Dynamic Spectrum Sharing Demystified: PDF and PPT Download
telcomatraining.com – Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) is one of the most practical and innovative solutions to accelerate 5G deployment while maintaining the quality of 4G services. By enabling simultaneous use of existing spectrum for both 4G LTE and 5G NR, DSS reduces the need for new spectrum auctions or costly refarming, allowing mobile network operators to roll out 5G coverage quickly and efficiently.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn the core principles behind Dynamic Spectrum Sharing, its benefits, challenges, and real-world deployment strategies. Plus, you can download a free PDF and PPT presentation to use for your training sessions, technical workshops, or academic purposes.
What Is Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS)?
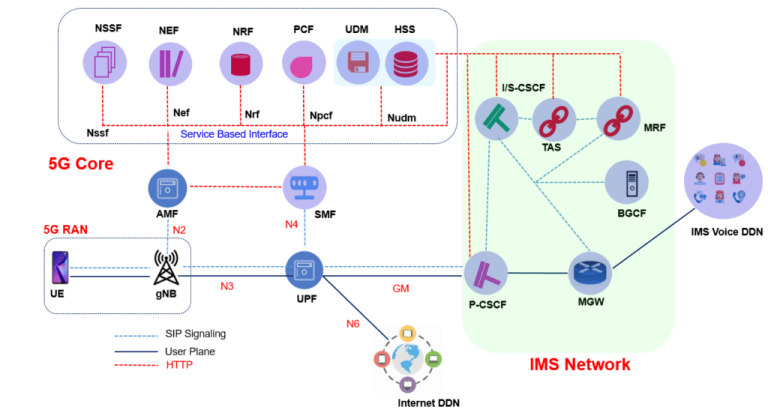
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing is a radio access network (RAN) technology that lets operators deploy 4G LTE and 5G NR on the same frequency band. Traditionally, adding new generations of wireless technology required dedicated, cleared spectrum—often an expensive and time-consuming process.
DSS solves this by dynamically allocating spectrum resources in real-time, based on actual traffic demands. For example, if more users are on 5G, DSS will allocate more resources to 5G NR while reducing LTE allocation, and vice versa. This approach enables a seamless user experience and broader 5G coverage without impacting legacy services.
How Does DSS Work?
At the core of DSS is advanced scheduling and signaling. The technology relies on features defined in 3GPP standards (notably Release 15 and later), including:
- Frequency domain multiplexing: Dividing the spectrum into time slots for LTE and 5G.
- Overhead signaling management: Efficiently sharing control channels.
- Real-time adaptation: Dynamically adjusting the resource allocation based on user traffic demand.
In practice, DSS is implemented in the base station software with minimal hardware changes, making it a cost-effective upgrade for operators who already have 4G LTE infrastructure in place.
Benefits of Dynamic Spectrum Sharing
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing offers several clear advantages:
✅ Cost Savings: No need to clear or buy new spectrum immediately.
✅ Rapid 5G Coverage Expansion: Operators can deploy 5G on existing 4G bands.
✅ Seamless User Experience: Both LTE and 5G users are served simultaneously.
✅ Future-Proofing: Flexible upgrades as 5G user adoption grows.
Because of these benefits, DSS has become a popular choice for operators seeking nationwide 5G coverage without waiting for exclusive mid-band or mmWave auctions.
Challenges of DSS
Despite its promise, DSS is not without challenges:
- Spectral Efficiency Penalties: Shared signaling overhead reduces effective throughput.
- Device Compatibility: Requires devices supporting DSS-enabled 5G NR.
- Complex Network Optimization: Balancing LTE and 5G demands in real time can be tricky.
Operators must carefully plan DSS deployment to avoid unintended service degradation, especially in busy urban environments.
Download Free Dynamic Spectrum Sharing PDF and PPT
To help you better understand DSS, we offer a free PDF and PowerPoint (PPT) download. These resources cover:
- Fundamentals of DSS technology.
- Technical diagrams and architecture.
- Benefits and deployment case studies.
- Best practices for network engineers.
These materials are perfect for training sessions, academic courses, or self-study.
✅ Download the Dynamic Spectrum Sharing PDF
✅ Download the Dynamic Spectrum Sharing PPT
Conclusion
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing is an essential bridge between 4G and 5G, allowing operators to deliver improved coverage and capacity without massive new spectrum investments. While DSS has certain technical trade-offs, it remains one of the most pragmatic approaches to accelerate 5G rollout.
By downloading our free PDF and PPT resources, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of DSS technology, empowering you to make informed decisions about deployment, planning, and optimization. Don’t miss this opportunity to stay ahead in the evolving world of mobile communications.