5G New Radio (NR): Key Concepts & Deployment Strategies
telcomatraining.com – The rollout of 5G technology marks a significant leap in wireless communication, promising faster speeds, lower latency, and massive connectivity improvements. At the heart of this revolution lies 5G New Radio (NR)—the global standard for a new air interface developed by 3GPP to support 5G networks. Understanding the core concepts and deployment strategies of 5G NR is critical for telecom operators, technology providers, and businesses aiming to leverage next-generation connectivity.
What is 5G New Radio (NR)?
5G NR is the radio access technology designed specifically for 5G networks. Unlike previous generations, 5G NR introduces a flexible, scalable framework that supports a wide range of frequency bands—from sub-6 GHz to millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies. This flexibility enables improved spectral efficiency and supports diverse use cases including enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
Key Concepts of 5G NR
1. Flexible Numerology and Frame Structure
5G NR adopts a flexible subcarrier spacing ranging from 15 kHz up to 240 kHz, allowing dynamic adaptation to various deployment scenarios. The frame structure also supports mini-slots for ultra-low latency applications, enabling faster data transmission and responsiveness.
2. Massive MIMO and Beamforming
Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology combined with advanced beamforming techniques dramatically improves signal quality and network capacity. By directing focused beams to specific users, 5G NR enhances coverage and reduces interference, particularly important for high-frequency bands.
3. Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS)
DSS allows 4G LTE and 5G NR to share the same frequency band simultaneously. This strategy facilitates a smooth transition from 4G to 5G without requiring additional spectrum allocation, making network evolution more cost-effective and efficient.
4. Network Slicing
5G NR supports network slicing, a capability that enables operators to create multiple virtual networks within a single physical infrastructure. Each slice can be tailored for different service requirements—such as IoT devices, mission-critical communications, or high-bandwidth mobile users.
Deployment Strategies for 5G NR
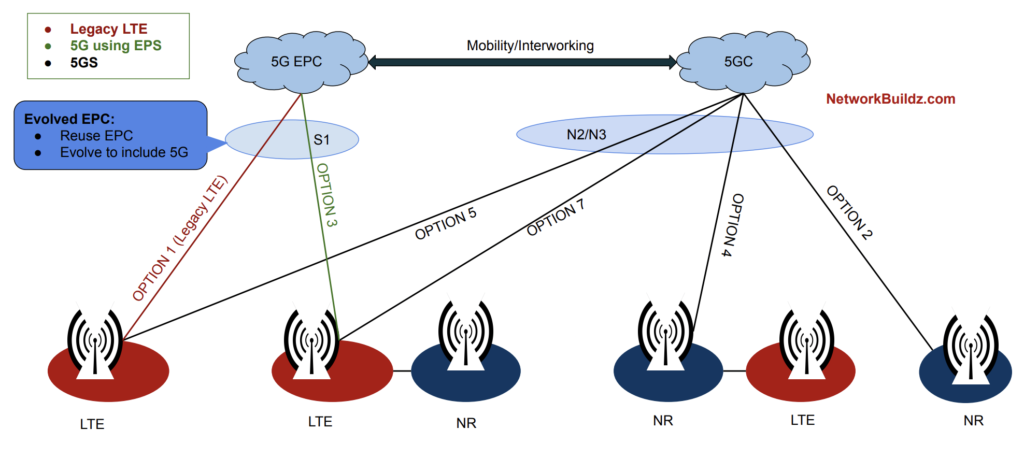
1. Standalone (SA) vs Non-Standalone (NSA) Deployment
Operators typically start with Non-Standalone (NSA) deployments, where 5G NR radios work alongside existing 4G LTE infrastructure to deliver enhanced speeds. This approach minimizes initial investment and accelerates 5G availability. Eventually, networks migrate to Standalone (SA) mode, where 5G NR operates independently, unlocking full 5G capabilities such as ultra-low latency and network slicing.
2. Spectrum Allocation and Management
Efficient spectrum usage is vital for successful 5G NR deployment. Operators must balance the use of low-band spectrum for broad coverage and high-band (mmWave) spectrum for ultra-high data rates in dense urban areas. Dynamic spectrum sharing further optimizes spectrum efficiency during the transition phase.
3. Infrastructure Upgrades
Deploying 5G NR involves upgrading existing base stations and integrating new equipment capable of handling massive MIMO antennas and advanced beamforming. Additionally, the backhaul network must be enhanced to support increased data throughput and reduced latency.
4. Edge Computing Integration
To fully leverage 5G NR’s low latency, edge computing resources are deployed closer to end-users. This reduces the time data takes to travel between devices and servers, supporting applications like autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and industrial automation.
5. Security and Reliability Measures
5G NR introduces enhanced security protocols to protect data integrity and user privacy. Robust authentication, encryption, and network slicing isolation are critical to maintaining trust in 5G services, especially for mission-critical applications.
Conclusion
5G New Radio (NR) is the foundational technology enabling the next generation of wireless connectivity. Its flexible design and advanced features open up new possibilities for mobile broadband, IoT, and real-time communications. By adopting smart deployment strategies—balancing spectrum use, infrastructure upgrades, and network evolution—stakeholders can maximize the benefits of 5G NR. As 5G continues to expand globally, understanding these key concepts and strategies will be essential for anyone involved in the digital transformation journey.