Understanding vRAN and Open RAN: Key Enablers of the 5G Network
telcomatraining.com – As the world shifts rapidly towards advanced connectivity, the fifth-generation (5G) mobile network is playing a critical role in transforming how we communicate, work, and live. Among the foundational technologies driving this evolution are vRAN (Virtualized Radio Access Network) and Open RAN (Open Radio Access Network). These two innovations are redefining the mobile infrastructure landscape, making it more flexible, cost-efficient, and open to competition.
What is vRAN?
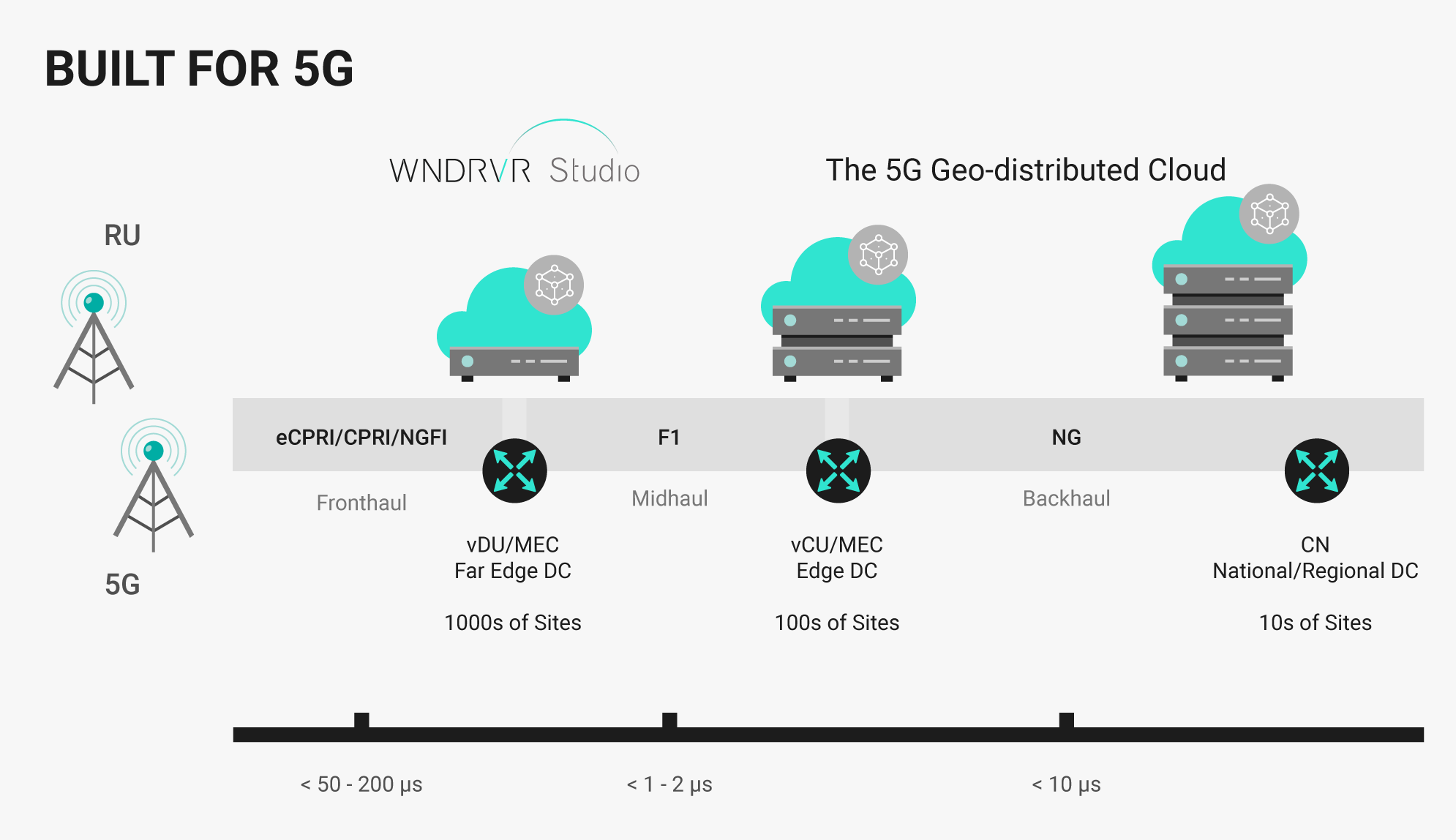
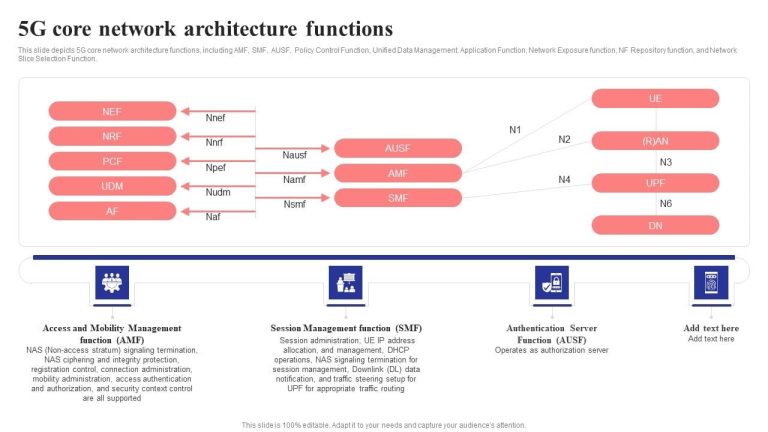
Virtualized Radio Access Network (vRAN) refers to the decoupling of hardware and software in the traditional radio access network. In a conventional RAN architecture, baseband processing units and radio units are tightly integrated, often using proprietary hardware from a single vendor. vRAN changes this by using software-based baseband functions running on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware.
This virtualization allows network operators to deploy and manage network functions through software, making the infrastructure more scalable and adaptable. Operators can also optimize resource usage, reduce energy consumption, and improve maintenance efficiency through centralized control.
What is Open RAN?
Open RAN (O-RAN) takes the principles of vRAN further by introducing openness and interoperability into the RAN ecosystem. Traditionally, mobile networks have been dominated by a few large vendors who provide end-to-end solutions. Open RAN aims to break this vendor lock-in by standardizing interfaces and allowing different components from multiple vendors to work seamlessly together.
Open RAN architecture promotes innovation and vendor diversity, enabling smaller players and startups to contribute to the network landscape. This fosters a competitive environment, potentially lowering costs and accelerating technological advancements in 5G networks.
Key Differences Between vRAN and Open RAN
While both technologies promote flexibility and virtualization, they serve different purposes:
- vRAN focuses on virtualizing network functions, mainly the baseband unit, to run on general-purpose hardware.
- Open RAN emphasizes openness and standardization of hardware and software interfaces, enabling interoperability among vendors.
These technologies are complementary. Many Open RAN implementations use vRAN architectures as their foundation, leveraging both virtualization and open interfaces to build next-generation RAN systems.
Benefits of vRAN and Open RAN in 5G Networks
The integration of vRAN and Open RAN into 5G networks brings several key benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: By using general-purpose hardware and allowing vendor mix-and-match, operators can reduce capital and operational expenditures.
- Network Flexibility: Virtualization enables dynamic resource allocation, allowing networks to adapt to demand in real-time.
- Faster Innovation: Open standards attract a broader ecosystem of developers and vendors, leading to rapid technological advancement.
- Scalability: Cloud-native infrastructure makes it easier to scale networks based on demand without massive infrastructure changes.
- Improved Network Performance: Advanced automation and AI integration in vRAN and Open RAN can optimize network traffic and reduce latency.
Challenges to Consider
Despite the advantages, there are still challenges in deploying vRAN and Open RAN:
- Integration Complexity: Ensuring different components from multiple vendors work seamlessly requires robust testing and collaboration.
- Security Risks: More components and open interfaces may introduce new security vulnerabilities that need proactive mitigation.
- Performance Trade-offs: Some operators express concerns over potential latency and performance issues in software-based solutions compared to dedicated hardware.
The Future of 5G with vRAN and Open RAN
The global telecom industry is actively investing in vRAN and Open RAN to future-proof 5G networks and prepare for upcoming technologies like 6G. Major operators, including AT&T, Vodafone, and Rakuten, are already deploying these technologies on a wide scale. With the support of open standards bodies like the O-RAN Alliance, the vision of a fully open, flexible, and intelligent RAN ecosystem is becoming a reality.
Conclusion
vRAN and Open RAN are not just technological upgrades—they are transformational shifts in how mobile networks are designed, deployed, and managed. As 5G adoption accelerates, embracing these innovations will be critical for network operators looking to deliver high-speed, low-latency, and future-ready connectivity.
By understanding and leveraging vRAN and Open RAN, we pave the way for a more open, competitive, and agile telecom environment—a true enabler for the connected world of tomorrow.