5G Network Architecture: How It Works and Why It’s Important
The 5G network is revolutionizing the way we connect and communicate. With faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity, 5G is set to power innovations in smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT). But how does 5G technology actually work? This article explores the architecture of 5G networks, their key components, and why they are essential for the future of connectivity.
Understanding 5G Network Architecture
5G network architecture consists of multiple layers and components designed to provide seamless and high-speed connectivity. The main elements of 5G architecture include:
1. Core Network (5G Core)
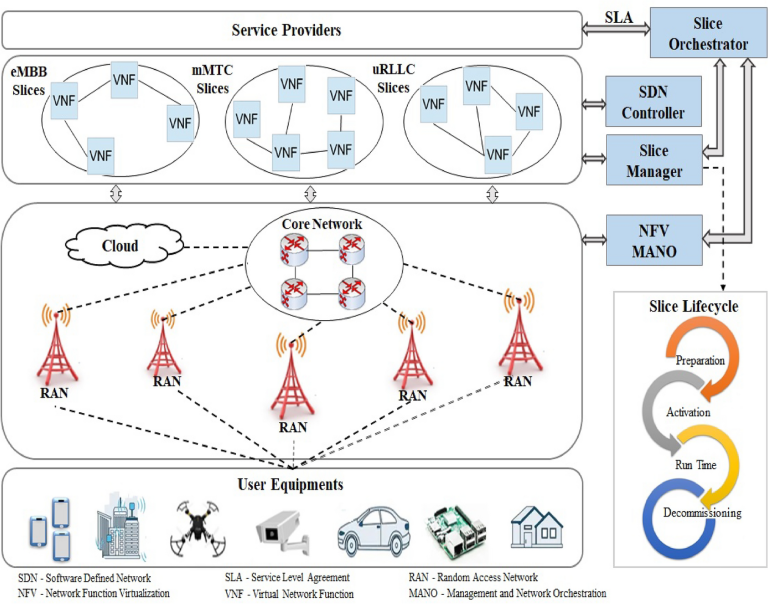
The 5G Core (5GC) is the backbone of the 5G network. It manages data routing, connectivity, and security while enabling features like network slicing. Unlike the 4G LTE core, which relies on a centralized architecture, 5G Core is cloud-native and supports more flexible and scalable deployments.
Key features of the 5G Core include:
- Network Slicing: Allows operators to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, optimizing services for different applications.
- Cloud-Native Architecture: Uses software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) for improved scalability.
- Service-Based Architecture (SBA): Enhances flexibility by enabling modular deployment of network functions.
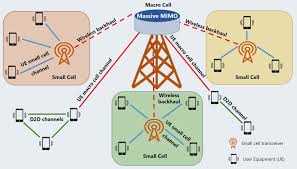
2. Radio Access Network (RAN)
The Radio Access Network (RAN) is responsible for connecting devices to the 5G core. 5G RAN consists of several components:
- Small Cells: Low-power base stations deployed in dense areas to improve coverage and capacity.
- Macro Cells: Large base stations using high-power antennas to cover broad areas.
- Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output): Uses multiple antennas to enhance data transmission and improve efficiency.
- Beamforming: Directs signals to specific users, reducing interference and increasing reliability.
3. Edge Computing
5G integrates Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) to process data closer to the user, reducing latency and improving real-time applications like autonomous driving and smart factories.
4. Transport Network
The transport network connects the RAN to the core network, ensuring efficient data transmission through fiber-optic cables, microwave links, and satellite connections.
Why 5G is Important
5G technology is not just about speed; it plays a crucial role in transforming industries and enhancing digital experiences. Here’s why 5G is essential:
1. Faster and More Reliable Connectivity
With speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G, 5G enables seamless streaming, gaming, and ultra-fast downloads.
2. Ultra-Low Latency
5G reduces latency to as low as 1 millisecond, making it ideal for real-time applications such as telemedicine, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
3. Greater Network Capacity
5G supports a massive number of connected devices, making it the backbone of IoT ecosystems and smart city infrastructures.
4. Enhanced Security and Efficiency
The cloud-native design and AI-driven security protocols of 5G improve data protection and network efficiency.
Conclusion
The 5G network architecture is a complex yet powerful system designed to meet the demands of future digital advancements. With a cloud-based core, advanced RAN technologies, edge computing, and robust transport networks, 5G is set to redefine connectivity, enabling innovations across industries. As global adoption increases, businesses and consumers alike will benefit from its transformative capabilities.