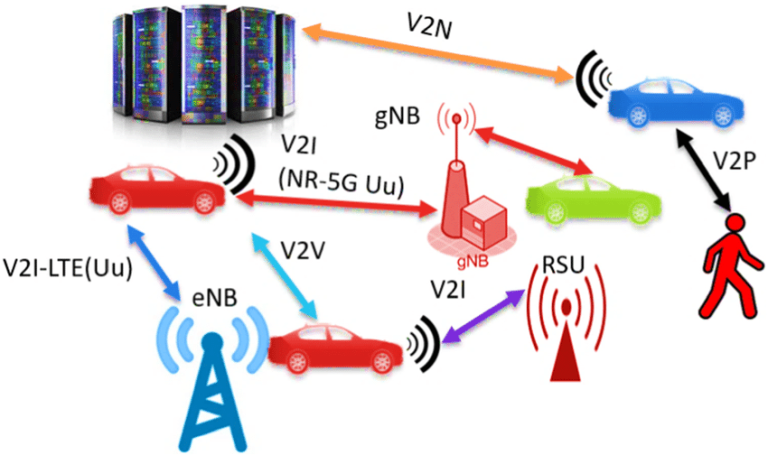
5G RU, CU, and DU Explained: The Backbone of Next-Gen Networks
telcomatraining.com – As 5G networks continue to roll out worldwide, the technology behind them is becoming increasingly sophisticated. One of the key innovations in 5G architecture is the division of the radio access network (RAN) into three essential components: Radio Unit (RU), Centralized Unit (CU), and Distributed Unit (DU). This modular approach enhances network efficiency, reduces latency, and improves overall performance. In this article, we will explore these components and their roles in the 5G infrastructure.
Understanding the 5G RAN Architecture
Traditionally, mobile networks relied on a monolithic base station where all functions were centralized. However, with the advent of 5G, network architecture has evolved into a more distributed model. The 5G RAN architecture is divided into three key components:
- Radio Unit (RU)
- Distributed Unit (DU)
- Centralized Unit (CU)
This split architecture optimizes network performance, enabling better scalability, reduced energy consumption, and improved user experience.
Radio Unit (RU): The Frontline of 5G Connectivity
The Radio Unit (RU) is the component responsible for transmitting and receiving wireless signals between user devices and the network. Positioned at the cell sites or tower locations, RUs handle the physical layer processing and are connected to the DU via high-speed optical fiber links.
Key Features of RU:
- Converts digital signals into radio waves for transmission.
- Supports multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology to enhance signal strength and coverage.
- Ensures efficient spectrum usage to maximize bandwidth capacity.
- Works with advanced antenna systems to improve connectivity and reduce interference.
Distributed Unit (DU): Bridging the Gap Between RU and CU
The Distributed Unit (DU) sits between the RU and CU and is responsible for real-time data processing and lower-layer functions. It plays a crucial role in reducing network latency, as it processes critical functions closer to the edge, rather than relying entirely on a central core.
Key Functions of DU:
- Handles lower-layer processing, including MAC (Medium Access Control) and RLC (Radio Link Control) layers.
- Reduces network congestion by processing data closer to the source.
- Ensures seamless communication between multiple RUs and the CU.
- Improves edge computing capabilities, enabling ultra-low latency applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Centralized Unit (CU): The Brain of 5G Networks
The Centralized Unit (CU) is the high-level processing entity responsible for network control and management. Unlike the DU, the CU is often located in centralized data centers or cloud environments, where it manages multiple DUs and RUs efficiently.
Key Functions of CU:
- Handles non-real-time processing functions, such as mobility management and quality-of-service (QoS) control.
- Manages multiple DUs, enabling dynamic resource allocation.
- Improves network efficiency through intelligent traffic routing and optimization.
- Supports network slicing, allowing operators to allocate resources based on application needs (e.g., IoT, gaming, streaming).
Benefits of the 5G RAN Split Architecture
The separation of RAN into RU, DU, and CU offers several advantages that are pivotal to 5G deployment and future advancements:
1. Lower Latency
By processing data at the DU, closer to end-users, 5G networks can significantly reduce latency, enabling ultra-fast response times essential for applications like autonomous driving and telemedicine.
2. Enhanced Scalability
Operators can deploy RUs, DUs, and CUs in different locations based on network demand, making it easier to expand 5G coverage without overloading the core network.
3. Cost Efficiency
Decoupling these units reduces infrastructure costs by allowing network providers to use cost-effective solutions for different network functions. It also facilitates the adoption of open RAN (O-RAN), which promotes interoperability and vendor diversity.
4. Improved Network Performance
By distributing processing tasks across RU, DU, and CU, 5G networks can optimize performance, ensure efficient resource allocation, and support higher data rates with better reliability.
Conclusion
The 5G RAN architecture, consisting of the RU, DU, and CU, represents a significant evolution in mobile networking. This modular approach enhances network flexibility, reduces latency, and enables advanced applications that will define the future of connectivity. As 5G adoption continues to grow, understanding these components will be crucial for network operators, businesses, and consumers alike.