3GPP NR Specifications Explained: What You Need to Know for 5G Success
telcomatraining.com – As 5G technology continues to expand across the globe, understanding the technical foundation behind it becomes increasingly important. At the heart of this transformation lies the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and its New Radio (NR) specifications. These standards define how 5G networks operate, ensuring consistency, interoperability, and performance across all devices and networks. Whether you’re a telecom professional, developer, or tech enthusiast, understanding 3GPP NR specifications is key to navigating the 5G landscape.
What Is 3GPP?
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is a global collaboration between several telecommunications standard development organizations. Established in 1998, 3GPP’s primary goal is to produce standardized specifications for mobile systems. These include GSM, UMTS (3G), LTE (4G), and now NR (5G).
By unifying global efforts, 3GPP ensures that network operators, equipment manufacturers, and service providers follow the same guidelines, fostering cross-border compatibility and innovation.
Understanding New Radio (NR)
New Radio (NR) is the air interface developed by 3GPP specifically for 5G. Unlike its predecessors, NR is designed to support a wide variety of use cases, from enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) and massive machine-type communication (mMTC). These use cases make NR the most flexible and scalable radio interface to date.
NR operates on a wide range of spectrum bands, including:
- Sub-6 GHz (FR1): Used for wide-area coverage.
- Millimeter Wave (FR2): Enables extremely high data rates over shorter distances.
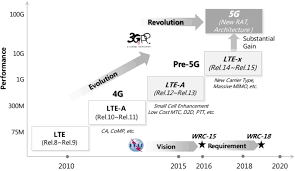
Key 3GPP NR Specifications and Releases
3GPP defines its specifications in “Releases,” with each release introducing new features and capabilities. The most relevant releases for 5G NR are:
- Release 15: This is the first release to support standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) 5G NR. It focused on providing a baseline for 5G deployment and integrating with existing 4G LTE networks.
- Release 16: Introduced advanced features such as URLLC enhancements, improved mobility, and support for industrial IoT and V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communication.
- Release 17 and beyond: Focus on expanding 5G applications with features like NR-Light for low-power IoT, satellite access, and advanced positioning.
These releases are fundamental in shaping how networks evolve and how 5G capabilities expand across industries.
Why 3GPP NR Specifications Matter
Understanding 3GPP NR specifications is critical for several reasons:
- Network Compatibility: Devices and networks built according to the same specifications ensure seamless communication and roaming.
- Performance Optimization: Specifications define how to achieve peak data rates, ultra-low latency, and reliability.
- Innovation Enablement: Standardization offers a stable platform for developing cutting-edge services such as smart factories, autonomous vehicles, and AR/VR applications.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many national regulators align with 3GPP standards, making them crucial for global market entry.
Challenges and Considerations
While the NR specifications offer a roadmap for innovation, implementing them is not without challenges. The complexity of multi-band operations, backward compatibility with LTE, and network slicing management demand sophisticated infrastructure and software intelligence.
Moreover, as 3GPP continues to evolve with new releases, stakeholders must stay updated to remain competitive.
Final Thoughts
The 3GPP NR specifications are the backbone of the 5G ecosystem. They define the rules of engagement for network performance, device behavior, and service delivery. As 5G adoption grows, having a solid understanding of these standards isn’t just beneficial—it’s essential.
Whether you’re developing applications, deploying networks, or planning strategic investments, aligning with 3GPP NR specifications is a cornerstone of 5G success.