Exploring Open Midhaul in 5G: A Deep Dive into F1-C and F1-U Interfaces
telcomatraining.com – As 5G continues to reshape the landscape of wireless communication, the architecture of mobile networks is evolving to meet the demands of ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and enhanced reliability. One critical component in this architecture is the Open Midhaul, a concept gaining traction as a means of optimizing the connection between the Centralized Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU) in 5G networks. This article delves into the significance of Open Midhaul and explores the roles of the F1-C and F1-U interfaces in facilitating seamless 5G communication.
What is Open Midhaul?
In a traditional mobile network, the transport between baseband units and radio units was typically vendor-locked and proprietary. However, with 5G’s service-based architecture and the need for scalability and interoperability, Open Midhaul introduces a more flexible and open framework. It allows for interoperability between multi-vendor systems, enabling operators to choose components based on performance and cost without being restricted to a single vendor.
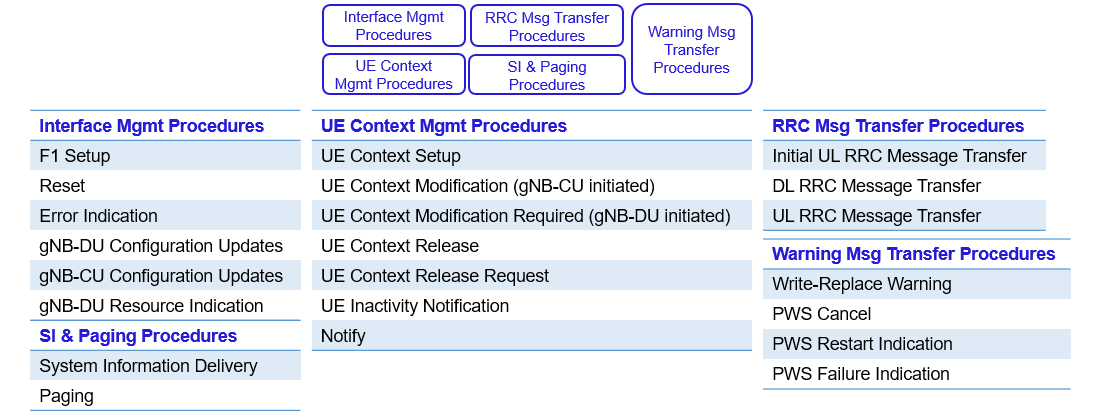
Open Midhaul connects the CU and DU components of the Open RAN (Radio Access Network). The Centralized Unit handles higher-layer protocols such as Radio Resource Control (RRC), while the Distributed Unit manages lower-layer protocols like PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol) and RLC (Radio Link Control). To facilitate communication between these two units, 3GPP has defined the F1 interface, which is further split into F1-C and F1-U.
Understanding F1-C and F1-U Interfaces
The F1 interface plays a crucial role in 5G midhaul networks. It defines the protocols and signaling mechanisms that ensure data and control information flows efficiently between the CU and DU.
- F1-C (Control Plane Interface):
This interface is responsible for control signaling. It manages RRC setup, mobility control, session management, and other control plane functionalities. F1-C ensures that the network adapts dynamically to changes, such as user mobility or quality of service requirements. By decoupling control from user data, F1-C allows centralized coordination, enhancing network intelligence and flexibility. - F1-U (User Plane Interface):
In contrast, F1-U handles the user data traffic. It enables the transmission of actual user payloads such as voice, video, and internet data. F1-U is designed to be low latency and high throughput, ensuring that end-user experiences are seamless and responsive. It operates independently of F1-C, which helps reduce latency and improve reliability for time-sensitive applications.
Advantages of Open Midhaul with F1-C and F1-U
The combination of Open Midhaul and standardized F1 interfaces offers numerous advantages for mobile network operators:
- Vendor Interoperability: Operators can mix and match DU and CU components from different vendors, fostering innovation and cost efficiency.
- Network Flexibility: By separating the control and user planes, operators can independently scale and optimize each part of the network.
- Enhanced Performance: F1-U’s dedicated path for user data minimizes delay, which is essential for applications like AR/VR and autonomous vehicles.
- Simplified Operations: The use of open and standardized protocols reduces complexity in integration, deployment, and maintenance.
- Cost Reduction: Open Midhaul enables the use of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware and software, leading to reduced CapEx and OpEx.
Real-World Use Cases
Telecom providers worldwide are experimenting with Open Midhaul architectures. For instance, trials involving Open RAN deployments in rural areas have shown how F1-C and F1-U interfaces can reduce total infrastructure costs while delivering high performance. Similarly, private 5G networks in manufacturing utilize Open Midhaul to ensure low-latency communication between robotic systems and edge servers.
Conclusion
Open Midhaul is poised to become a foundational element in 5G and beyond. By leveraging the F1-C and F1-U interfaces, operators can build flexible, high-performance, and cost-effective mobile networks. As the ecosystem continues to mature, Open Midhaul will play a crucial role in achieving the full potential of 5G’s promises.