Maximizing Network Control with SDN Tools and Functionalities
telcomatraining.com – In today’s digital era, businesses demand more from their networks—higher performance, better flexibility, and increased security. Traditional network architectures often struggle to meet these demands due to their rigid and hardware-centric designs. This is where Software-Defined Networking (SDN) comes into play. SDN revolutionizes the way networks are managed by providing centralized control, programmability, and real-time automation. Leveraging the right SDN tools and functionalities can significantly maximize network control, optimize performance, and reduce operational costs.
What is Software-Defined Networking?
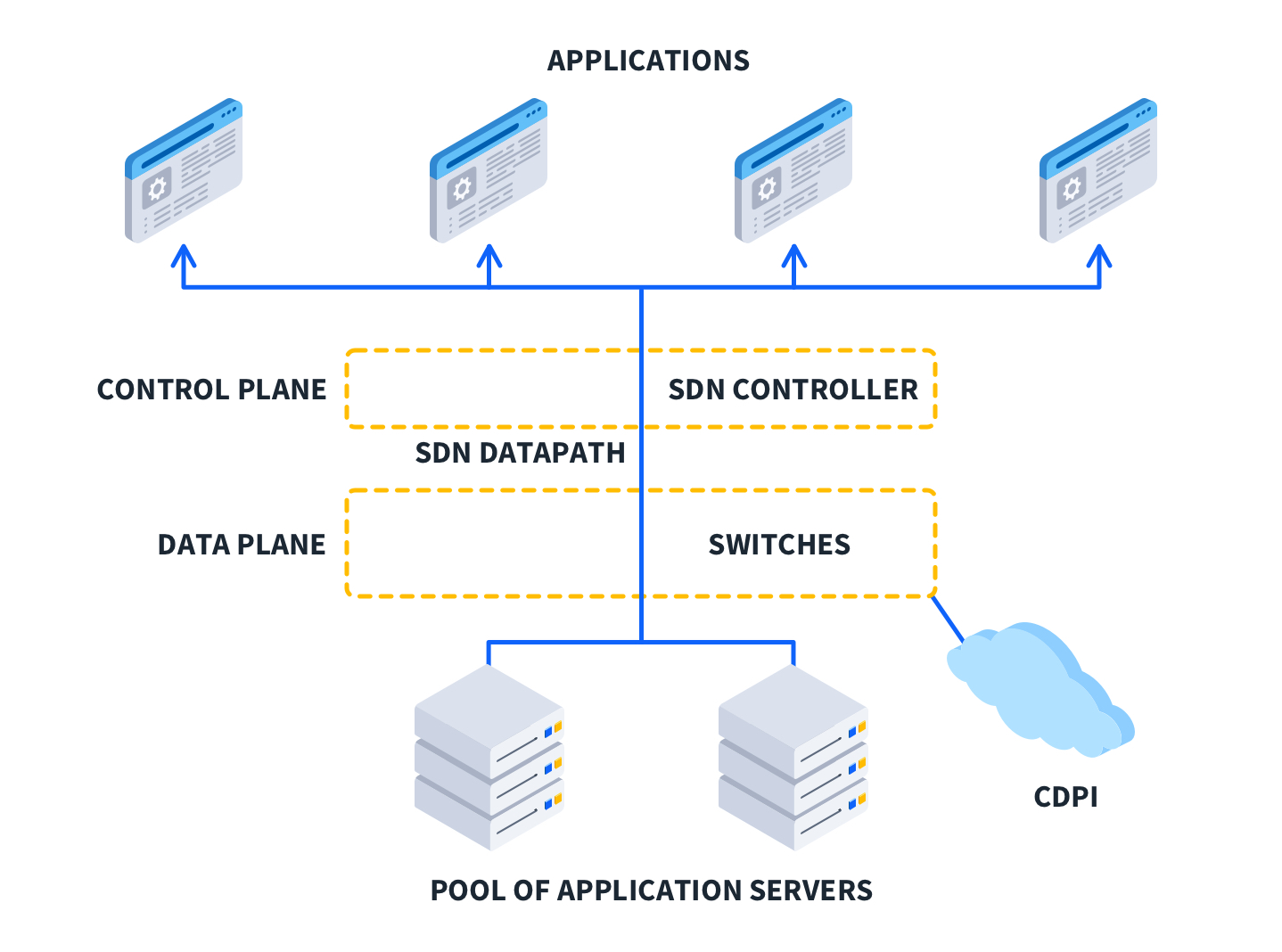
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is an architectural approach that separates the network control plane from the data plane, allowing centralized management of network traffic. With SDN, network administrators can programmatically configure, manage, and optimize network resources through software applications.
This separation enhances network flexibility and enables rapid adjustments to meet dynamic business needs. Instead of configuring individual devices manually, SDN offers a unified view of the network, streamlining operations and improving scalability.
Core SDN Functionalities Enhancing Network Control
To fully harness the benefits of SDN, it’s essential to understand its core functionalities:
1. Centralized Control
SDN’s most significant feature is its centralized control plane. This allows administrators to manage the entire network from a single dashboard. It provides real-time insights into network behavior, enabling quick decision-making and immediate implementation of policies.
2. Programmability
With SDN, networks become programmable via APIs, allowing automation of repetitive tasks and rapid deployment of new services. This programmability leads to reduced errors, enhanced agility, and faster troubleshooting.
3. Dynamic Traffic Management
SDN tools enable dynamic path selection and load balancing based on current traffic conditions. This helps in optimizing bandwidth usage, minimizing latency, and ensuring seamless data transmission even during peak times.
4. Enhanced Security
By centralizing control and providing granular visibility, SDN makes it easier to detect anomalies, enforce security policies, and isolate threats. Features such as micro-segmentation further strengthen network defenses by limiting lateral movement within the network.
Top SDN Tools Empowering Network Management
Several open-source and commercial SDN tools are available that provide advanced functionalities to boost network performance and control:
– OpenDaylight
An open-source SDN controller designed for flexibility and extensibility. OpenDaylight supports a wide range of southbound and northbound protocols, making it ideal for complex enterprise environments.
– ONOS (Open Network Operating System)
ONOS is built for service providers, focusing on high availability and scalability. It is perfect for managing large-scale networks, offering robust features like intent-based networking.
– Ryu
A component-based SDN framework written in Python, Ryu supports various protocols and offers a rich API set for custom application development.
– Cisco ACI (Application Centric Infrastructure)
A commercial SDN solution, Cisco ACI integrates both physical and virtual environments. It simplifies operations, enhances security, and provides policy-driven automation.
Benefits of Using SDN Tools for Network Control
- Improved Agility: Quickly adapt to new business needs and scale network resources on demand.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduce hardware dependency and lower operational expenditures through automation.
- Better Network Visibility: Gain end-to-end insights into network performance and health.
- Stronger Security: Quickly detect, isolate, and respond to security threats.
- Faster Troubleshooting: Identify and resolve issues in real time, minimizing downtime.
Conclusion
Maximizing network control in a rapidly evolving digital landscape requires more than traditional solutions. Software-Defined Networking tools and functionalities offer the agility, visibility, and security modern networks need. By leveraging the power of SDN, organizations can not only streamline operations but also future-proof their infrastructure. As networks grow more complex, the role of SDN in maintaining control, optimizing resources, and driving innovation becomes increasingly critical.