Exploring WMAN: Wireless Metropolitan Area Network Overview
telcomatraining.com – Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMAN) is an advanced communication technology designed to connect multiple users across a wide geographical area, such as a city or a large urban region. As a vital component of modern connectivity, WMAN provides high-speed wireless communication services to businesses, government institutions, and individual users. This article explores the key aspects of WMAN, including its features, benefits, and applications.
What is WMAN?
WMAN refers to a type of wireless network that covers a metropolitan area, providing broadband internet access and other communication services. Unlike Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN), which are limited to small areas such as homes or offices, WMAN offers broader coverage. It bridges the gap between local area networks (LAN) and wide area networks (WAN), making it a critical solution for urban connectivity.
WMAN utilizes technologies like WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) to deliver high-speed, reliable connections over distances ranging from a few kilometers to tens of kilometers. These networks often rely on base stations, which transmit signals to various user devices, ensuring seamless connectivity.
Key Features of WMAN
- Wide Coverage
WMAN networks are specifically designed to cover large urban or metropolitan areas, making them suitable for city-wide communication needs. - High Data Transfer Rates
With advanced wireless technologies like WiMAX, WMAN offers high-speed internet connections capable of supporting bandwidth-intensive applications. - Scalability
WMAN networks can easily scale to accommodate a growing number of users, making them ideal for expanding urban areas or densely populated cities. - Flexibility
The wireless nature of WMAN eliminates the need for extensive cabling, allowing for easier deployment and lower installation costs. - Interoperability
Many WMAN systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing communication infrastructures, such as cellular networks and wired broadband systems.
Benefits of WMAN
- Cost-Effective Connectivity
Deploying WMAN is often more affordable than laying extensive fiber-optic cables, especially in areas where infrastructure development is challenging. - Faster Deployment
The wireless nature of WMAN allows for quicker installation compared to wired networks, making it an efficient solution for rapidly growing urban centers. - Mobility Support
WMAN ensures uninterrupted connectivity for users on the move, such as public transport passengers or mobile workers. - Reliable Communication
Advanced technologies used in WMAN ensure stable connections even in densely populated areas or regions with high interference. - Accessibility
WMAN can bridge the digital divide by providing internet access to underserved areas within a metropolitan region.
Applications of WMAN
- Public Internet Access
Many cities utilize WMAN to provide free or affordable internet access in public spaces such as parks, libraries, and transportation hubs. - Corporate Networks
Businesses leverage WMAN to establish reliable and high-speed connections between branch offices and headquarters within a metropolitan area. - Smart Cities
WMAN is a cornerstone of smart city initiatives, supporting IoT (Internet of Things) devices for applications like traffic management, surveillance, and environmental monitoring. - Disaster Recovery
In emergencies, WMAN can provide quick and reliable communication channels for first responders and affected communities. - Educational Services
Schools and universities use WMAN to offer internet access to students and staff, enabling remote learning and collaborative projects.
Challenges of WMAN
While WMAN offers numerous advantages, it also faces some challenges. Signal interference from buildings, weather conditions, or other wireless devices can impact performance. Additionally, the initial setup costs for base stations and equipment may be significant, particularly for large-scale deployments. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and investment in advanced technologies to ensure consistent performance.
The Future of WMAN
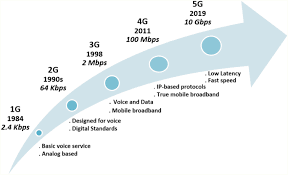
The evolution of WMAN is closely tied to advancements in wireless technology, such as 5G and beyond. As urban areas become increasingly interconnected, the demand for efficient and high-capacity networks like WMAN will continue to grow. Future developments may include improved data rates, enhanced security features, and greater integration with IoT systems.
Conclusion
WMAN is a powerful solution for meeting the growing communication needs of metropolitan areas. Its ability to provide wide coverage, high-speed connectivity, and flexibility makes it an essential component of modern infrastructure. As technology continues to advance, WMAN will play a pivotal role in enabling smart cities, bridging the digital divide, and supporting seamless connectivity for users in urban environments.