DMR Architecture Overview: How Digital Mobile Radio Systems Work
telcomatraining.com – Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) has become a cornerstone of modern communication systems, providing reliable, secure, and efficient digital voice and data services across industries such as public safety, transportation, utilities, and manufacturing. Unlike analog systems, DMR offers enhanced spectral efficiency, superior audio quality, and advanced network management features. This article explores the architecture of DMR systems, their core components, and how they work together to enable seamless digital communication.
Understanding the Basics of DMR
DMR is an open digital radio standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). It was designed to improve upon analog two-way radio systems by offering better audio clarity, channel efficiency, and data capabilities. DMR uses Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) technology, which divides a single 12.5 kHz channel into two time slots, allowing two simultaneous and independent communications on the same frequency. This effectively doubles the capacity without requiring additional spectrum.
DMR operates in three tiers:
- Tier I: License-free use for personal or small business communications.
- Tier II: Licensed conventional systems for professional and commercial users.
- Tier III: Trunked systems designed for large organizations or public safety networks requiring advanced call routing and control features.
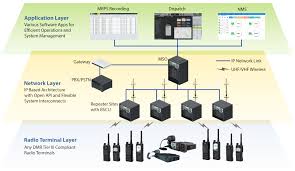
Core Components of DMR Architecture
A standard DMR system is built on several essential components that form a layered architecture ensuring flexibility, scalability, and interoperability:
- Subscriber Units (Radios): These are handheld or mobile radios used by end-users. They encode and decode voice signals digitally and support both direct and networked communications.
- Repeaters (Base Stations): Repeaters extend communication range and act as intermediaries between radios. They manage TDMA time slots and synchronize data transmission across the network.
- Core Network (Controller): In larger systems like Tier III, a DMR controller manages channel allocation, call routing, authentication, and system redundancy. It ensures efficient use of network resources and supports data applications.
- Dispatch Console: The dispatch system allows operators to monitor calls, send messages, and manage users in real time. It’s a vital tool for mission-critical operations such as emergency response.
- Network Management System (NMS): This software platform oversees the entire DMR infrastructure, tracking performance, faults, and configuration changes for optimal operation.
How DMR Systems Work
DMR systems convert voice signals into digital data using Advanced Multi-Band Excitation (AMBE+) vocoder technology, which compresses audio while preserving clarity. When a user speaks into a DMR radio, the voice is digitized, encoded, and transmitted over one of the TDMA time slots. The repeater or base station then directs this data to the intended receiver or group.
In Tier III trunked systems, calls are dynamically assigned to available channels through the control channel managed by the DMR controller. This automation enhances efficiency, reduces waiting time, and prioritizes emergency or group calls when necessary.
DMR also supports data services, including text messaging, GPS tracking, telemetry, and over-the-air programming (OTAP). These capabilities make DMR more than just a voice communication tool—it’s a complete digital ecosystem for workforce management and safety.
Benefits of DMR Architecture
The DMR framework offers several advantages:
- Spectrum Efficiency: TDMA doubles capacity within the same bandwidth.
- Enhanced Audio Quality: Digital processing eliminates background noise and signal degradation.
- Scalability: Modular design allows networks to grow with user demand.
- Interoperability: As an open standard, DMR ensures compatibility between different manufacturers.
- Security: Features such as authentication and encryption safeguard sensitive communications.
Conclusion
The DMR architecture represents a powerful evolution in digital communication, combining efficiency, reliability, and advanced features in one unified platform. By leveraging TDMA technology, robust network control, and versatile data integration, DMR systems continue to set the benchmark for professional mobile radio communications worldwide. As industries and public safety agencies transition toward smarter, more connected operations, understanding how DMR systems work is essential to harness their full potential in the digital age.