Carrier Aggregation in 5G NR: Benefits, Challenges, and Real-World Use Cases
telcomatraining.com – Carrier Aggregation (CA) is a crucial technology in the evolution of 5G New Radio (NR), offering significantly enhanced data speeds, improved reliability, and better network efficiency. It allows multiple frequency bands to be combined into one larger channel, improving the overall bandwidth and performance of mobile networks. While the technology has shown immense potential, it also presents some challenges that need to be addressed to fully exploit its capabilities in real-world scenarios. This article delves into the benefits, challenges, and real-world use cases of Carrier Aggregation in 5G NR.
What is Carrier Aggregation in 5G NR?
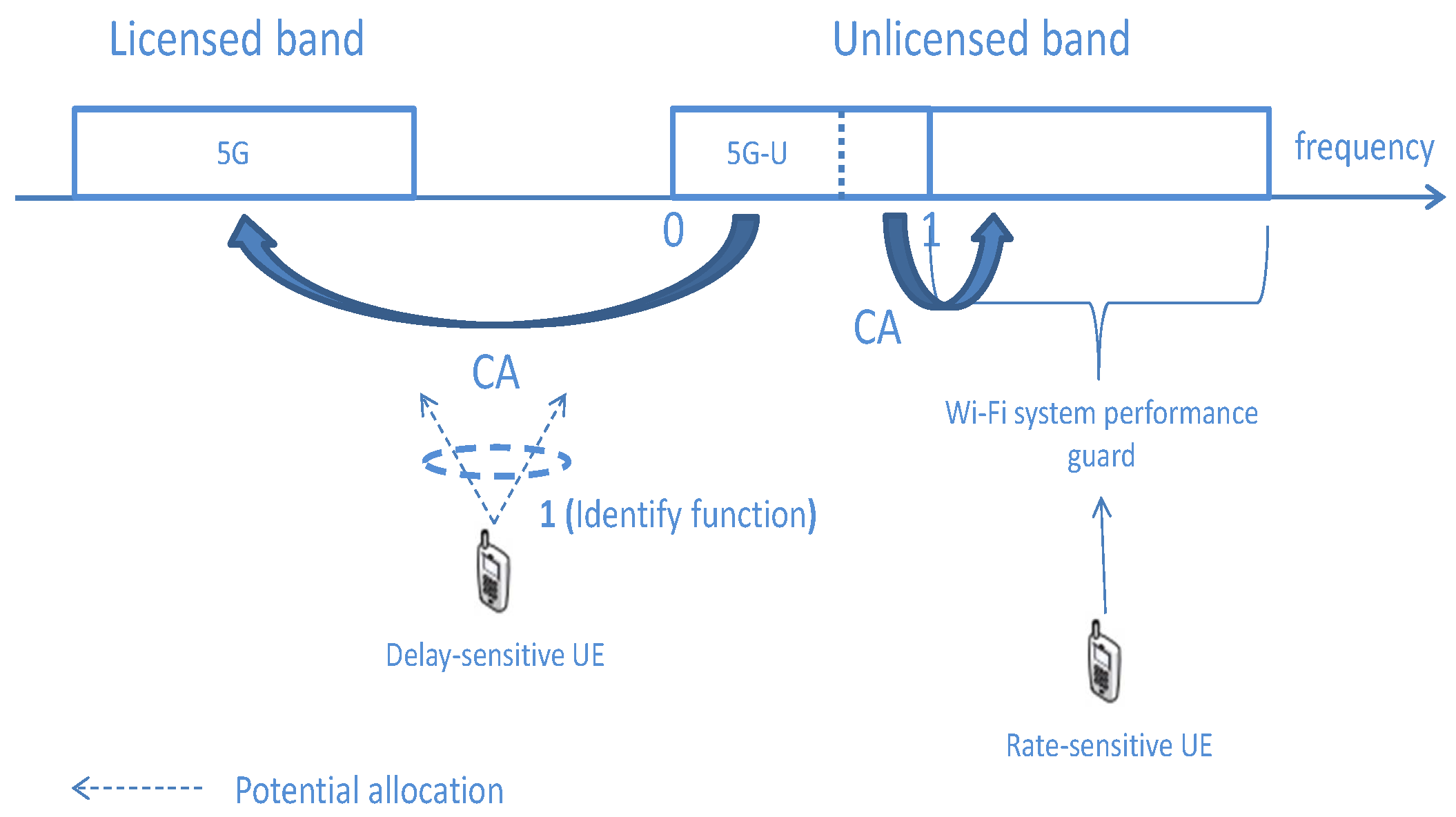
Carrier Aggregation is a technique used in wireless communication to combine two or more frequency bands to form a larger, more efficient communication channel. In the context of 5G NR, CA enables higher data rates, better spectrum utilization, and reduced latency by merging multiple carriers across different frequency ranges. This functionality is vital for meeting the increasing demand for high-speed data and seamless connectivity in 5G networks.
Benefits of Carrier Aggregation in 5G NR
- Enhanced Data Speeds
One of the primary benefits of Carrier Aggregation is the significant increase in data speeds. By combining multiple carriers, 5G NR can offer gigabit-level data rates. This improvement is particularly noticeable in high-density areas, such as urban environments, where the demand for data is enormous. - Improved Spectrum Efficiency
Carrier Aggregation allows operators to make better use of available spectrum. By aggregating multiple frequency bands, mobile operators can maximize the efficiency of their spectrum holdings, enabling faster data transfer without requiring additional frequency allocation. - Reduced Latency
With CA, data can be transmitted over multiple channels simultaneously, leading to lower latency in communication. This is crucial for applications that demand real-time data processing, such as autonomous driving, augmented reality, and virtual reality. - Better Network Coverage
Combining carriers from different frequency bands can also enhance coverage, especially in areas where certain frequency bands may struggle due to range limitations. For instance, low-frequency bands provide wider coverage, while higher-frequency bands deliver faster speeds. Aggregating these bands ensures a more balanced network performance.
Challenges of Carrier Aggregation in 5G NR
- Complexity in Network Management
While Carrier Aggregation offers multiple benefits, managing the aggregated carriers can be complex. It requires advanced coordination and management of different bands, especially when dealing with heterogeneous networks that combine low, mid, and high-frequency bands. - Interference Management
With multiple carriers operating simultaneously, the potential for interference increases. Efficient interference management is essential to ensure that the aggregated carriers do not negatively impact each other’s performance. This requires advanced algorithms and network optimization techniques. - Device Compatibility
Not all devices are capable of supporting Carrier Aggregation, and this can limit the widespread adoption of 5G NR. Devices must be equipped with the necessary hardware and software to support multiple frequency bands simultaneously, which can increase costs and complexity for both manufacturers and consumers. - Energy Consumption
While Carrier Aggregation improves data rates and network efficiency, it can also increase the energy consumption of mobile devices. Devices using multiple carriers simultaneously may require more power to maintain optimal performance, which could affect battery life.
Real-World Use Cases of Carrier Aggregation in 5G NR
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
One of the most common applications of Carrier Aggregation is in enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB). It allows users to experience faster download and upload speeds, better video streaming quality, and a more reliable connection, especially in crowded areas. - Smart Cities and IoT
Carrier Aggregation can support the high-density and low-latency requirements of smart city applications, such as connected infrastructure, real-time traffic monitoring, and large-scale IoT deployments. Aggregating carriers helps in managing the vast amounts of data generated by smart sensors and devices. - Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles require ultra-reliable, low-latency communication to process real-time data from various sensors and cameras. Carrier Aggregation can play a significant role in ensuring that these vehicles stay connected to the network without any lag or data loss. - Industrial Automation and Remote Surgery
Industries that rely on real-time communication, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, can greatly benefit from Carrier Aggregation. It helps improve communication reliability and speed, which is essential for applications like remote surgery, industrial automation, and precision agriculture.
Conclusion
Carrier Aggregation in 5G NR is a game-changing technology that brings enhanced data speeds, improved efficiency, and reduced latency to mobile networks. While it offers tremendous benefits, its implementation also comes with challenges, such as network management complexities and device compatibility. However, the real-world use cases, from eMBB to smart cities and autonomous vehicles, demonstrate the potential of CA to revolutionize industries and provide users with an unprecedented mobile experience. As the technology continues to evolve, Carrier Aggregation will play a critical role in the full realization of 5G’s capabilities.