlap by 50%, meaning each window shares half of its data with the next one.
- Window Function: A window function, such as a Hamming, Hann, or Blackman-Harris window, is applied to each segment. This function shapes the window to reduce the sharp edges of the signal that might cause discontinuities when recombined.
- Weighting: In WOLA, a set of weights is applied to the overlapping segments before they are summed. These weights can be based on factors like the frequency content of the signal or the desired output characteristics. Weights are often designed to ensure that the higher-energy regions of the signal contribute more to the final reconstruction.
- Overlap and Add: After each windowed segment is processed, the weighted segments are “added” together to form the final output signal. The overlap part means that each segment contributes to more than one point in the final signal, ensuring smoother transitions and better preservation of signal details.
- Reconstruction: The resulting signal is a combination of all these weighted windows. The output will usually be much cleaner and more accurate, especially in applications like audio where signal artifacts must be minimized.
Applications of WOLA
WOLA is commonly used in a variety of applications, particularly in audio and speech processing. Some of its most notable uses include:
- Speech Synthesis: WOLA is used in speech synthesis systems to enhance the quality of generated speech. By carefully weighing the windows and performing the overlap and add process, a more natural-sounding voice can be created.
- Audio Enhancement: In noise reduction and audio restoration, WOLA helps in reducing distortions by reconstructing the signal with minimal artifacts. It’s commonly used in both real-time and post-processing audio editing software.
- Time-Frequency Analysis: In applications like spectrogram generation and signal analysis, WOLA is used to ensure accurate frequency resolution, especially in non-stationary signals where the frequency content changes over time.
- Denoising: In areas where signals are noisy, such as in medical signal processing or telecommunications, WOLA helps clean up the data by smoothing out the noise while retaining the important features of the signal.
Advantages of WOLA
WOLA offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in many signal processing applications:
- Reduced Artifacts: The use of weights helps minimize common artifacts like spectral leakage and aliasing that can occur when windowing alone is used.
- Improved Signal Quality: By properly weighting overlapping windows, WOLA ensures that the signal’s finer details are preserved, leading to a higher-quality output.
- Flexibility: The weights can be tailored for specific tasks, allowing WOLA to be customized for various applications ranging from audio enhancement to more advanced signal reconstruction.
Conclusion
WOLA, or Weighted Overlap and Add, is a powerful and flexible technique in signal processing that addresses many of the challenges faced when working with windowed data. By applying weights to overlapping windows before summing them, WOLA reduces common artifacts and improves the overall quality of the reconstructed signal. Its applications in audio processing, speech synthesis, and noise reduction make it an invaluable tool for anyone working with complex signals that require high-quality reconstruction and minimal distortion.