Element Management Systems: The Foundation of Telecom Infrastructure
telcomatraining.com – In the modern digital age, the telecommunications industry is the lifeline that connects people, devices, and businesses globally. As telecom networks become more complex, managing their components efficiently becomes crucial. This is where Element Management Systems (EMS) come into play. EMS forms a critical layer in network management, acting as the bridge between individual network elements and overarching network management systems. Understanding the role of EMS in telecom is essential for appreciating how service providers ensure seamless communication and optimal performance.
What is an Element Management System?
An Element Management System is a specialized software platform designed to monitor, control, and manage individual network elements such as routers, switches, base stations, and optical transmission units. Each of these elements has unique configuration and performance characteristics that require constant supervision. EMS provides a centralized interface to handle these functions efficiently.
Typically, EMS operates at the second-lowest layer of the Telecommunications Management Network (TMN) model, just above the network elements themselves. It enables real-time fault detection, performance analysis, configuration management, and software updates across all associated hardware devices.
Key Functions of EMS in Telecom
- Fault Management
EMS continuously monitors network elements for errors or failures. It collects and reports alarms in real-time, helping technicians diagnose and resolve issues promptly, thus minimizing downtime. - Configuration Management
With EMS, telecom operators can manage device configurations, including settings, parameters, and firmware updates. This centralization simplifies the setup and reduces manual errors during network upgrades or expansions. - Performance Management
EMS gathers data on network usage, bandwidth, latency, and throughput. This information helps in analyzing trends, optimizing performance, and ensuring Quality of Service (QoS) for end users. - Security Management
EMS enforces security policies, manages access control, and monitors unauthorized activities at the element level, thus protecting the network from potential cyber threats.
Benefits of Using EMS in Telecom Infrastructure
The deployment of an EMS brings several advantages to telecom providers, including:
- Operational Efficiency: Automating routine management tasks reduces human intervention, cutting down operational costs and error rates.
- Scalability: As networks grow, EMS provides the tools needed to scale infrastructure without compromising visibility or control.
- Reliability: By quickly identifying and addressing faults, EMS enhances the reliability and uptime of telecom services.
- Interoperability: EMS systems often support standardized communication protocols like SNMP or TL1, allowing integration with other systems and equipment from different vendors.
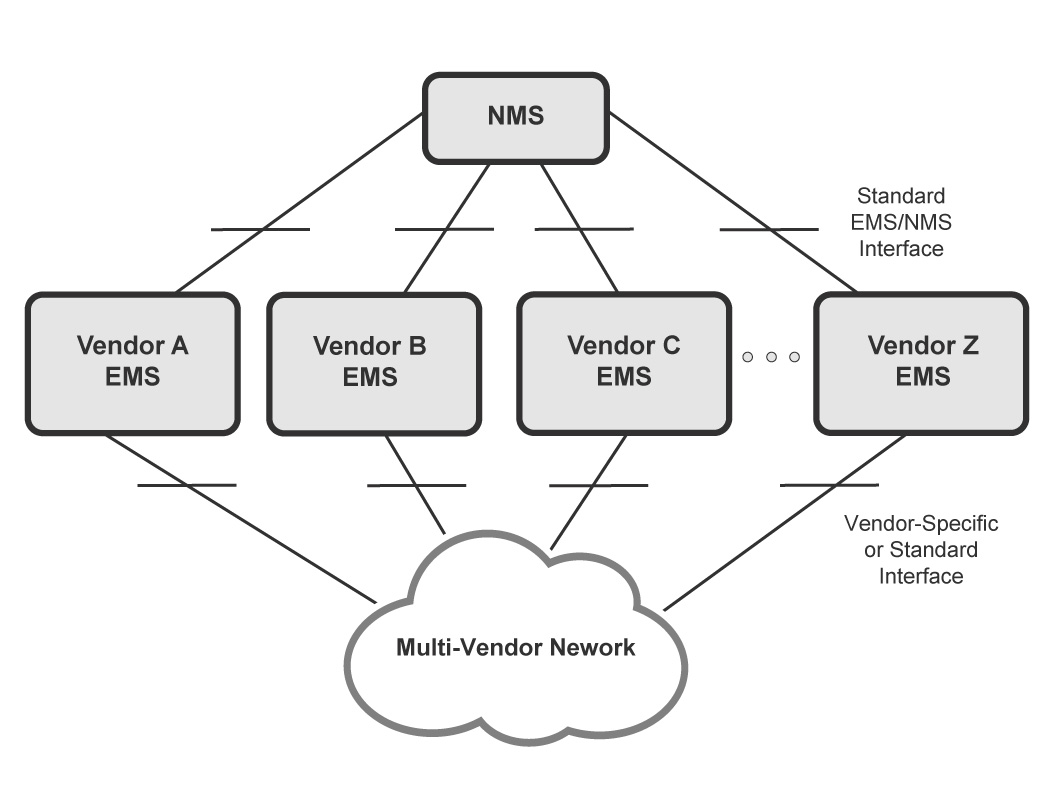
EMS vs. Network Management Systems (NMS)
While EMS focuses on managing individual network elements, Network Management Systems (NMS) provide a broader view of the network. NMS aggregates data from multiple EMSs to give a comprehensive overview of the entire telecom infrastructure. Together, EMS and NMS create a layered management architecture that ensures both micro and macro-level oversight.
The Future of EMS in 5G and Beyond
As telecom networks transition to 5G, EMS platforms are evolving to manage virtualized and software-defined network components. New challenges like network slicing, ultra-low latency, and dynamic resource allocation require more intelligent and adaptive EMS solutions. Integrating AI and machine learning into EMS is a growing trend, enabling predictive maintenance and automated fault resolution.
Conclusion
Element Management Systems are the backbone of telecom infrastructure, ensuring the smooth operation of every network element. Their ability to manage, monitor, and optimize complex hardware ecosystems makes them indispensable in today’s highly connected world. As technology advances, EMS will continue to evolve, playing a vital role in shaping the future of telecommunications.