A Beginner’s Guide to Mininet: Simulating SDN Networks Made Easy
telcomatraining.com – Software Defined Networking (SDN) is revolutionizing how networks are designed, managed, and optimized. As the demand for flexible, programmable networks grows, so does the need for efficient tools to simulate SDN environments. One such powerful yet lightweight tool is Mininet. This beginner’s guide introduces Mininet, explaining what it is, why it matters, and how you can start using it to simulate SDN networks effortlessly.
What is Mininet?
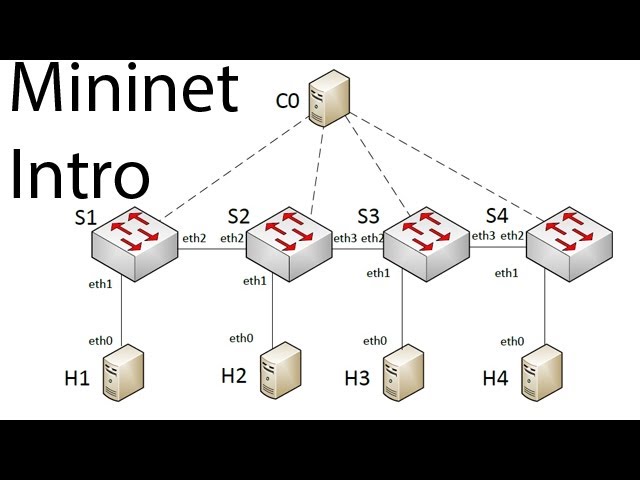
Mininet is a network emulator that creates a virtual network using software, running real kernel, switch, and application code on a single machine. It’s an open-source tool that is widely used for prototyping and testing SDN systems. By using Mininet, you can emulate complex network topologies without needing multiple physical devices.
Mininet supports OpenFlow, making it an ideal companion for SDN research and development. It allows users to simulate an entire network including hosts, switches, and controllers—all within a single virtual environment.
Why Use Mininet?
Mininet is popular among students, researchers, and developers because it offers several key advantages:
- Lightweight and Fast: It runs on a single Linux machine using lightweight virtualization.
- Cost-Effective: No need for expensive hardware.
- Reproducibility: Easily share your network setup using Python scripts.
- Realistic Testing: Runs real applications and OpenFlow switches.
- Integration Ready: Works seamlessly with SDN controllers like POX, Ryu, ONOS, and OpenDaylight.
Whether you’re learning about networking, developing SDN applications, or running experiments, Mininet gives you a flexible platform to explore and validate your ideas.
Installing Mininet
Installing Mininet is straightforward. It can be set up in several ways, including:
- Using a Pre-built VM: The Mininet team provides a ready-to-use virtual machine that includes all dependencies.
- From Source: Clone the official GitHub repository and run the installation script.
- On Ubuntu: You can use the command below to install Mininet on Ubuntu:
bashSalinEditsudo apt-get install mininet
Make sure to have dependencies like Python, Open vSwitch, and OpenFlow tools installed. After installation, test it with a simple command:
bashSalinEditsudo mn
This launches a basic topology with a single switch and two hosts.
Basic Mininet Commands
Mininet comes with a command-line interface (CLI) that allows users to interact with the virtual network. Here are a few essential commands:
sudo mn: Starts a default topology.pingall: Tests connectivity between all hosts.net: Displays the network topology.h1 ifconfig: Shows interface configuration of host h1.h1 ping h2: Sends ping from host h1 to h2.
You can also create custom topologies using Python scripts, giving you full control over the network architecture.
Creating a Custom Topology
Mininet allows users to define their own topologies using Python. For example:
pythonSalinEditfrom mininet.topo import Topo
class MyTopo(Topo):
def build(self):
h1 = self.addHost('h1')
h2 = self.addHost('h2')
s1 = self.addSwitch('s1')
self.addLink(h1, s1)
self.addLink(h2, s1)
topos = {'mytopo': (lambda: MyTopo())}
Save this in a .py file and run it with:
bashSalinEditsudo mn --custom yourfile.py --topo mytopo
This lets you test specific SDN scenarios and customize your simulations based on real-world requirements.
Conclusion
Mininet is an invaluable tool for anyone interested in SDN. It provides a simple, affordable, and powerful way to emulate networks and test SDN applications. With Mininet, you can go from theoretical concepts to practical simulations within minutes. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, mastering Mininet is a smart step toward becoming proficient in Software Defined Networking.