5G FWA Architecture Explained
telcomatraining.com – In the ever-evolving world of telecommunications, 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) is revolutionizing how high-speed internet is delivered, especially in underserved and rural areas. But what exactly is 5G FWA, and how does its architecture work? This article dives deep into the architecture of 5G FWA, breaking down its key components, benefits, and how it differs from traditional broadband solutions.
What is 5G FWA?
5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) is a method of delivering high-speed internet to homes and businesses using wireless 5G networks instead of traditional wired connections such as fiber or DSL. It enables operators to provide gigabit-level speeds without laying cables, making it cost-effective and quicker to deploy, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
FWA operates using millimeter-wave (mmWave) or sub-6 GHz frequencies, depending on the deployment. These frequencies offer high capacity and low latency, which are essential for modern digital needs.
Key Components of 5G FWA Architecture
To understand how 5G FWA works, it’s important to explore its architecture, which can be divided into several core components:
1. Customer Premises Equipment (CPE)
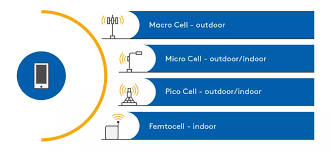
The CPE is the device installed at the user’s home or office. It connects to the 5G signal from the nearby base station and provides internet access to the user’s devices via Wi-Fi or Ethernet. The CPE can be outdoor or indoor, depending on the signal strength and line of sight to the 5G cell.
2. Radio Access Network (RAN)
The RAN is composed of the 5G base stations (gNodeBs) that communicate wirelessly with the CPE. These stations are connected to the core network and are responsible for handling user traffic, managing radio resources, and maintaining connection quality.
Advanced features like massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) and beamforming are utilized in the RAN to improve coverage and capacity, especially in dense urban environments.
3. Transport Network
The transport network connects the RAN to the core network. It is typically a high-capacity fiber or microwave link that ensures fast and reliable transmission of data. This part of the architecture plays a crucial role in maintaining low latency and high throughput.
4. 5G Core Network
The 5G Core (5GC) is the brain of the FWA system. It handles all the data routing, network management, authentication, and Quality of Service (QoS) policies. The 5GC is fully cloud-native, allowing it to scale dynamically and support various applications, including IoT, video streaming, and smart city services.
Benefits of 5G FWA Architecture
The architecture of 5G FWA offers numerous advantages over traditional broadband:
- Rapid Deployment: No need for trenching or cable installation.
- High Speeds: Gigabit-level speeds comparable to fiber optics.
- Low Latency: Ideal for real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing.
- Scalability: Easily expanded to meet growing demand.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced infrastructure costs make it viable in rural or developing areas.
Use Cases of 5G FWA
5G FWA is being adopted globally for various purposes:
- Residential broadband in suburban and rural areas.
- Enterprise connectivity where fiber is unavailable.
- Temporary deployments like events or construction sites.
- Smart cities and IoT hubs, providing consistent and high-speed access.
Challenges and Considerations
While 5G FWA brings many benefits, there are also challenges:
- Line-of-sight requirements, especially for mmWave frequencies.
- Weather interference, which can affect signal quality.
- Spectrum availability, which varies by region and regulation.
Operators need to carefully plan the deployment of base stations and CPE to ensure consistent service quality.
Conclusion
5G FWA architecture represents a significant shift in broadband delivery, offering fast, flexible, and reliable internet access without the need for physical cabling. As 5G continues to expand, FWA will play a vital role in bridging the digital divide, connecting millions of users to the digital world. Understanding its architecture helps highlight why 5G FWA is a game-changer in the broadband industry.