5G Device Interoperability: Unlocking Seamless Integration in Modern Ecosystems
telcomatraining.com – In the era of rapid technological advancements, the interoperability of 5G devices plays a pivotal role in driving innovation across industries. As 5G networks expand their reach, ensuring that devices communicate seamlessly within this ecosystem is vital for maximizing the technology’s potential. Below, we delve into the technical aspects of 5G device interoperability, highlighting its importance, challenges, and future prospects.
The Importance of Interoperability
1. Transforming Manufacturing Ecosystems
The manufacturing sector stands to benefit significantly from the adoption of private 5G networks. These networks offer low latency, high-speed connectivity, and reliable performance, which are essential for automating operations and improving efficiency. For manufacturers to realize these benefits, devices must be designed to work harmoniously within a 5G-enabled environment.
2. Coexisting with Legacy Systems
In many industrial settings, legacy systems such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Ethernet are deeply entrenched. For 5G to gain widespread acceptance, it must integrate with these existing technologies without causing disruptions. Seamless interoperability between old and new systems ensures a smooth transition and prevents costly operational downtime.
Challenges in Achieving Interoperability
1. Immaturity of the 5G Ecosystem
One of the initial hurdles for manufacturers adopting 5G has been the ecosystem’s immaturity. During the early stages of 5G deployment, a lack of compatible devices, incomplete standards, and limited spectrum availability posed significant barriers. Although progress has been made, many industrial players still encounter challenges in fully leveraging 5G capabilities.
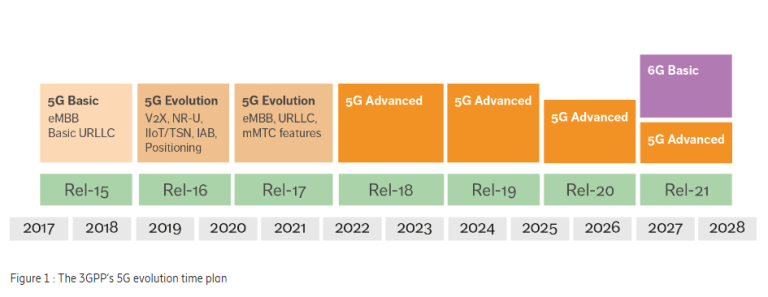
2. Slow Implementation of Advanced Standards
The introduction of advanced standards, such as 5G Release 16, marked a significant milestone in addressing industrial needs. However, practical implementation has lagged, with few devices on the market fully supporting these advancements. Without widespread adoption of Release-16-capable devices tailored for industrial use, the potential of 5G remains constrained.
3. Device Limitations and Fragmentation
The lack of specialized 5G devices for manufacturing environments continues to hinder progress. Unlike consumer-grade devices, industrial applications require rugged, reliable hardware capable of operating in challenging conditions. Additionally, as manufacturers transition from wired to wireless systems, the resulting technological fragmentation underscores the need for devices that bridge the gap between legacy protocols and modern 5G networks.
Overcoming Technical Limitations
1. Bridging the Device Gap
Addressing device availability is critical for accelerating 5G adoption. Industry stakeholders, including manufacturers and network providers, must collaborate to develop and deploy devices optimized for industrial applications. These devices should support the unique demands of manufacturing, such as ultra-low latency, enhanced security, and robust reliability.
2. Enhancing Compatibility Standards
To ensure seamless interoperability, industry-wide compatibility standards must evolve. These standards should emphasize backward compatibility with legacy technologies while promoting the development of forward-looking solutions. Collaborative efforts between standardization bodies, device manufacturers, and network providers will be crucial in achieving this goal.
The Future of 5G Device Interoperability
1. Reaching a Critical Inflection Point
The years between 2026 and 2028 are expected to mark a turning point for 5G technologies. During this period, advancements in device availability, network infrastructure, and standardization are anticipated to converge, enabling widespread adoption in industrial settings. This critical phase will pave the way for innovative use cases and unlock the full potential of 5G in manufacturing.
2. Growth of Private 5G Networks
Private 5G networks are set to play a transformative role in the industrial landscape. By offering dedicated bandwidth, enhanced security, and tailored performance, these networks cater to the specific needs of manufacturers. Analysts predict that private 5G networks will account for nearly a quarter of private network revenues in the coming years, highlighting their significance in the broader 5G ecosystem.
Conclusion
The path to achieving seamless 5G device interoperability is fraught with challenges but holds immense promise for industries worldwide. By addressing ecosystem immaturity, device limitations, and technological fragmentation, stakeholders can unlock new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. As 5G technologies mature and adoption accelerates, their impact will extend far beyond manufacturing, reshaping how industries connect, collaborate, and grow in the digital age.