Introduction to UTRA: Exploring UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access
telcomatraining.com – UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA) is a key component of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS), a third-generation (3G) mobile communication technology. UTRA is responsible for the air interface that connects mobile devices to the network, providing high-speed data transmission, improved voice quality, and enhanced multimedia capabilities. This article explores the fundamentals of UTRA, its architecture, and its significance in modern telecommunications.
What is UTRA?
UTRA, or UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, is the radio access technology used in UMTS networks. It enables wireless communication between mobile devices and base stations, ensuring seamless connectivity and efficient data transmission. UTRA is designed to operate in two different modes:
- Frequency Division Duplex (FDD): This mode uses separate frequency bands for uplink and downlink transmissions, allowing simultaneous communication in both directions.
- Time Division Duplex (TDD): This mode utilizes the same frequency band for both uplink and downlink but separates them using time slots.
Both modes cater to different network requirements and spectrum availability, making UTRA a flexible solution for various mobile communication needs.
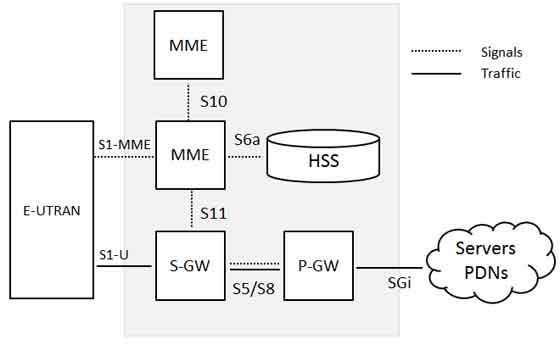
UTRA Architecture and Components
The UTRA system consists of several key components that work together to provide seamless connectivity and efficient data transmission:
- User Equipment (UE): The mobile device or terminal that connects to the network.
- Node B (Base Station): The infrastructure that facilitates communication between UE and the core network.
- Radio Network Controller (RNC): Manages radio resources, handovers, and mobility within the network.
These components ensure that users experience uninterrupted communication, whether for voice calls, video streaming, or internet browsing.
Advantages of UTRA in Mobile Networks
UTRA offers several benefits that have contributed to its widespread adoption in 3G networks:
- High Data Rates: Supports speeds up to 2 Mbps, enhancing mobile internet and multimedia services.
- Improved Spectral Efficiency: Efficiently utilizes available frequency spectrum to maximize network capacity.
- Enhanced Mobility Management: Ensures smooth handovers and minimal service interruptions during movement.
- Better Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritizes different types of data traffic, optimizing user experience.
These advantages make UTRA an essential technology in the evolution of mobile networks.
UTRA’s Role in the Evolution of Mobile Networks
UTRA has played a crucial role in the transition from 2G to 3G, paving the way for modern high-speed mobile networks. Its introduction enabled new applications such as video calls, mobile gaming, and high-speed internet access, which were not feasible with previous generations.
With the advent of 4G and 5G technologies, UTRA has been succeeded by more advanced radio access technologies like LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and NR (New Radio). However, its impact on mobile communication remains significant, as it laid the groundwork for future wireless advancements.
Conclusion
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA) has been a cornerstone in the development of 3G networks, enabling high-speed data transmission, improved voice quality, and seamless mobility. Its two operational modes, FDD and TDD, offer flexibility for different network requirements. While newer technologies have emerged, UTRA’s contributions to mobile communications continue to be relevant.
As mobile networks continue to evolve, understanding foundational technologies like UTRA helps in appreciating the progress and innovation in wireless communication. Whether for academic purposes or industry applications, UTRA remains a fundamental topic in telecommunications.