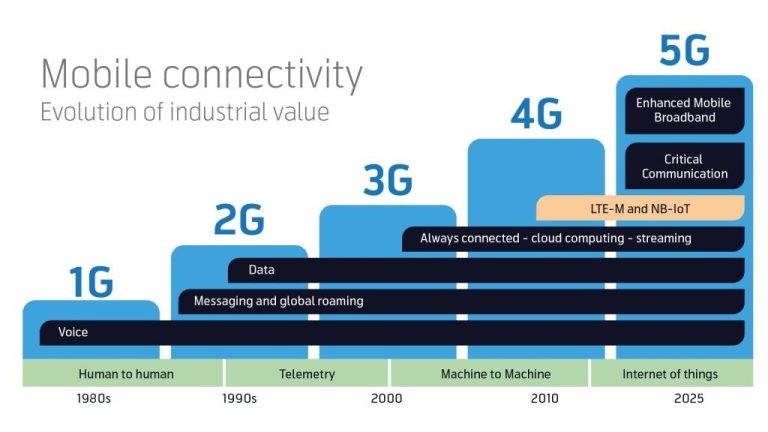
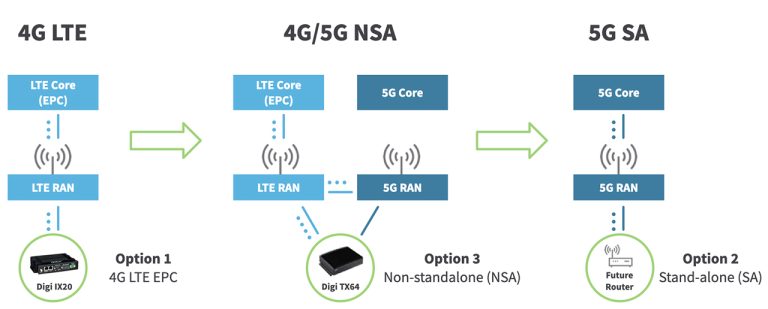
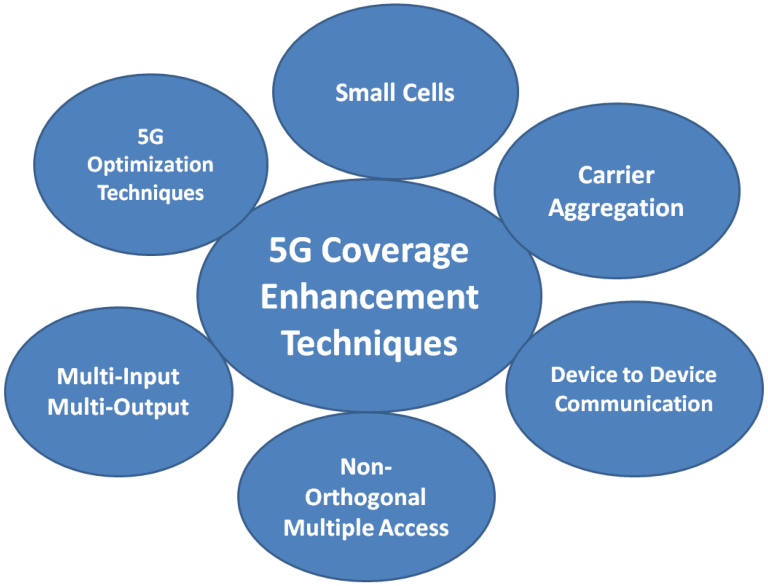
What is WAN (Wide Area Network)? Definition, Benefits, and Examples
telcomatraining.com – In the digital era, networks play a crucial role in connecting people and devices worldwide. One of the most important types of networks is the Wide Area Network (WAN). This article explores the definition of WAN, its benefits, and real-world examples of its applications.
Definition of WAN
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a telecommunications network that extends over a large geographical area, often covering multiple cities, countries, or even continents. Unlike Local Area Networks (LANs) that operate within a limited space like homes or offices, WANs enable long-distance communication between remote locations.
WANs rely on a variety of communication technologies, including satellite links, fiber optics, leased lines, and wireless connections. These networks are commonly used by businesses, government agencies, and service providers to facilitate seamless data exchange across vast distances.
How WAN Works
WANs connect different LANs and MANs (Metropolitan Area Networks) using routers, modems, and other networking devices. The data transmission occurs through public or private infrastructures, such as:
- Internet (Public WAN)
- Leased Lines (Private WAN)
- Cloud-Based WAN Solutions
Modern WANs are often enhanced with Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) technology, which improves network efficiency by optimizing traffic and ensuring security.
Benefits of WAN
Implementing a WAN offers several advantages, especially for organizations that operate across multiple locations. Some key benefits include:
1. Global Connectivity
WANs allow businesses and individuals to stay connected across different geographical locations. Companies with branches worldwide can communicate and share data in real time.
2. Efficient Data Transfer
Organizations use WANs to transfer large amounts of data quickly and securely. This is particularly useful for cloud computing, video conferencing, and remote work environments.
3. Cost-Effective Communication
WANs reduce communication costs by integrating voice, video, and data over a single network infrastructure. Businesses can use Voice over IP (VoIP) and cloud-based applications to minimize expenses.
4. Centralized IT Resources
A WAN enables businesses to centralize their IT infrastructure, such as data centers and cloud services. This simplifies management, enhances security, and ensures better resource utilization.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
WANs are highly scalable, allowing businesses to expand their network as needed. Whether adding new branches or integrating cloud-based applications, WANs offer flexible solutions for growth.
Examples of WAN Applications
WANs are widely used in various industries to facilitate seamless operations. Here are some real-world examples:
1. The Internet
The most well-known example of a WAN is the internet itself. It connects millions of devices worldwide, enabling communication, online transactions, and access to information.
2. Banking and Financial Institutions
Banks use WANs to connect ATMs, branches, and headquarters. This ensures secure transactions, real-time account updates, and global banking services.
3. Corporate Networks
Multinational corporations use WANs to link offices across different locations, enabling employees to collaborate efficiently, share data, and access enterprise applications.
4. Cloud Computing Services
Companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure use WANs to deliver cloud-based solutions to users worldwide. This supports remote work, online storage, and virtual applications.
5. Military and Government Networks
Government agencies and defense organizations use secure WANs for communication, intelligence sharing, and mission-critical operations across different regions.
Conclusion
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is an essential technology that enables long-distance communication and data exchange. It connects businesses, institutions, and individuals across the globe, offering benefits such as enhanced connectivity, efficiency, and scalability.
With advancements like SD-WAN and cloud computing, WANs continue to evolve, supporting the growing demand for high-speed and secure network solutions. Understanding WAN technology is crucial for businesses and IT professionals looking to optimize their connectivity and digital infrastructure.
By leveraging WAN solutions, organizations can ensure seamless operations, improve collaboration, and stay ahead in the competitive digital landscape.