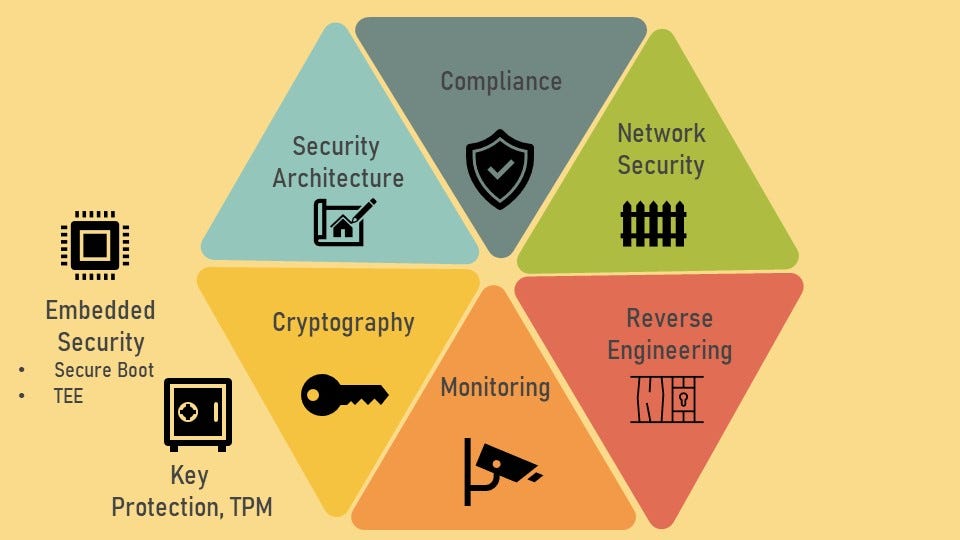
What is Vertical Security and Trust Domains (VSTD)?
telcomatraining.com – Vertical Security and Trust Domains (VSTD) is a cybersecurity model that organizes security measures into hierarchical layers or domains. Each domain represents a specific level of security, ensuring that access and control mechanisms are applied consistently to prevent vulnerabilities from cascading throughout an entire system.
VSTD divides security into vertical segments, allowing for granular control over user privileges, data access, and application security. This segmentation helps mitigate risks by restricting movement within a system, thereby reducing the potential impact of cyber threats.
Key Components of VSTD
1. Trust Domains
Trust domains refer to different zones within an IT ecosystem where trust levels are defined. Each domain is governed by specific policies, authentication mechanisms, and access controls. Examples of trust domains include:
- User Trust Domains: Segregates users based on roles and permissions.
- Application Trust Domains: Ensures that applications operate within secure boundaries.
- Network Trust Domains: Protects communication channels and data exchanges.
2. Access Control Policies
To implement VSTD effectively, robust access control policies are necessary. These policies enforce restrictions based on user roles, device types, and data sensitivity. Common access control models used in VSTD include:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
3. Layered Security Mechanisms
VSTD employs multiple layers of security to ensure comprehensive protection. This includes:
- Encryption: Protecting data at rest and in transit.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhancing user identity verification.
- Endpoint Security: Ensuring devices comply with security standards before accessing systems.
Benefits of VSTD in Cybersecurity
1. Reduced Attack Surface
By segmenting security into distinct domains, VSTD minimizes the risk of lateral movement within a network. Attackers find it more challenging to escalate privileges or gain unauthorized access.
2. Enhanced Compliance and Governance
Regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 require strict access controls. VSTD provides a structured approach to compliance by enforcing security policies at multiple levels.
3. Improved Incident Response
Since VSTD isolates security breaches within specific domains, it simplifies threat detection and containment. Security teams can quickly identify compromised areas and implement targeted remediation strategies.
4. Stronger Identity and Access Management (IAM)
VSTD ensures that only authenticated and authorized users can access sensitive resources. This reduces the likelihood of credential-based attacks and insider threats.
Implementing VSTD in an Organization
1. Assess Existing Security Architecture
Organizations should evaluate their current security framework to identify gaps and define trust domains.
2. Define Security Policies and Controls
Clear access control policies should be established to govern interactions between trust domains.
3. Implement Zero Trust Principles
Adopting a Zero Trust model complements VSTD by ensuring continuous verification of users and devices before granting access.
4. Monitor and Optimize Continuously
Regular security audits, monitoring tools, and threat intelligence should be leveraged to enhance VSTD effectiveness.
Conclusion
Vertical Security and Trust Domains (VSTD) is a powerful cybersecurity framework that enhances organizational security by segmenting trust and security layers. By reducing attack surfaces, improving compliance, and strengthening identity management, VSTD helps businesses build resilient cybersecurity defenses. As cyber threats continue to evolve, adopting VSTD can be a proactive step toward securing digital assets and maintaining robust cybersecurity practices.