5G NR RRC State Transitions: How Connections Are Managed
telcomatraining.com – With the rapid evolution of 5G New Radio (NR), the efficient management of radio resources is critical for ensuring seamless connectivity and optimal performance. One of the key components in this process is the Radio Resource Control (RRC) state machine, which governs how devices connect, transmit, and transition between different network states. This article explores the RRC states in 5G NR, their transitions, and how they enhance network efficiency.
Understanding 5G NR RRC States
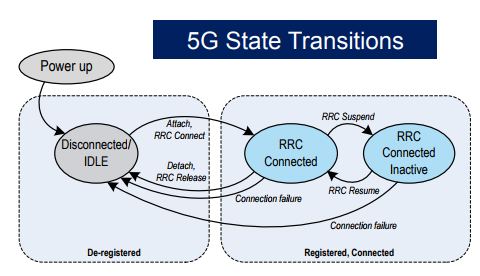
The RRC protocol in 5G NR defines different states for User Equipment (UE) to optimize power consumption and network resources. These states include:
- RRC_IDLE: In this state, the UE is not actively connected to the network but remains registered. It can receive system information and paging messages from the network.
- RRC_INACTIVE: This is a new state introduced in 5G NR to improve energy efficiency. The UE maintains its context but does not have an active connection, reducing signaling overhead while allowing quick reactivation.
- RRC_CONNECTED: The UE has an established connection with the network, enabling data transmission and reception. This state is essential for active data communication and mobility management.
RRC State Transitions in 5G NR
The transitions between these states play a vital role in optimizing network efficiency and device power consumption. Below are the key transitions:
1. RRC_IDLE to RRC_CONNECTED
- When a UE needs to establish a connection (e.g., for data transmission or call setup), it initiates an RRC setup request.
- The network responds with an RRC setup message, and upon completion, the UE moves to the RRC_CONNECTED state.
- This transition ensures that the device can send and receive data with minimal delay.
2. RRC_CONNECTED to RRC_IDLE
- If the UE remains inactive for a prolonged period, the network may release the RRC connection to free up resources.
- The UE then transitions back to RRC_IDLE, where it relies on paging messages for any further communication.
- This helps in reducing network congestion and UE power consumption.
3. RRC_CONNECTED to RRC_INACTIVE
- The introduction of RRC_INACTIVE provides an efficient mechanism for quick state reactivation without a full connection setup.
- When transitioning to RRC_INACTIVE, the UE retains its network context, allowing it to resume data transfer faster compared to RRC_IDLE.
- This transition is particularly useful for applications with intermittent data activity, such as messaging and IoT devices.
4. RRC_INACTIVE to RRC_CONNECTED
- When the UE requires data transmission, it sends a resume request to the network.
- The network restores the connection with minimal signaling overhead, transitioning the UE back to RRC_CONNECTED.
- This ensures lower latency and power efficiency compared to establishing a new connection from RRC_IDLE.
5. RRC_IDLE to RRC_INACTIVE
- In certain scenarios, the network may move a UE from RRC_IDLE to RRC_INACTIVE instead of directly to RRC_CONNECTED.
- This allows for a balance between power saving and fast reactivation.
- The transition mechanism is particularly beneficial in high-mobility scenarios, ensuring better connectivity without excessive signaling.
Benefits of Efficient RRC State Management
Effective management of RRC state transitions in 5G NR offers several advantages:
- Reduced Power Consumption: Efficient state transitions minimize power usage in UEs, extending battery life, especially for mobile and IoT devices.
- Optimized Network Resources: By intelligently managing active and inactive connections, networks can reduce congestion and improve overall efficiency.
- Lower Latency: Quick state transitions ensure lower latency, which is critical for applications like real-time gaming, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
- Enhanced User Experience: Seamless connectivity transitions provide users with uninterrupted service, enhancing satisfaction and network reliability.
Conclusion
The 5G NR RRC state transitions are fundamental to managing connections efficiently while balancing power consumption and network performance. The introduction of the RRC_INACTIVE state has significantly improved connection re-establishment, reducing signaling overhead and ensuring seamless transitions. As 5G adoption continues to grow, optimizing these state transitions will remain a key focus for network operators and device manufacturers, ensuring a high-quality user experience.