Evolution and Complexity in 5G Hardware Development
telcomatraining.com – The evolution of mobile communication has reached an unprecedented milestone with the introduction of 5G technology. As the fifth generation of wireless communication, 5G promises ultra-fast data speeds, low latency, and seamless connectivity. However, behind this leap in performance lies a web of intricate developments in hardware. The complexity in 5G hardware development stems from the need to support new frequency bands, high data throughput, and increased device connectivity — all while maintaining power efficiency and reliability.
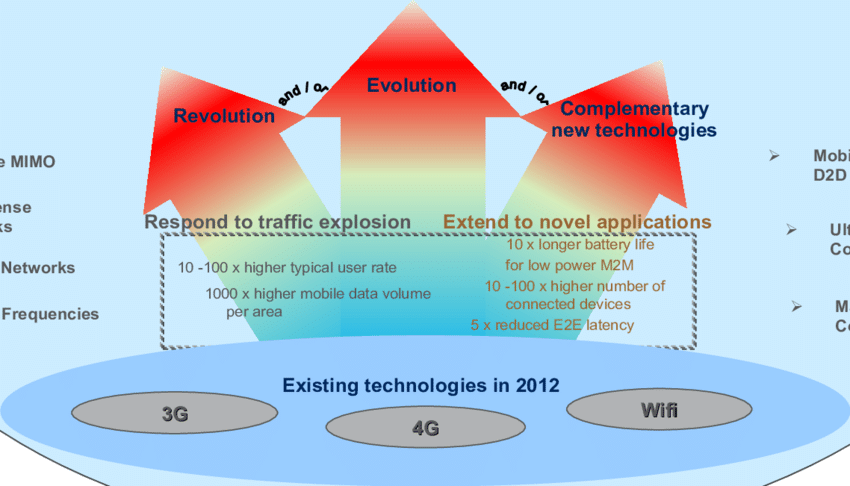
The Journey from 1G to 5G: A Brief Overview
To understand the significance of 5G hardware, it’s essential to look back at the journey from 1G to 5G. Each generation of mobile networks introduced technological leaps:
- 1G offered analog voice communication.
- 2G introduced digital voice and SMS.
- 3G enabled mobile internet.
- 4G brought high-speed data and HD video streaming.
- 5G, however, is far more transformative. It supports enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC).
This transformation requires an entirely new hardware ecosystem, marking a significant shift from previous generations.
Key Components of 5G Hardware
The core components of 5G hardware include base stations, antennas, RF (radio frequency) front-ends, modems, and network infrastructure equipment. These components must support higher frequencies — including mmWave (millimeter wave) bands — which can deliver gigabit speeds but have shorter ranges and require more dense network deployments.
- Antennas and Beamforming
One of the standout features in 5G is the use of massive MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) and beamforming technologies. These require complex antenna arrays capable of directing signals precisely to user devices. The development of compact, high-performance antenna modules that can fit into smartphones and small cell stations is a major engineering challenge. - RF Front-End Modules
RF front-end modules are critical in processing high-frequency signals. They include filters, power amplifiers, and switches. Designing these components to handle a wide range of frequencies with minimal loss and maximum efficiency is one of the most difficult aspects of 5G hardware engineering. - Semiconductor Innovation
The need for faster data processing and lower latency demands cutting-edge semiconductors. Chipmakers have developed new generations of SoCs (System on Chips) using advanced manufacturing nodes like 5nm and 3nm. These chips integrate AI capabilities, 5G modems, and high-performance CPUs and GPUs to manage complex data streams in real time.
Challenges in 5G Hardware Development
The complexity of 5G hardware stems from several factors:
- Spectrum Diversity: 5G operates across low, mid, and high bands. Each band has unique hardware requirements, making universal design difficult.
- Thermal Management: Higher data rates and processing power generate more heat. Efficient thermal design is crucial to maintain performance and reliability.
- Miniaturization: As hardware becomes more capable, it must also become smaller — especially for smartphones and IoT devices.
- Power Efficiency: Devices must handle complex tasks without draining the battery too quickly, demanding breakthroughs in power management technologies.
The Future of 5G Hardware
As 5G continues to expand, hardware will evolve to become more intelligent, energy-efficient, and integrated. The development of AI-driven network hardware, edge computing devices, and reconfigurable antennas will further push the boundaries of what’s possible. Additionally, 5G hardware must remain adaptable to future enhancements like 5G Advanced and eventually 6G.
Conclusion
The development of 5G hardware is a complex yet fascinating journey of innovation. It merges advancements in material science, chip design, antenna engineering, and system integration. As global reliance on 5G increases, so does the importance of robust, scalable, and efficient hardware solutions. The evolution of 5G is not just about faster internet — it’s about building the technological foundation for a more connected, intelligent future.