UTRA in UMTS: Exploring Universal Mobile Telecommunications System Access
telcomatraining.com – Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is one of the most significant advancements in mobile communication technology. As part of the third-generation (3G) mobile systems, UMTS offers high-speed data transmission, enhanced voice quality, and improved multimedia capabilities. A crucial component of UMTS is the UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA), which facilitates seamless communication by ensuring efficient data transfer. This article explores the significance of UTRA in UMTS, its architecture, and its role in modern mobile communications.
Understanding UTRA in UMTS
UTRA (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access) is the radio access technology used in UMTS networks. It provides the interface between mobile devices and the core network, allowing seamless voice, data, and multimedia communication. UTRA operates in two distinct modes:
- Frequency Division Duplex (FDD): Uses separate frequency bands for uplink and downlink transmissions, ensuring minimal interference and stable communication.
- Time Division Duplex (TDD): Uses a single frequency band, alternating between uplink and downlink transmissions, which is ideal for high-density urban environments.
These modes help optimize spectrum utilization, providing flexibility for different network deployment scenarios.
Key Features of UTRA
UTRA is designed to enhance communication efficiency and support the growing demand for mobile connectivity. Some of its key features include:
- Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA): UTRA employs WCDMA technology, which allows multiple users to share the same frequency band without interference, improving spectrum efficiency.
- High Data Rates: UMTS networks with UTRA support data rates up to 2 Mbps, enabling smooth video streaming, web browsing, and other multimedia applications.
- Seamless Mobility: UTRA ensures smooth handover between base stations, providing uninterrupted connectivity even during high-speed travel.
- Enhanced Coverage: The radio access technology extends coverage in rural and urban areas, ensuring reliable communication.
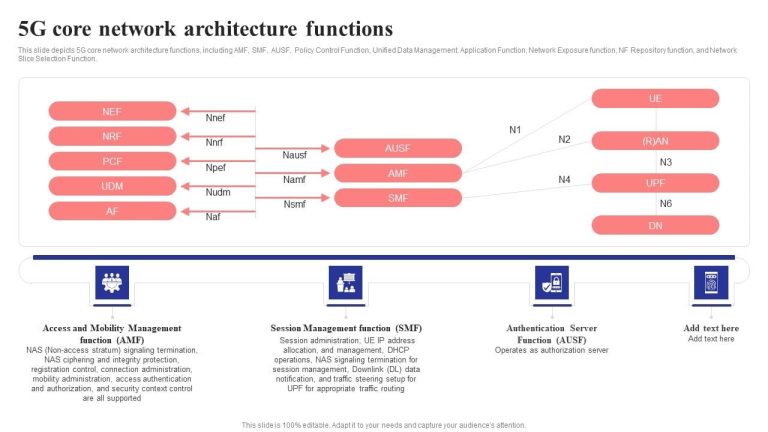
UTRA Architecture
The UTRA architecture consists of several critical components that work together to enable efficient mobile communication. These include:
1. Node B (Base Station)
Node B serves as the radio transmitter and receiver in the UMTS network. It connects mobile devices to the Radio Network Controller (RNC) and manages radio signals for efficient data transmission.
2. Radio Network Controller (RNC)
The RNC oversees multiple Node Bs, managing radio resources, handovers, and power control to ensure optimal network performance.
3. Core Network
The core network processes voice and data traffic, enabling communication with external networks such as the internet and the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
Advantages of UTRA in UMTS
UTRA provides numerous advantages in mobile communication, making UMTS a reliable and efficient network technology. Some key benefits include:
- Improved Spectral Efficiency: WCDMA technology allows better spectrum utilization, accommodating more users within the same bandwidth.
- Better Quality of Service (QoS): UTRA ensures higher data rates, lower latency, and better voice quality, enhancing user experience.
- Support for Advanced Services: UTRA enables services such as mobile internet, video conferencing, and multimedia messaging, making UMTS a versatile communication platform.
- Seamless Global Connectivity: UMTS with UTRA is widely deployed worldwide, ensuring international roaming and broad coverage.
Future of UTRA and UMTS
While UMTS and UTRA have significantly improved mobile communications, the emergence of 4G LTE and 5G networks is shaping the future of wireless connectivity. However, UTRA continues to play a crucial role in providing reliable 3G coverage, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
The ongoing advancements in mobile technology may lead to further enhancements in UTRA, improving data rates, energy efficiency, and network capacity. Additionally, as mobile networks transition to newer generations, UMTS infrastructure can still support IoT (Internet of Things) applications and other legacy services.
Conclusion
UTRA is a fundamental component of UMTS, providing robust radio access for mobile communication. With its WCDMA-based technology, UTRA ensures efficient data transmission, seamless mobility, and high-quality service. While newer technologies such as LTE and 5G are gaining traction, UTRA remains an essential part of global communication networks. Understanding its role and capabilities is vital for network engineers, mobile operators, and tech enthusiasts looking to explore the evolution of wireless communication.
By leveraging UTRA’s capabilities, UMTS continues to provide reliable connectivity, ensuring seamless mobile experiences for users worldwide. As mobile networks evolve, the legacy of UTRA in UMTS will remain a crucial foundation for future innovations in wireless communication.