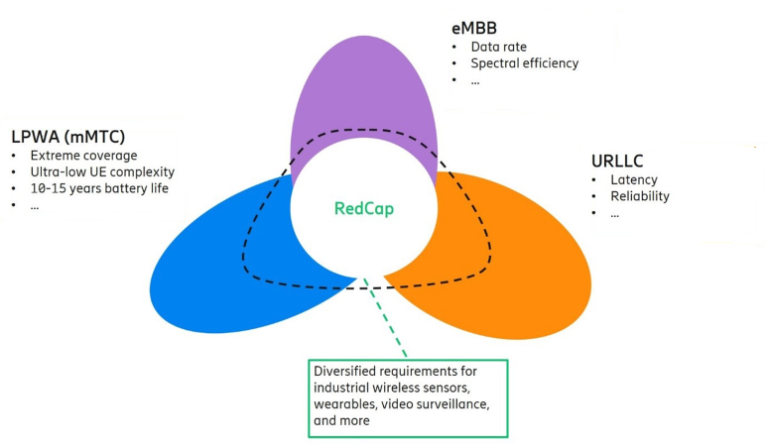
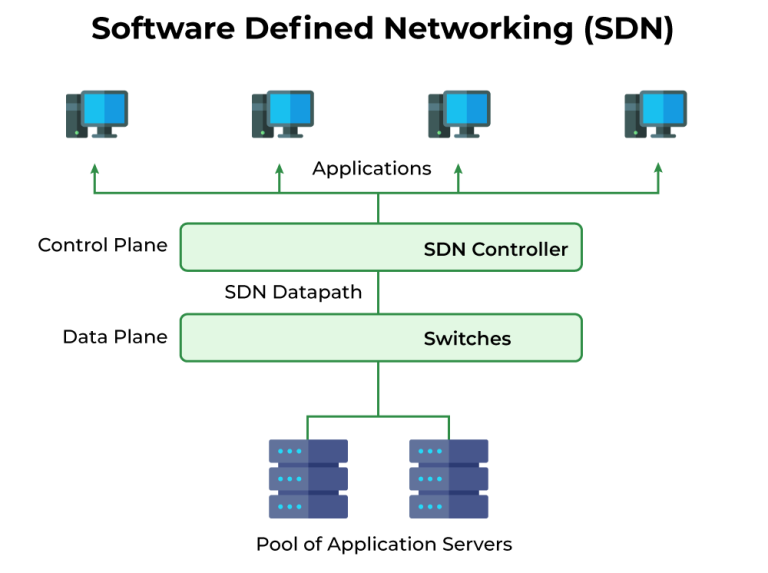
WAN (Wireless Access Network): Definition, Functions, and How It Works
telcomatraining.com – In today’s digital world, fast and reliable internet connectivity is essential. One of the key technologies enabling seamless communication is the Wireless Access Network (WAN). This article explores what WAN is, its functions, and how it works, helping you understand its significance in modern networking.
What is WAN (Wireless Access Network)?
A Wireless Access Network (WAN) is a type of network that provides wireless connectivity to users over a large geographical area. Unlike Local Area Networks (LANs), which cover small spaces such as homes or offices, WANs connect multiple LANs and devices over long distances using wireless technology.
WANs rely on various wireless communication methods, including cellular networks, satellite links, and microwave transmissions, to provide internet access without physical cables. These networks are commonly used by mobile service providers, enterprises, and public Wi-Fi hotspots to enable connectivity across cities, countries, and even globally.
Functions of WAN
WAN plays a crucial role in modern communication by facilitating high-speed, reliable, and secure wireless connectivity. Below are some of the primary functions of WAN:
1. Connecting Remote Locations
WAN enables communication between distant offices, branch locations, and users across the world. This is essential for businesses with multiple locations that need to stay connected.
2. Providing Internet Access
WAN serves as the backbone of the internet, allowing individuals and businesses to access online services, browse websites, and use cloud-based applications.
3. Supporting Mobile Connectivity
Mobile networks, such as 3G, 4G, and 5G, rely on WAN technology to provide seamless internet access to smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices.
4. Enabling Cloud Computing
Many businesses use cloud-based applications and services. WAN ensures a stable and secure connection to cloud platforms, allowing remote work and data storage.
5. Enhancing Security and Data Transfer
Modern WANs incorporate encryption, firewalls, and VPN (Virtual Private Network) technologies to protect data transmitted over the network.
How WAN Works
WAN operates through a combination of wireless technologies and network infrastructure components. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
1. Data Transmission
When a user sends a request (such as accessing a website), the data is transmitted wirelessly using radio waves, satellite signals, or microwave frequencies.
2. Network Access Points
Wireless Access Points (APs), cell towers, or satellite stations receive the transmitted data and forward it to the next network node.
3. Routing and Switching
The data passes through various network nodes, including routers, gateways, and servers, to reach its destination. Advanced routing protocols ensure fast and efficient data transfer.
4. Connectivity to Internet Backbone
WANs are connected to fiber-optic backbone networks that handle massive amounts of data traffic globally. These backbones interconnect different WANs, ensuring worldwide communication.
5. Delivery to End User
Once the data reaches the target network, it is transmitted wirelessly to the end user through Wi-Fi, mobile networks, or satellite connections.
Benefits of WAN
WAN technology offers several advantages, making it essential for modern businesses and individuals. Here are some key benefits:
- Scalability – Easily expands to connect more users and locations.
- Mobility – Provides internet access anytime and anywhere.
- Cost-Effective – Reduces the need for extensive cabling infrastructure.
- High-Speed Access – Advanced technologies like 5G and fiber-optic backbones improve data speeds.
- Enhanced Security – Encrypted communication ensures data privacy and protection.
Conclusion
The Wireless Access Network (WAN) is a crucial component of modern connectivity, enabling seamless communication across large distances. By leveraging wireless technologies like cellular networks, satellites, and microwave transmissions, WAN ensures fast, reliable, and secure internet access. Whether for businesses, remote work, or mobile users, WAN continues to evolve, supporting the growing demands of the digital era.
By understanding WAN’s definition, functions, and working mechanisms, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions about their networking needs, ensuring a more connected and efficient future.