Exploring 3GPP Releases: Evolution from 4G LTE to 5G Release 18
telcomatraining.com – The development of mobile communication technology is shaped by a series of global standards, most notably those published by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). From the early days of 4G LTE to the transformative capabilities of 5G Release 18, 3GPP releases mark the milestones of the wireless industry’s evolution. This article explores the key features and innovations in each phase and what to expect from the most recent and upcoming releases.
What Is 3GPP?
3GPP is an international collaborative body that develops protocols for mobile telecommunications. These protocols are divided into “releases,” each containing a set of standardized features that guide the development of network infrastructure, mobile devices, and services. Each release builds on the previous one, pushing the boundaries of speed, efficiency, and connectivity.
The Rise of 4G LTE (Releases 8–13)
The journey toward modern connectivity began with Release 8, which introduced Long Term Evolution (LTE). LTE brought significant improvements in speed and latency compared to 3G. Key highlights included:
- OFDM and MIMO technologies
- Peak download speeds of up to 300 Mbps
- Lower latency (as low as 10 ms)
Subsequent releases such as Release 9–13 introduced enhancements like:
- LTE-Advanced (Carrier Aggregation)
- Enhanced Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (eICIC)
- Voice over LTE (VoLTE)
- Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) for low-power devices
These enhancements laid the groundwork for the massive connectivity required by 5G.
The Shift to 5G: Releases 14–17
As the world demanded faster, more reliable networks, 3GPP shifted focus to 5G, starting with Release 14, which included LTE enhancements and initial support for 5G NR (New Radio).
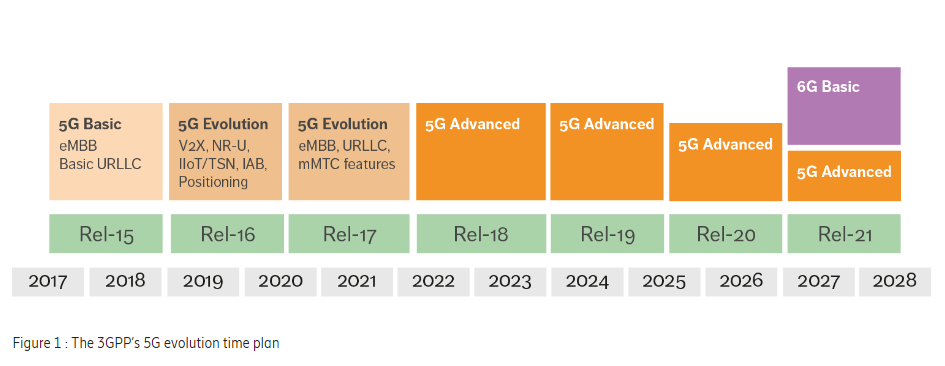
- Release 15 (2018) officially introduced the first standardized version of 5G NR. It enabled enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and set the foundation for ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC) and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
- Release 16 (2020) added industrial IoT use cases, integrated access and backhaul, and introduced V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communications.
- Release 17 (2022) focused on expanding 5G coverage and efficiency. It introduced RedCap (Reduced Capability) devices, better satellite integration, and further improvements to IoT connectivity.
These releases marked the beginning of true 5G networks, transforming sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
The Future: 5G Advanced in Release 18
3GPP Release 18, often referred to as 5G Advanced, represents a pivotal step in the roadmap toward 6G. Key focus areas include:
- Enhanced AI/ML integration for dynamic network optimization
- Improved energy efficiency across devices and base stations
- Support for non-terrestrial networks (NTN) including satellite communications
- Improved positioning accuracy (within 10 cm in some use cases)
- Expanded XR (Extended Reality) and metaverse support
With Release 18, the 5G ecosystem becomes more intelligent, adaptable, and capable of supporting diverse enterprise and consumer needs.
Why 3GPP Releases Matter
Each 3GPP release serves as a catalyst for innovation, guiding operators, manufacturers, and developers. Without these standardized roadmaps, global interoperability and technological progression would be inconsistent. Understanding these releases helps businesses anticipate future trends and align their strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
From 4G LTE to 5G Release 18, the evolution of 3GPP releases has fueled a new era of global communication. These standards continue to shape the future of connectivity, enabling smarter cities, autonomous systems, and immersive digital experiences. As we move toward 5G Advanced and beyond, staying informed about these releases will be key to unlocking the next generation of technological innovation.