5G NR Grant-Free Dynamic Scheduling Enabling Transmission Without Prior Grants
telcomatraining.com – The evolution of 5G New Radio (NR) has introduced innovative mechanisms to meet the growing demands for ultra-reliable, low-latency communication (URLLC), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC). One such breakthrough is Grant-Free Dynamic Scheduling, which enables data transmission without waiting for prior scheduling grants from the base station. This article explores how this feature works, its benefits, and its role in optimizing real-time wireless communication.
What Is Grant-Free Dynamic Scheduling?
Traditional 5G scheduling involves a two-step grant-based process: a User Equipment (UE) first sends a scheduling request (SR), and the base station, or gNB, responds with an uplink grant. This method ensures resource control but introduces inevitable latency.
Grant-Free Dynamic Scheduling breaks this pattern by allowing UEs to transmit data packets instantly without waiting for uplink grants. Instead, UEs are pre-configured with resources that can be accessed directly, dynamically adjusting their transmission patterns based on network conditions and configurations.
Key Mechanisms Behind Grant-Free Transmission
To enable grant-free transmission, 5G NR uses:
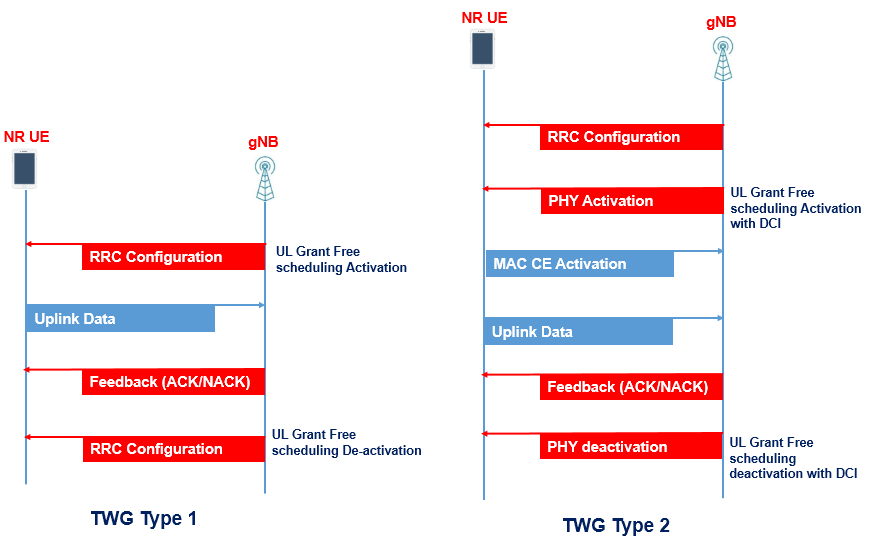
- Configured Grant (CG): Pre-allocated resources are assigned to the UE, which can use them periodically or upon the occurrence of certain events.
- Dynamic Resource Assignment: The system can adapt transmission parameters like time, frequency, and power to suit changing traffic demands.
- Semi-Persistent Scheduling (SPS): This method supports regular transmissions, ideal for applications like voice over NR (VoNR) or video streaming.
These mechanisms are essential to supporting mission-critical services, where even a few milliseconds of delay could lead to failure.
Benefits of Grant-Free Dynamic Scheduling
1. Reduced Latency
By eliminating the need for uplink grants, transmissions can begin almost instantly. This ultra-low latency is vital for URLLC applications such as autonomous driving, smart grids, and remote surgery.
2. Enhanced Reliability
Grant-free methods reduce signaling overhead, making the system more robust and reliable—especially in dense environments where many devices attempt to communicate simultaneously.
3. Improved Support for mMTC
Massive machine-type communication benefits from grant-free scheduling because it allows low-power, sporadic transmissions without the need for extensive signaling exchanges.
4. Energy Efficiency
Reducing control signaling minimizes the UE’s need to stay active, thus conserving battery life, which is particularly important for IoT devices with limited power sources.
Challenges and Considerations
While grant-free scheduling offers many advantages, it also introduces challenges such as:
- Collision Risk: Without prior scheduling, there’s a higher chance of multiple UEs attempting to use the same resources simultaneously.
- Interference Management: Dynamic and unscheduled transmissions may increase interference, requiring sophisticated coordination mechanisms.
- Resource Utilization Efficiency: Pre-allocated resources might remain underutilized if not carefully managed, reducing overall system efficiency.
To mitigate these issues, advanced techniques such as Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) and Machine Learning-based Resource Prediction are being explored to optimize resource usage and minimize collisions.
Real-World Applications
Industries adopting Industry 4.0 practices are rapidly deploying 5G networks with grant-free features. Examples include:
- Smart Manufacturing: Real-time monitoring and control require instant, reliable data exchange.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Vehicles need to share real-time data without latency.
- Healthcare IoT: Devices like wireless ECG monitors benefit from ultra-reliable, energy-efficient communication.
Conclusion
5G NR Grant-Free Dynamic Scheduling is a pivotal feature enabling real-time, low-latency communication without relying on traditional scheduling grants. It enhances performance in URLLC and mMTC scenarios, paving the way for innovations in smart cities, industrial automation, and next-generation healthcare. As 5G technology evolves, grant-free communication will play a central role in achieving seamless, intelligent connectivity.