Understanding WMSC: Wideband CDMA Mobile Switching Centre Explained
telcomatraining.com – In the world of mobile telecommunications, ensuring seamless and efficient communication between users is paramount. One of the key components that enable this functionality is the Mobile Switching Centre (MSC). Specifically, the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) Mobile Switching Centre (WMSC) plays a critical role in managing call routing, data transmission, and network resources within a mobile network using WCDMA technology. This article explores what WMSC is, how it works, and its significance in modern mobile communications.
What is WMSC?
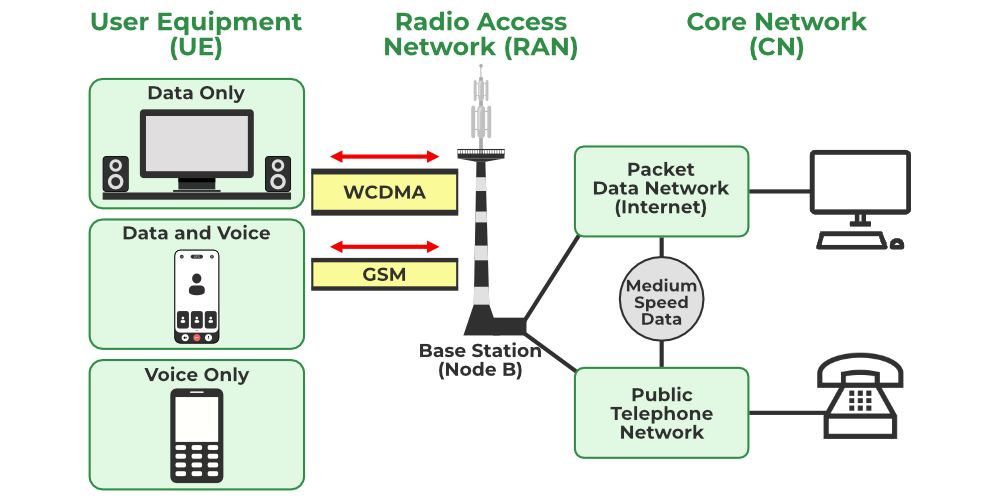
The Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) is a third-generation (3G) mobile telecommunication technology that offers high-speed data and voice communication over cellular networks. The Mobile Switching Centre (MSC), on the other hand, is a central node in the mobile network responsible for managing the routing of calls and data between mobile users and other network elements, such as base stations and core network components.
When we combine these terms, the Wideband CDMA Mobile Switching Centre (WMSC) refers to the MSC that specifically handles the call and data management in networks based on WCDMA technology. WMSC ensures that both voice and data services are provided efficiently, supporting faster internet speeds and better connectivity, which are crucial for modern mobile users.
Functions of WMSC in a Mobile Network
The primary functions of a WMSC are to manage mobile calls, control data traffic, and ensure smooth communication between the user and the wider telecommunications network. Some of its key tasks include:
- Call Routing and Management: WMSC is responsible for routing calls from the originating mobile device to the destination. This involves authentication, signal processing, and ensuring that the call is connected without interruption.
- Handover Management: As mobile users move from one cell area to another, the WMSC ensures that the ongoing communication is transferred seamlessly from one base station to another, preventing call drops.
- Mobility Management: WMSC keeps track of users as they move within the network, ensuring that calls or data sessions are maintained while adapting to the user’s changing location.
- Data Management: With WCDMA offering high-speed internet access, WMSC also plays a role in managing data transmission. It ensures that data requests are processed efficiently, facilitating browsing, video streaming, and other high-bandwidth applications.
- Interoperability: WMSC ensures that the WCDMA network can communicate with other networks, such as GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and LTE (Long-Term Evolution), enabling mobile users to seamlessly switch between different technologies.
Key Features of WMSC
- Enhanced Data Transmission: WCDMA, being a wideband technology, offers significant improvements in data rates compared to older 2G networks. WMSC manages the smooth transmission of data over wideband channels, allowing faster web browsing, video calls, and multimedia streaming.
- Scalability: The architecture of WMSC allows network operators to scale their operations effectively. As the demand for data and mobile services increases, WMSC systems can be upgraded to handle higher loads and more users, ensuring consistent service quality.
- Quality of Service (QoS): WMSC helps to maintain a high-quality user experience by managing traffic prioritization. This ensures that critical services, such as voice calls, are given higher priority over less time-sensitive data transmissions.
- Security: In addition to managing calls and data, WMSC plays an important role in the security of the mobile network. It ensures that users’ communications are encrypted and that there are mechanisms in place to prevent unauthorized access to the network.
The Evolution of WMSC and Future Prospects
While WCDMA networks were a significant leap forward in terms of mobile technology, the advent of newer technologies such as LTE (4G) and 5G has led to the evolution of mobile switching. However, the WMSC remains relevant in many regions where WCDMA infrastructure is still in use. As mobile networks continue to evolve, there is a shift towards the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) and Next-Generation Networks (NGN), but WMSC continues to play an essential role in ensuring backward compatibility and smooth transitions for users migrating to newer technologies.
Conclusion
The Wideband CDMA Mobile Switching Centre (WMSC) is a crucial component of modern 3G mobile networks. It facilitates efficient communication by managing call routing, data transmission, and user mobility. As mobile networks evolve to meet the increasing demand for higher speeds and more reliable connections, WMSC remains an integral part of ensuring that users continue to experience seamless service. With advancements in mobile technology, WMSC will adapt and integrate with future systems, ensuring that the foundation of mobile communications remains strong and reliable for years to come.