5G Mission-Critical Services: Importance and Industry Applications
telcomatraining.com – The advent of 5G technology has revolutionized the telecommunications industry, offering ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC). Among these, mission-critical services stand out as a pivotal aspect of 5G, enabling real-time applications that require high reliability and minimal latency. This article explores the importance of 5G mission-critical services and their applications across various industries.
Importance of 5G Mission-Critical Services
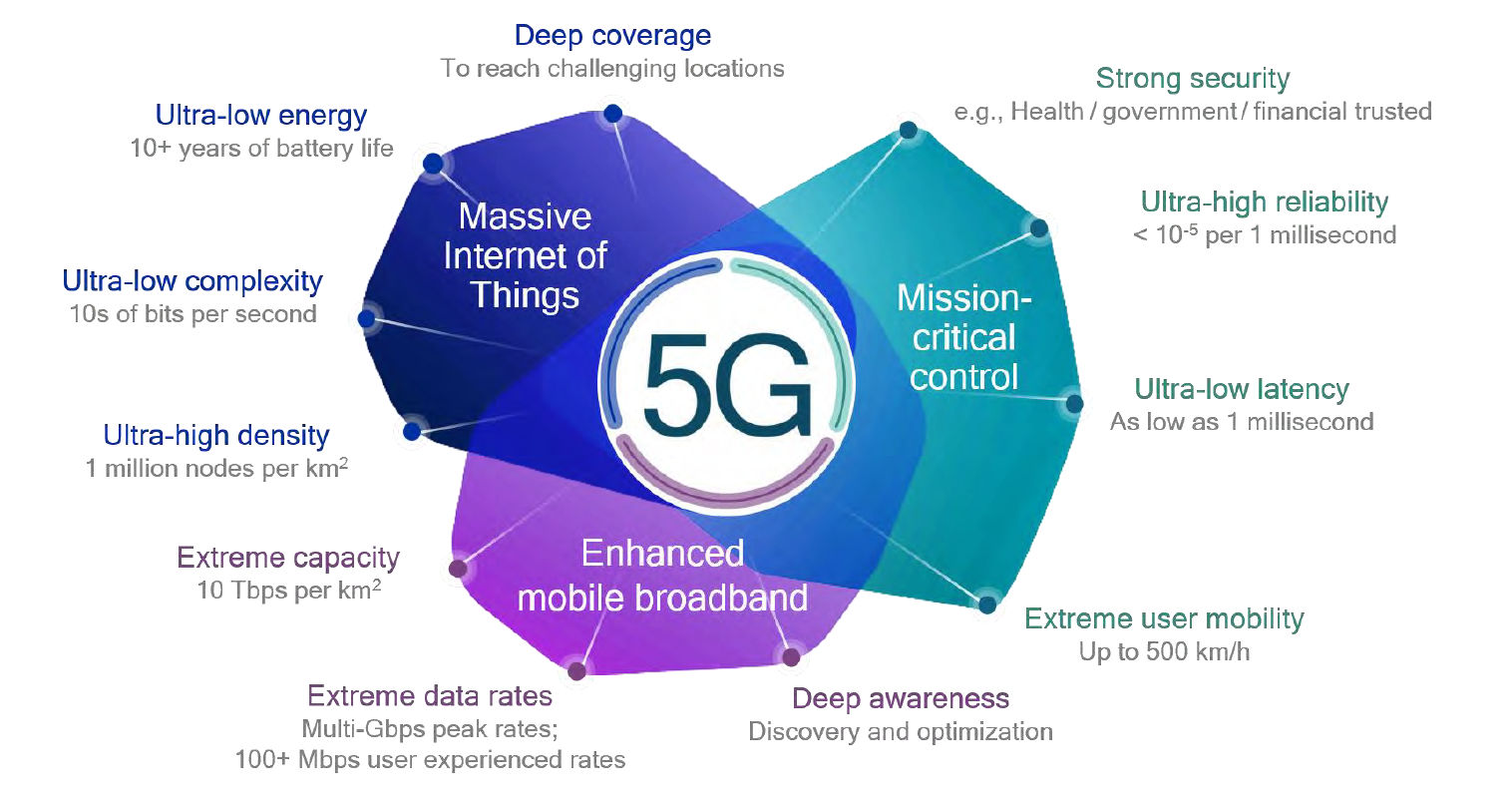
1. Ultra-Low Latency
One of the most significant advantages of 5G mission-critical services is ultra-low latency. With latencies as low as one millisecond, 5G ensures real-time responsiveness, crucial for applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote surgeries. Low latency minimizes delays, enabling seamless communication between devices and systems.
2. High Reliability
Mission-critical applications demand an uninterrupted connection with minimal downtime. 5G networks provide high reliability through network slicing and edge computing, ensuring dedicated resources for critical applications. This prevents service disruptions, making 5G ideal for emergency response, defense, and public safety.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
5G technology offers scalability to support a vast number of connected devices. This flexibility enables industries to deploy customized network solutions tailored to specific needs, from smart cities to intelligent transport systems. With adaptive bandwidth allocation, businesses can optimize performance according to real-time demands.
Industry Applications of 5G Mission-Critical Services
1. Healthcare: Remote Surgeries and Telemedicine
The healthcare sector greatly benefits from 5G’s low latency and high reliability. Surgeons can perform remote robotic surgeries with precision, reducing the need for travel and expanding access to specialized care. Additionally, telemedicine services can offer real-time consultations and monitoring, improving patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
2. Automotive: Autonomous Vehicles and V2X Communication
5G enables vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, a critical component for autonomous vehicles. Cars can communicate with each other, traffic infrastructure, and pedestrians in real time, enhancing road safety and traffic efficiency. The reliability of 5G ensures accurate and instantaneous decision-making, reducing accidents and congestion.
3. Industrial Automation: Smart Manufacturing
Industries are increasingly adopting 5G-enabled smart factories, where automated machines and robots perform tasks with minimal human intervention. Real-time data exchange between machines enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and optimizes production. Predictive maintenance, powered by AI and 5G, prevents equipment failures and boosts operational continuity.
4. Public Safety: Emergency Response and Disaster Management
5G plays a crucial role in public safety by providing reliable communication for emergency responders. First responders, such as firefighters, police, and medical teams, can receive real-time updates, live video feeds, and critical data during emergencies. This improves coordination and response times, ultimately saving lives.
5. Energy and Utilities: Smart Grids and Remote Monitoring
The energy sector benefits from 5G by enabling smart grids that efficiently manage power distribution. Remote monitoring of critical infrastructure, such as power plants and pipelines, ensures early detection of faults and reduces downtime. This results in a more stable and resilient energy supply.
Conclusion
5G mission-critical services are transforming industries by offering ultra-reliable connectivity, low latency, and scalability. From healthcare and automotive to industrial automation and public safety, 5G is paving the way for next-generation applications that demand high-performance networks. As 5G adoption continues to grow, businesses and governments must invest in infrastructure and security measures to maximize its potential and ensure a seamless transition into a connected future.