VNI (Virtual Network Identifier): A Guide to Its Function in Virtual Networks
telcomatraining.com – In the modern networking world, especially in virtualization-based environments, the Virtual Network Identifier (VNI) plays a crucial role in managing and identifying network segments. VNI is a unique number used to differentiate various virtual networks within the same environment, particularly in the VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) protocol.
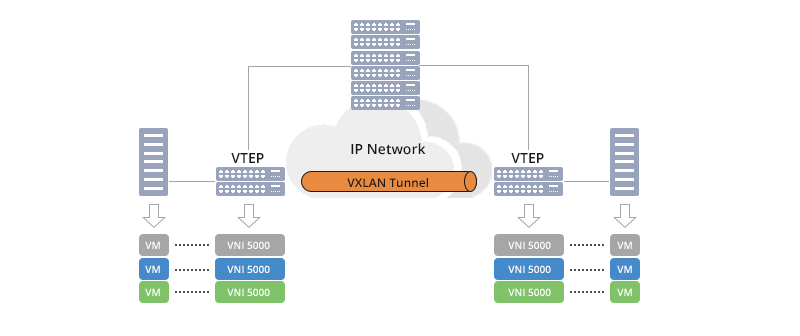
VXLAN is a technology that enables Layer 2 network extension over Layer 3 infrastructure. In the VXLAN architecture, VNI serves as a unique identifier for each virtual network segment, similar to a VLAN ID in traditional networking but on a much larger scale.
How Virtual Network Identifier (VNI) Works
VNI is used in the VXLAN protocol to encapsulate network traffic within UDP packets. Here are the key steps in how VNI works:
- Creating Virtual Network Segments
When a virtual network is created, a VNI is assigned as a unique identifier. This VNI allows administrators to isolate traffic from other networks. - VXLAN Encapsulation
Network packets from hosts within the same segment are encapsulated with a VXLAN header that includes the VNI. These packets are then transmitted over Layer 3 infrastructure. - Decapsulation by VTEP (VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint)
Devices functioning as VTEPs read the VNI from the received VXLAN packet and forward the data to the appropriate virtual network segment. - Security and Isolation
Since each segment has a unique VNI, traffic between virtual networks remains isolated, enhancing security and flexibility in network management.
Why is VNI Important in Virtual Networks?
1. Higher Scalability Compared to VLAN
Traditional VLANs support up to 4,096 segments, whereas VXLAN with VNI can support up to 16 million virtual networks, making it more suitable for cloud environments and modern data centers.
2. Enhanced Security and Isolation
By using VNI, traffic between networks remains separate, preventing unauthorized access and improving network security.
3. Supports Multi-Tenant Networks
In cloud environments or large data centers, multiple tenants or departments may share the same infrastructure. VNI ensures that each tenant has a completely isolated network.
4. Reduces Physical Topology Limitations
VXLAN and VNI allow Layer 2 networks to extend over Layer 3, enabling more flexible and efficient network management.
Implementing Virtual Network Identifier (VNI)
To implement VNI in a network, the following steps are typically followed:
- Setting Up VXLAN Infrastructure
Administrators need to configure network devices that support VXLAN, such as compatible switches and routers. - Defining the VNI Range
VNIs are typically assigned within the range of 1 to 16,777,215, providing greater flexibility compared to traditional VLANs. - Configuring VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint (VTEP)
Each device connecting to the VXLAN network must be configured as a VTEP, responsible for VXLAN packet encapsulation and decapsulation. - Testing and Monitoring
After implementation, it is essential to test and monitor network traffic to ensure segmentation and performance are working as expected.
Conclusion
The Virtual Network Identifier (VNI) is a crucial element in modern virtual networks using VXLAN. By providing greater scalability than VLANs and enabling secure and flexible network segmentation, VNI helps organizations manage complex network infrastructures. With a solid understanding of how VNI works, network administrators can optimize the use of this technology to support growing business needs.