5G Wireless Hardware Evolution: From Legacy Tech to Smart Connectivity
telcomatraining.com – In the ever-changing landscape of telecommunications, the journey from early wireless technology to the cutting-edge 5G era marks a revolutionary shift. The evolution of 5G wireless hardware has transformed not just network speed and latency but also how devices, systems, and industries interact in a hyper-connected world. This article explores the significant milestones in 5G wireless hardware development and how it’s reshaping smart connectivity.
From 1G to 4G: Building the Foundation
Before 5G, the world witnessed a series of generational upgrades in wireless communication. The first generation (1G) in the 1980s introduced analog voice. Then came 2G with digital voice, followed by 3G, which brought mobile data into everyday life. The fourth generation (4G LTE) delivered faster internet speeds and supported video streaming, mobile apps, and real-time communication.
Each generation not only improved data transmission rates but also required advancements in wireless hardware—antennas, chipsets, modems, and network infrastructure. However, the jump to 5G demanded an entirely new approach to hardware design and deployment.
The Leap to 5G: More Than Just Speed
5G is not just a speed upgrade; it’s a paradigm shift. Designed to handle ultra-low latency, massive machine-type communication (mMTC), and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), 5G required a new class of hardware. Its rollout has been accompanied by the development of powerful base stations, compact yet robust antennas, and energy-efficient chipsets.
Unlike previous networks, 5G operates across three frequency bands: low-band, mid-band, and high-band (millimeter wave). This diversity required hardware that could support multiple frequencies simultaneously—something legacy technology could not handle efficiently.
Small Cells and mmWave Technology
One of the key innovations in 5G wireless hardware is the use of small cell networks. Unlike traditional cell towers, small cells are compact, low-powered radio access nodes that are densely deployed in urban environments. They are crucial for ensuring high-speed connectivity in areas with heavy data traffic.
Millimeter wave (mmWave) technology also became a cornerstone of 5G hardware evolution. Operating at higher frequencies (24GHz and above), mmWave offers ultra-fast speeds but has a limited range. To compensate, hardware engineers developed advanced antenna arrays, beamforming techniques, and MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) systems that direct signals precisely where needed.
Edge Computing and Hardware Intelligence
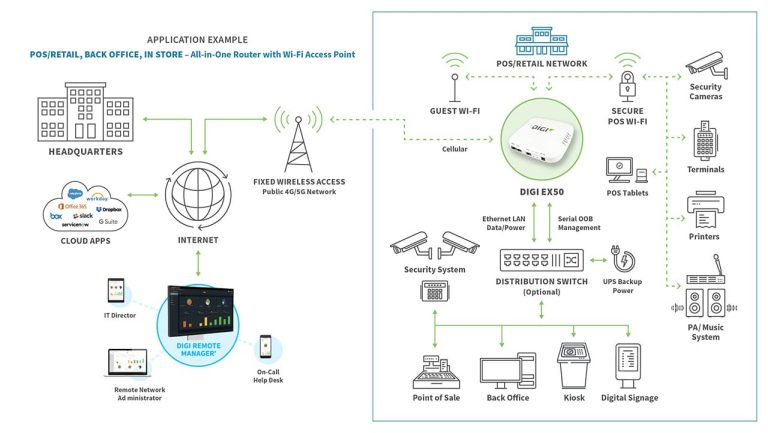
Another leap in 5G hardware evolution is the integration of edge computing. To reduce latency and enable real-time decision-making, more processing is being done at the edge of the network, closer to the user. This shift has led to the creation of intelligent hardware such as smart routers, IoT gateways, and edge servers equipped with AI capabilities.
These edge devices not only handle connectivity but also perform data analytics, manage security protocols, and support device orchestration—key components of smart connectivity.
Impact on Devices and IoT
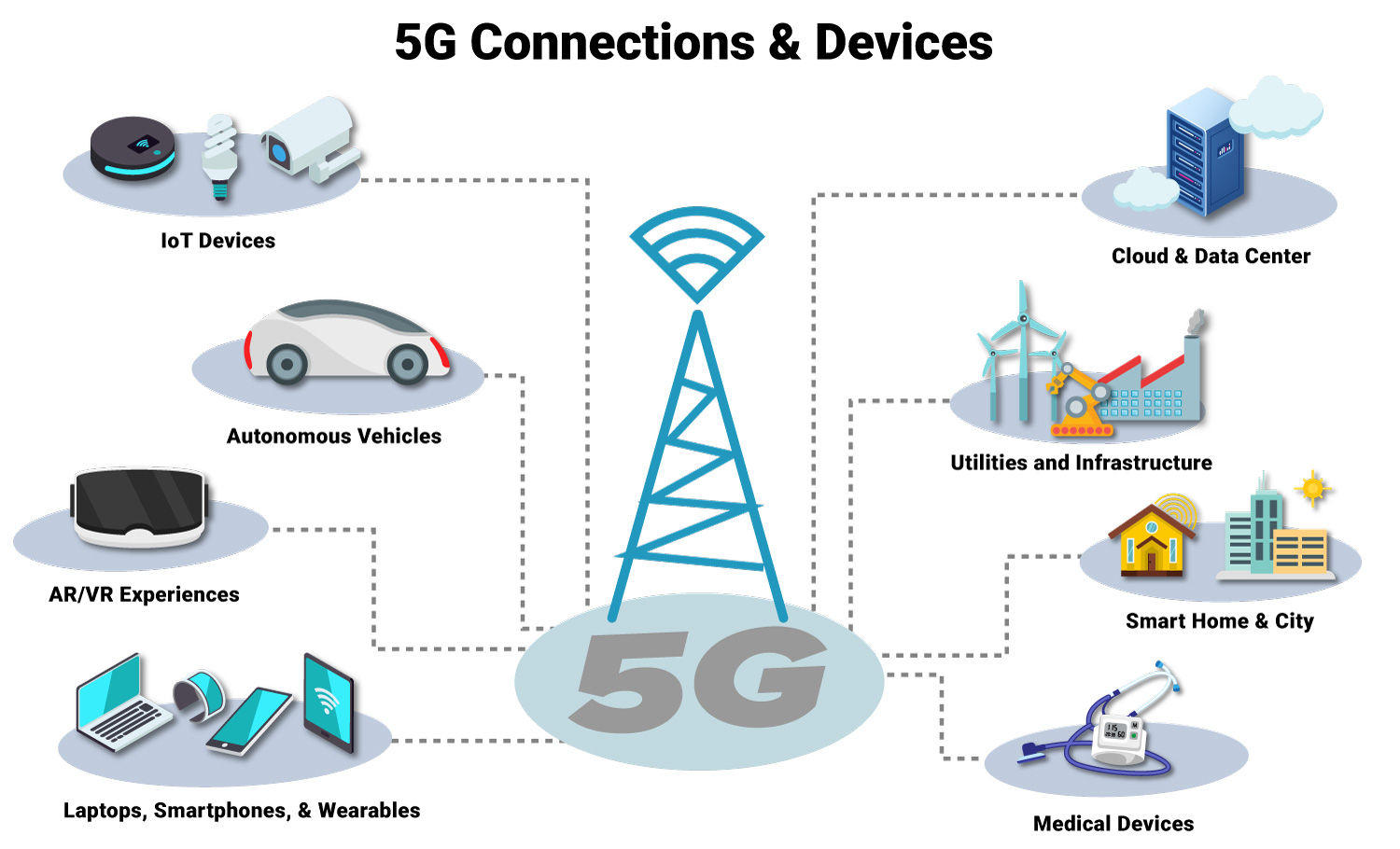
The evolution of 5G hardware isn’t limited to network infrastructure; it’s also transforming user devices. Smartphones now come equipped with 5G modems and antenna systems capable of adapting to different frequencies. More importantly, 5G is powering the Internet of Things (IoT) revolution.
From autonomous vehicles to smart cities and industrial automation, 5G hardware supports billions of connected devices communicating simultaneously. These systems rely on ultra-reliable, low-latency connections enabled by cutting-edge hardware.
Looking Ahead: Toward 6G and Beyond
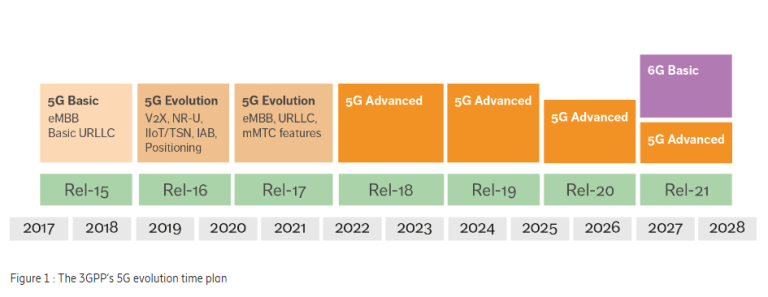
While 5G deployment continues worldwide, researchers and developers are already exploring the possibilities of 6G. Future wireless hardware will need to handle even higher frequencies, greater data volumes, and more complex AI integration. This continuous evolution underscores the need for flexible, sustainable, and future-proof hardware solutions.
Conclusion
The evolution of 5G wireless hardware reflects a broader transformation in global connectivity. From legacy networks focused solely on voice to intelligent systems enabling real-time, data-driven experiences, the progress is remarkable. As 5G continues to expand, its hardware backbone will play a critical role in shaping the smart, connected future we are heading toward.